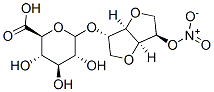
Isosorbide 5-mononitrate
Synonym(s):1,4:3,6-Dianhydro-D -glucitol 5-nitrate
- CAS NO.:16051-77-7
- Empirical Formula: C6H9NO6
- Molecular Weight: 191.14
- MDL number: MFCD00143462
- EINECS: 240-197-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-11 08:41:34
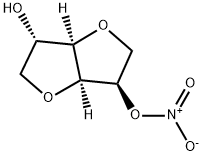
What is Isosorbide 5-mononitrate?
Absorption
Upon oral administration, isosorbide mononitrate is rapidly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Isosorbide mononitrate has a dose-linear kinetics and the absolute bioavailability is nearly 100%. The Cmax is reached within 30 to 60 minutes following administration.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 is 2010 mg/kg in rats and 1771 mg/kg in mice.
The symptoms of overdose from isosorbide mononitrate is associated with vasodilatation, venous pooling, reduced cardiac output, and hypotension. These symptoms can be accompanied by several manifestations, including increased intracranial pressure (possibly along with persistent throbbing headache, confusion, and moderate fever), vertigo, palpitations, visual disturbances, nausea and vomiting (possibly along with colic and bloody diarrhea), syncope (especially in the upright posture), air hunger and dyspnea (later followed by reduced ventilatory effort), diaphoresis (with flushed or cold and clammy skin), heart blocks and bradycardia, paralysis, coma, seizures, and death.
There is limited clinical information on the management of isosorbide mononitrate overdose; it is advised that venodilatation and arterial hypovolemia from overdose are responded with therapy aimed to increase in central fluid volume. However, this method may be potentially hazardous in patients with renal disease or congestive heart failure: invasive monitoring may be required in these patients. The patient's legs should be passively elevated, and intravenous infusion of normal saline or similar fluid is recommended. Isosorbide mononitrate was shown to be significantly removed from the systemic circulation via hemodialysis. The use of epinephrine or other arterial vasoconstrictors is not recommended.
Chemical properties
white to light yellow crystal powde
The Uses of Isosorbide 5-mononitrate
Isosorbide 5-Mononitrate is a metabolite of Isosorbide Dinitrate; used as an antianginal.
The Uses of Isosorbide 5-mononitrate
A metabolite of Isosorbide Dinitrate. Used as an antianginal
The Uses of Isosorbide 5-mononitrate
antidepressant, 5HT reuptake inhibitor
Background
Isosorbide mononitrate is an organic nitrate with vasodilating properties. It is an anti-anginal agent that works by relaxing the smooth muscles of both arteries and veins, but but predominantly veins to reduce cardiac preload. Isosorbide mononitrate is an active metabolite of isosorbide dinitrate. Like other organic nitrates, isosorbide mononitrate acts as a prodrug for its active metabolite, nitric oxide, which mediates the therapeutic action of isosorbide mononitrate. Isosorbide mononitrate has a longer duration of action than nitroglycerin due to its slow onset of absorption and metabolism.
First approved by the FDA in 1991, isosorbide mononitrate is used for the prevention and management of angina pectoris caused by coronary artery disease; however, the onset of action of orally-administered isosorbide mononitrate is not rapid enough to offset an acute anginal episode. It is available in oral tablets generically and under the brand name ISMO and Monoket. The extended-release forms of the drug are also available generically and under the brand name Imdur.
Indications
Isosorbide mononitrate is indicated for the prevention and management of angina pectoris due to coronary artery disease. The onset of action of oral isosorbide mononitrate is not sufficiently rapid to be useful in aborting an acute anginal episode.
What are the applications of Application
Isosorbide Mononitrate is a coronary vasodilator
Definition
ChEBI: Isosorbide mononitrate is a nitrate ester and a glucitol derivative. It has a role as a nitric oxide donor and a vasodilator agent.
brand name
Imdur (Schering-Plough); Ismo (Dr. Reddy’s); Monoket (Schwarz Pharma) .
General Description
Isosorbide 5-mononitrate is a crystalline solid. Isosorbide 5-mononitrate is very flammable and may be toxic by ingestion.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable.
Reactivity Profile
The dinitrate, a heart drug, can detonate when dry, but is non explosive with 30% of water [J. Haz.. Mater., 1992, 32(1), 87]. The mononitrate would be expected to be less reactive.
Health Hazard
Fire may produce irritating and/or toxic gases. Contact may cause burns to skin and eyes. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Runoff from fire control may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Flammable/combustible material. May be ignited by friction, heat, sparks or flames. Some may burn rapidly with flare burning effect. Powders, dusts, shavings, borings, turnings or cuttings may explode or burn with explosive violence. Substance may be transported in a molten form at a temperature that may be above its flash point. May re-ignite after fire is extinguished.
Pharmacokinetics
Isosorbide mononitrate is an anti-anginal agent and vasodilator that relaxes vascular smooth muscle to prevent and manage angina pectoris. The pharmacological action is mediated by the active metabolite, nitric oxide, which is released when isosorbide mononitrate is metabolized. Nitric oxide works on both arteries and veins, but predominantly veins: by relaxing veins and reducing the central venous pressure, nitric oxide causes venous pooling and a decrease in the venous return to the heart, thus decreasing cardiac preload. In healthy subjects, the stroke volume is decreased and venous pooling can occur in the standing posture, leading to postural hypotension and dizziness.
At therapeutic doses of isosorbide mononitrate, nitric oxide has a bigger effect on larger muscular arteries over small resistance arteries. Arterial relaxation leads to reduced systemic vascular resistance and systolic blood (aortic) pressure, decreasing to decreased cardiac afterload. The direct dilator effect on coronary arteries opposes the coronary artery spasm in variant angina or angina pectoris. At larger doses, nitric oxide causes the resistance arteries and arterioles to dilate, reducing arterial pressure via coronary vasodilatation. This leads to increased coronary blood flow. Reduced cardiac preload and afterload caused by nitric oxide causes a reduction in myocardial oxygen consumption; decreased myocardial oxygen demand, along with increased coronary blood flow, leads to an increased in the oxygen content of coronary sinus blood and the relief from ischemia.
The end effect of isosorbide mononitrate include decreased cardiac oxygen consumption, redistribution coronary flow toward ischemic areas via collaterals, and the relief of coronary spasms. Nitric oxide can also increase the rate of relaxation of cardiac muscles, which is an effect outside of vascular smooth muscles. Organic nitrates can also relax other types of smooth muscles, including esophageal and biliary smooth muscle. The anti-anginal activity of isosorbide mononitrate was observed about 1 hour after dosing, and the peak effect was achieved from 1-4 hours after dosing. The duration of anti-anginal action of at least 12 hours was observed with an asymmetrical dosing regimen.
Clinical Use
Vasodilator:
Treatment and prophylaxis of angina
Adjunct in congestive heart failure
Metabolism
Isosorbide mononitrate is not subject to first pass metabolism in human liver. Detectable metabolites include isosorbide, sorbitol, and 2-glucuronide of mononitrate, which are pharmacologically inactive.
Properties of Isosorbide 5-mononitrate
| Melting point: | 88-93 °C |
| Boiling point: | 326.86°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | 170 º (c=1, EtOH) |
| Density | 1.5784 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 145 ° (C=5, H2O) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | Undiluted isosorbide mononitrate is freely soluble in water, in acetone, in ethanol (96 per cent) and in methylene chloride. The solubility of the diluted product depends on the diluent and its concentration. |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 13.09±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Merck | 5225 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 16051-77-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | D-Glucitol, 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-, 5-nitrate (16051-77-7) |
Safety information for Isosorbide 5-mononitrate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H228:Flammable solids |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P241:Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/…/equipment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P370+P378:In case of fire: Use … for extinction. |
Computed Descriptors for Isosorbide 5-mononitrate
| InChIKey | YWXYYJSYQOXTPL-SLPGGIOYSA-N |
Isosorbide 5-mononitrate manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 16051-77-7 99%View Details
16051-77-7 99%View Details
16051-77-7 -
 Isosorbide 5-mononitrate 98%View Details
Isosorbide 5-mononitrate 98%View Details
16051-77-7 -
 Monotrate Tablet (Isosorbide Mononitrate), 10 mg, Sun Pharmaceutical Industries LtdView Details
Monotrate Tablet (Isosorbide Mononitrate), 10 mg, Sun Pharmaceutical Industries LtdView Details
16051-77-7 -
 Isosorbide-5-Mononitrate 60 mg (Sustained Release) TabletsView Details
Isosorbide-5-Mononitrate 60 mg (Sustained Release) TabletsView Details
16051-77-7 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
