Isosorbide dinitrate
Synonym(s):ISDN
- CAS NO.:87-33-2
- Empirical Formula: C6H8N2O8
- Molecular Weight: 236.14
- MDL number: MFCD00868238
- EINECS: 201-740-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
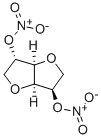
What is Isosorbide dinitrate?
Absorption
Absorption of isosorbide dinitrate after oral dosing is nearly complete, but bioavailability is highly variable (10% to 90%), with extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver. The average bioavailability of isosorbide dinitrate is about 25%.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include reduced cardiac output and hypotension.
Chemical properties
white to light yellow crystal powde
Originator
Isordil,Ives,US,1959
The Uses of Isosorbide dinitrate
Isosorbide dinitrate is also used in chronic cardiac insufficiency for preventing angina pectoris attacks. It is a long-lasting drug.
The Uses of Isosorbide dinitrate
Coronary vasodilator
The Uses of Isosorbide dinitrate
Antianginal;Nitric oxide (NO) donor
Indications
For the prevention of angina pectoris due to coronary artery disease.
Background
A vasodilator used in the treatment of angina pectoris. Its actions are similar to nitroglycerin but with a slower onset of action.
Definition
ChEBI: Isosorbide dinitrate is a nitrate ester and a glucitol derivative. It has a role as a vasodilator agent and a nitric oxide donor.
Manufacturing Process
An aqueous syrup of 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-D-glucitol is slowly added to a cooled mixture of HNO3 and H2SO4. After standing a few minutes the mixture is poured into cold water and the precipitated product is collected and recrystallized from ethanol.
brand name
Dilatrate (Schwarz Pharma); Isordil (Biovail); Isordil (Wyeth); Sorbitrate (AstraZeneca).
Therapeutic Function
Coronary vasodilator
General Description
A crystalline solid. May be toxic by ingestion. Used to make pharmaceuticals. Used as a heart drug.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Slightly soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Nitroalkanes, such as Isosorbide dinitrate, range from slight to strong oxidizing agents. If mixed with reducing agents, including hydrides, sulfides and nitrides, they may begin a vigorous reaction that culminates in a detonation. Nitroalkanes are milder oxidizing agents, but still react violently with reducing agents at higher temperature and pressures. Nitroalkanes react with inorganic bases to form explosive salts. The presence of metal oxides increases the thermal sensitivity of nitroalkanes. Nitroalkanes with more than one nitro group are generally explosive. Nitroalkanes are insoluble in water. This heart drug is detonable when dry, but non-explosive with 30% of water.
Health Hazard
Fire may produce irritating and/or toxic gases. Contact may cause burns to skin and eyes. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Runoff from fire control may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Flammable/combustible material. May be ignited by friction, heat, sparks or flames. Some may burn rapidly with flare burning effect. Powders, dusts, shavings, borings, turnings or cuttings may explode or burn with explosive violence. Substance may be transported in a molten form at a temperature that may be above its flash point. May re-ignite after fire is extinguished.
Pharmacokinetics
Isosorbide Dinitrate is a moderate to long acting oral organic nitrate used for the relief and prophylactic management of angina pectoris. It relaxes the vascular smooth muscle and consequent dilatation of peripheral arteries and veins, especially the latter. Dilatation of the veins promotes peripheral pooling of blood and decreases venous return to the heart, thereby reducing left ventricular end- diastolic pressure and pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (preload). Arteriolar relaxation reduces systemic vascular resistance, systolic arterial pressure, and mean arterial pressure.
Clinical Use
Vasodilator:
Prophylaxis and treatment of angina
Left ventricular failure
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion, intraperitoneal, intramuscular, and subcutaneous routes. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. A flammable solid. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. A coronary vasodilator. See also NITRATES.
Synthesis
Isosorbiddinitrate, 1,4:3,6-dianhydrosorbate-2,5-dinitrate (19.1.4), is synthesized by intermolecular dehydration of D-sorbite into isosorbide (19.1.3) using paratoluenesulfonic acid and subsequent nitration of the two hydroxyl groups by nitric acid.

Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Isosorbide mononitrate (ISMN) and dinitrate (ISDN) are organic
nitrates potentially useful as preload reducing agents in treating
heart failure in small animals, however, research and clinical experience
demonstrating clinical efficacy are lacking in dogs or cats.
Limited research indicates that dogs may require much higher dosages
of isosorbide dinitrate to achieve therapeutic effects than do
humans.
In humans, isosorbide nitrates are used for treating or preventing
angina, treating esophageal spasm, and as an adjunctive treatment
in CHF.
Metabolism
Hepatic
Properties of Isosorbide dinitrate
| Melting point: | 700C |
| Boiling point: | 378.59°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D20 +135° (alc) |
| Density | 1.7503 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5010 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | Undiluted isosorbide dinitrate is very slightly soluble in water, very soluble in acetone, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). The solubility of the diluted product depends on the diluent and its concentration. |
| form | neat |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 549.7mg/L(25 ºC) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 87-33-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | D-Glucitol, 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-, dinitrate (87-33-2) |
Safety information for Isosorbide dinitrate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P230:Keep wetted with … P233:Keep container tightly closed. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P370+P380+P375:in case of fire: Evacuate area. Fight fire remotely due to the risk of explosion. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Isosorbide dinitrate
| InChIKey | MOYKHGMNXAOIAT-JGWLITMVSA-N |
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 87-33-2 98%View Details
87-33-2 98%View Details
87-33-2 -
 Isosorbide dinitrate 99%View Details
Isosorbide dinitrate 99%View Details
87-33-2 -
 Isosorbide dinitrate 87-33-2 98%View Details
Isosorbide dinitrate 87-33-2 98%View Details
87-33-2 -
 Diluted isosorbide dinitrate 98%; 40% Isosorbide dinitrate CAS 87-33-2View Details
Diluted isosorbide dinitrate 98%; 40% Isosorbide dinitrate CAS 87-33-2View Details
87-33-2 -
 Isosorbide dinitrate CAS 87-33-2View Details
Isosorbide dinitrate CAS 87-33-2View Details
87-33-2 -
 Sorbitrate 5mg TabletView Details
Sorbitrate 5mg TabletView Details
87-33-2 -
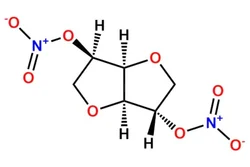 99% Isosorbide Dinitrate (working standard), Analytical GradeView Details
99% Isosorbide Dinitrate (working standard), Analytical GradeView Details
87-33-2 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
