Matrine
Synonym(s):Matridin-15-one;Sophocarpidine
- CAS NO.:519-02-8
- Empirical Formula: C15H24N2O
- Molecular Weight: 248.36
- MDL number: MFCD00210527
- EINECS: 610-750-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 13:58:55
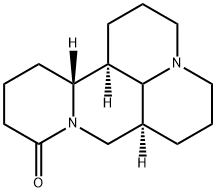
What is Matrine?
Description
Matrine is extracted by organic solvents from the dry roots, plants, and fruits of kushen 苦参 (Sophora flavescens Ait) and also existed in S. alopecuroides L. and S. subprostrata Chun et T.?Chen.Chinese medicine Radix sophorae flavescentis have dampness eliminating insecticide and diuretic effects. Sophora flavescens is used for heat dysentery, hemafecia, jaundice and anuria, red leukorrhea, vulva pruritus, eczema, wet sores, skin itching, scabies, ringworm, and trichomonas vaginitis. Sophora flavescens is recorded in the ancient Materia Medica. “Southern Yunnan Materia Medica” also recorded the effects of Saphora flavescens .Sophora flavescens is a species of Sophora japonica and distributed in temperate and subtropical regions. Sophora flavescens is widely distributed in China, mainly in the north of Hebei, the west of Henan, and southwest of Shandong, Anhui, Hubei, and Guizhou. Matrine is extracted and isolated from the Chinese medicine Sophora flavescens
Chemical properties
Matrine is a white crystal or powder in the form of needles, which can turn yellow with prolonged exposure to air. It is soluble in water, benzene, chloroform, and methanol, but only slightly soluble in petroleum ether. Matrine has a melting point of 76°C (α-matrine), 87°C (β-matrine), 223°C (γ-matrine), and 84°C (δ-matrine), and a specific optical rotation of +31 to +36°.
History
As early as the 1930s, the Soviet Union began to study Sophora flavescens, and the china research began in 1972. Sophora flavescens in the chemical composition are divided into two major categories of alkaloids and flavonoids. Global research efforts are currently concentrated on studying alkaloids. So far, there are 23 species of alkaloids isolated and identified in roots, stems, leaves, and flowers of Sophora flavescens. The main components of Sophora flavescens have obvious anti-cancer effects, and oxymatrine has anti-cancer and antiaging effects.
The Uses of Matrine
(+)-Matrine is an alkaloid compound extracted from the roots of Sophora species which maintain anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer and a host of other positive pharmacological effects. Apoptotic agent.
What are the applications of Application
Matrine is an alkaloid that displays κ-opioid receptor agonism
Indications
In clinical settings, matrine injection was used for chronic active hepatitis, and suppository was used for trichomoniasis or Candida vaginitis and chronic cervicitis and can also be used for senile vaginitis and pelvic inflammatory disease.
Definition
ChEBI: Matrine is an alkaloid found in plants from the Sophora genus. It has a variety of pharmacological effects, including anti-cancer effects, and action as a kappa opioid receptor and μ-receptor agonist.
Pharmacology
Matrine has antiarrhythmic, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrosis, and anti-tumor effects. It has significant effects of negative frequency and positive inotropic action, which can enhance myocardial contractility, slow down the heart rate, and extend the PR and QTC interval. Matrine can promote the expression of the bcl-2 gene and can improve the ratio of bcl-2/Bax to inhibit apoptosis of myocardial cell caused by myocardial ischemia reperfusion and then reduce myocardial deficiency caused by coronary atherosclerotic heart disease and myocardial infarction to achieve the role of antiarrhythmic. In addition, matrine can also play an anti-pulmonary fibrosis effect by inhibiting the proliferation of lung fibroblasts and the expression of pulmonary interstitial fibroblasts (FN).
Clinical Use
Matrine has multiple pharmacological effects and can treat a variety of diseases in clinical setting. At present, the researches on matrine are mainly focused on antiliver injury and liver fibrosis and anti-tumor and anti-cardiovascular diseases. It was worthy of attention that matrine has other pharmacological activities, such as leukocyte-elevating effects and anti-virus effects, and these effects were necessary for further development and utilization. The pharmacological effects of matrine stayed in the experimental phase, and they need further development and research to promote the development of clinical practice. Improvements in the modern formulation of matrine can improve their clinical application.
in vitro
mtt assay showed that the matrine was able to inhibit gastric cancer cell line mnk45 in a dose-dependent manner. the concentration required for 50% inhibition (ic50) was found to be 540 μg/ml. this anti-tumor function was achieved through modulation of the nf-κb, xiap, ciap, and p-erk proteins expression in cell line mnk45. matrine induces apoptosis of human nsclc cells with anti-apoptotic factors inhibited and dependent on caspase activity. in addition, we found that matrine increases the phosphorylation of p38 but not its total protein, and inhibition of the p38 pathway with sb202190 partially prevents matrine-induced apoptosis. furthermore, matrine generates reactive oxygen species (ros) in a dose- and time-dependent manner, which is reversed by pretreatment with n-acetyl-l-cysteine (nac) [2].
in vivo
oral administration of matrine (200, 100 and 50 mg/kg) significantly attenuated isoproterenol-induced cardiac necrosis and left ventricular dysfunction [3]. high dose of matrine significantly reduced the mortality rate of mice with lps administration. treatment with matrine improved lps-induced lung histopathologic changes, alleviated pulmonary edema and lung vascular leak, inhibited mpo and mda activity,and reduced the production of inflammatory mediators including tnf-α, il-6 and hmgb1 [4].
References
Inotropic effects and mechanisms of matrine, a main alkaloid from Sophora flavescens AIT DOI: 10.1248/bpb.31.2057
The alkaloid matrine of the root of Sophora flavescens prevents arrhythmogenic effect of ouabain DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2014.02.008
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9010661/
https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/SG/en/product/sigma/m5319
Properties of Matrine
| Melting point: | 77 C |
| Boiling point: | 86-88C/2,5Torr |
| alpha | D20 +38° (alc) |
| Density | 1,191g/cm |
| refractive index | 1,536 |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in Water (up to 25 mg/ml) |
| form | solid |
| pka | 9.47±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Merck | 14,5759 |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in distilled water may be stored at -20°C for up to 3 months. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 519-02-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Matrine(519-02-8) |
Safety information for Matrine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Matrine
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Matrine, puriss, 99% CAS 519-02-8View Details
Matrine, puriss, 99% CAS 519-02-8View Details
519-02-8 -
 Matrine CAS 519-02-8View Details
Matrine CAS 519-02-8View Details
519-02-8 -
 Matrine 98% (GC) CAS 519-02-8View Details
Matrine 98% (GC) CAS 519-02-8View Details
519-02-8 -
 Matrine CAS 519-02-8View Details
Matrine CAS 519-02-8View Details
519-02-8 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
