Lithium oxide
Synonym(s):Dilithium monoxide;Dilithium oxide;Kickerite;Lithia
- CAS NO.:12057-24-8
- Empirical Formula: Li2O
- Molecular Weight: 29.88
- MDL number: MFCD00016183
- EINECS: 235-019-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
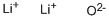
What is Lithium oxide?
Chemical properties
finely divided white powder(s) or crusty material; readily absorbs CO2 and H2O from the atmospheric; made by heating LiOH to ~800°C in a vacuum or by thermal decomposition of lithium peroxide; used in ceramics and special glass formulations and in lithium thermal batteries [HAW93] [MER06] [KIR81] [FMC93]
The Uses of Lithium oxide
Lithium oxide is a strong alkali that absorbs carbon dioxide and water from the atmosphere. It is used in manufacturing ceramics and special types of glass.
The Uses of Lithium oxide
Ceramics and special glass formulations, carbon dioxide absorbent.Lithium oxide is used as a flux in ceramic glazes, co-dopant with yttria in the zirconia ceramic top coat and as the cathode in the lithium ion batteries, which is used in power electronic devices like mobile phones, laptop computers and battery-powered cars. It is also used to prepare lithium hydroxide and lithium metal by electrolysis.
Preparation
Industrial and laboratory preparations. Only small volumes of material are prepared
industrially. Both industrial and laboratory preparations require the thermal decomposition
of lithium peroxide or of lithium hydroxide.
Lithium peroxide, Li202 , is converted to lithium oxide, Li20, and oxygen by heating
to 450° in a stream of helium gas.
Thermal dehydration of lithium hydroxide is carried out at 675°C±10° under vacuum
in a nickel container lined with silver foil.
Lithium carbonate may be converted to lithium oxide and carbon dioxide by heating
the material to 700°C under vacuum in a platinum boat.
Industrial uses. There are no current industrial uses which consume large quantities of
lithium oxide.
Lithium oxide reacts with water as it dissolves to form a solution of lithium hydroxide.
Lithium oxide is a strong base and reacts typically with acidic gases and liquids to form
lithium salts. At elevated temperatures, lithium oxide also reacts with many solid nonmetal
oxides (Si02, B2O3, etc.) and metal oxides (A1203 , Fe2C>3, etc.). High-temperature
reactions are the basis for the fluxing action of lithium oxide, lithium hydroxide and
lithium carbonate. Care must be taken to avoid the reaction of lithium oxide with reaction
vessels at high temperatures.
General Description
Lithium oxide is a white crystalline solid. Its a strong base. It reacts with water and forms lithium hydroxide.
Structure and conformation
Solid lithium oxide adopts an antifluorite structure with four-coordinated Li+ centers and eight-coordinated oxides.The ground state gas phase Li2O molecule is linear with a bond length consistent with strong ionic bonding.VSEPR theory would predict a bent shape similar to H2O.
Properties of Lithium oxide
| Melting point: | 1427°C |
| Density | 2.013 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| form | Powder |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 2.013 |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Sensitive | Air & Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,5538 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 12057-24-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Dilithium monoxide(12057-24-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dilithium oxide (12057-24-8) |
Safety information for Lithium oxide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P330+P331:IF SWALLOWED: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Lithium oxide
Lithium oxide manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Lithium oxide CAS 12057-24-8View Details
Lithium oxide CAS 12057-24-8View Details
12057-24-8 -
 Lithium oxide CAS 12057-24-8View Details
Lithium oxide CAS 12057-24-8View Details
12057-24-8 -
 Lithium oxide CAS 12057-24-8View Details
Lithium oxide CAS 12057-24-8View Details
12057-24-8 -
 Lithium oxide 98.00% CAS 12057-24-8View Details
Lithium oxide 98.00% CAS 12057-24-8View Details
12057-24-8 -
 Lithium oxide, ≥99.5% CAS 12057-24-8View Details
Lithium oxide, ≥99.5% CAS 12057-24-8View Details
12057-24-8 -
 Lithium oxide CAS 12057-24-8View Details
Lithium oxide CAS 12057-24-8View Details
12057-24-8 -
 5 kg Lithium Oxide, PowderView Details
5 kg Lithium Oxide, PowderView Details
12057-24-8 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
