L-Cystine
Synonym(s):Cys;L-Cystine;L-Cystine - CAS 56-89-3 - Calbiochem;Nephrin;NPHN
- CAS NO.:56-89-3
- Empirical Formula: C6H12N2O4S2
- Molecular Weight: 240.3
- MDL number: MFCD00064228
- EINECS: 200-296-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 16:58:18
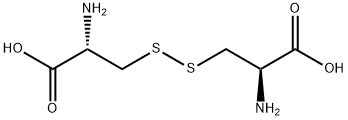
What is L-Cystine?
Chemical properties
A white or almost white, crystalline powder, practically insoluble in water and in alcohol.
The Uses of L-Cystine
L-Cystine is a non-essential amino acid for human development. L-Cystine is formed by the dimerization of two cysteines through the sulfur.
The Uses of L-Cystine
L-Cystine is used as an antioxidant, protecting tissues against radiation and pollution. It finds application in protein synthesis. It is required for utilization of vitamin B6 and is useful in healing burns and wounds. It is also is required by certain malignant cell lines in the culture medium as well as for the growth of certain micro-organisms. It is useful in the stimulation of hematopoietic system and promotes the formation of white and red blood cells. It is an active ingredient in medications used to treat dermatitis.
The Uses of L-Cystine
L-Cystine has been used in in vitro cystine solubility assay to identify potential drugs that influence cystine solubility. It is also used as a supplement of phosphate-buffered saline to slice and wash periprosthetic tissues.
Background
A covalently linked dimeric nonessential amino acid formed by the oxidation of cysteine. Two molecules of cysteine are joined together by a disulfide bridge to form cystine.
Indications
It has been claimed that L-cysteine has anti-inflammatory properties, that it can protect against various toxins, and that it might be helpful in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. More research will have to be done before L-cysteine can be indicated for any of these conditions. Research to date has mostly been in animal models.
Definition
ChEBI: L-cystine is the L-enantiomer of the sulfur-containing amino acid cystine. It has a role as a flour treatment agent, a human metabolite, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite, a mouse metabolite and an EC 1.2.1.11 (aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase) inhibitor. It is a cystine, a L-cysteine derivative and a non-proteinogenic L-alpha-amino acid. It is a conjugate acid of a L-cystine anion. It is an enantiomer of a D-cystine. It is a tautomer of a L-cystine zwitterion.
Physiological effects
L-Cystine is an amino acid and intracellular thiol, which plays a critical role in the regulation of cellular processes.
Health benefits
As a natural amino acid, L-cystine has the ability to eliminate free radicals that cause skin aging, and at the same time push out the dark pigmentation on the skin. Besides, L-cystine also helps to eliminate the old stratum corneum on the skin and regenerate new skin quickly.
Side Effects
L-cystine can cause some unwanted side effects on the digestive system such as diarrhea, nausea, vomiting or acne in the early stages of taking the drug.
Toxicity
With typical doses of 1 to 1.5 grams daily, the most commonly reported side effects have been gastrointestinal, such as nausea. There are rare reports of cystine renal stone formation, Single injections of L-cysteine (0.6-1.5 g/kg) into 4-day-old pups resulted in massive damage to cortical neurons, permanent retinal dystrophy, atrophy of the brain and hyperactivity.
General Description
This Standard Reference Material (SRM) is intended primarily for use in validating microchemical procedures for the determination of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur in organic matter. SRM 143d is pure crystalline cystine supplied in a 2 g unit size. For more information, please refer to the SDS and COA.
SRM 143D_cert SRM 143D _SDS
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cysteine is the source of disulfide linkages in proteins and has a role in sulfur transport. It undergoes rapid oxidation to form cystine at physiological pH. L-cystine is crucial for oxygen production and low density lipoprotein modification by arterial smooth muscle cells. It also has a role in the synthesis of glutathione.
Pharmacokinetics
L-Cystine is a covalently linked dimeric nonessential amino acid formed by the oxidation of cysteine. Two molecules of cysteine are joined together by a disulfide bridge to form cystine. Cystine is a chemical substance which naturally occurs as a deposit in the urine, and can form a calculus (hard mineral formation) when deposited in the kidney. The compound produced when two cysteine molecules linked by a disulfide (S-S) bond. Cystine is required for proper vitamin B6 utilization and is also helpful in the healing of burns and wounds, breaking down mucus deposits in illnesses such as bronchitis as well as cystic fibrosis. Cysteine also assists in the supply of insulin to the pancreas, which is needed for the assimilation of sugars and starches. It increases the level of glutathione in the lungs, liver, kidneys and bone marrow, and this may have an anti-aging effect on the body by reducing age-spots etc.
Safety Profile
Low toxicity by ingestion. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of PO, and SOx
Purification Methods
Cystine disulfoxide impurity is removed by treating an aqueous suspension with H2S. The cystine is filtered off, washed with distilled water and dried at 100o under a vacuum over P2O5. Crystallise it by dissolving in 1.5M HCl, then adjusting to neutral pH with ammonia. Likely impurities are D-cystine, meso-cystine and tyrosine. Also purify it by dissolving it in 10% NH3 and adding gradually dilute AcOH until the point of precipitation and cooling slowly [Dughton & Harrison Acta Cryst 12 396, 402 1959.] Alternatively dissolve it in 6N NH4OH and evaporate it at room temperature for crystallisation to occur. [Chaney & Steinrauf Acta Cryst 30 711 1974, Beilstein 4 IV 3155.]
Properties of L-Cystine
| Melting point: | >240 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 468.2±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | -224 º(c=2 in 1M HCl) |
| Density | 1.68 |
| refractive index | -222.5 ° (C=1, 1mol/L HCl) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 1 M HCl: 100 mg/mL |
| form | Powder/Solid |
| pka | 1.0, 2.1, 8.02, 8.71(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| optical activity | [α]20/D 219±5°, c = 1% in 1 M HCl |
| Water Solubility | 0.112 g/L (25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,2782 |
| BRN | 1728094 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 56-89-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | L-Cystine(56-89-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | L-Cystine (56-89-3) |
Safety information for L-Cystine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for L-Cystine
| InChIKey | LEVWYRKDKASIDU-IMJSIDKUSA-N |
L-Cystine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 56-89-3 98%View Details
56-89-3 98%View Details
56-89-3 -
 L-Cystine CAS 56-89-3View Details
L-Cystine CAS 56-89-3View Details
56-89-3 -
 L-Cystine for tissue culture CAS 56-89-3View Details
L-Cystine for tissue culture CAS 56-89-3View Details
56-89-3 -
 L-(-)-Cystine CAS 56-89-3View Details
L-(-)-Cystine CAS 56-89-3View Details
56-89-3 -
 L-CYSTINE For Biochemistry CAS 56-89-3View Details
L-CYSTINE For Biochemistry CAS 56-89-3View Details
56-89-3 -
 L-Cystine 99% CAS 56-89-3View Details
L-Cystine 99% CAS 56-89-3View Details
56-89-3 -
 Cystine CAS 56-89-3View Details
Cystine CAS 56-89-3View Details
56-89-3 -
 L-Cystine CAS 56-89-3View Details
L-Cystine CAS 56-89-3View Details
56-89-3
