Iodine monochloride
Synonym(s):Iodine monochloride;Wijs solution;Chloroiodide;Chloroiodide solution;Iodine chloride, Chlorine iodide
- CAS NO.:7790-99-0
- Empirical Formula: ClI
- Molecular Weight: 162.36
- MDL number: MFCD00011354
- EINECS: 232-236-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
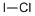
What is Iodine monochloride?
Chemical properties
Iodine monochloride is a reddish brown liquid or black crystals, there are two variants of crystals. α-type is black needles, stable, ruby red under light. β-type is black flakes, unstable, brownish red under light. It has the odor of chlorine and iodine. It does not absorb moisture but can form iodine pentoxide when contacting air. Soluble in water, ethanol, ether, carbon disulfide, and acetic acid, relative density (d0) α-type 3.1822, (d34) β-type 3.24. Melting point α-type 27.2 ℃, β-type 13.9 ℃. Boiling point α-type 97.4°C, β-type 97.4, 100°C (decomposition). It also exhibits corrosive properties. It has the flavor of chlorine and iodine, and it is oxidative and strongly corrosive, and iodination with organic matter, it also shows chlorination, and it can be used for the substitution of the aromatic ring.
The Uses of Iodine monochloride
Iodine monochloride is used to estimate theiodine values of fats and oils and as a topicalanti-infective (Merck 1996). For determination of iodine absorption number of fats Iodine monochloride is used as a catalyst in organic synthesis. It is the source of electrophilic iodine in the synthesis of certain aromatic iodides.
The Uses of Iodine monochloride
In Wijs' solution (iodine monochloride in glacial acetic acid), used to determine iodine values of fats and oils.
Preparation
Iodine monochloride is prepared by the action of liquid or dry chlorine on astoichiometric quantity of solid iodine. Aqueous solutions of ICl are preparedby passing chlorine gas into a suspension of iodine in moderately stronghydrochloric acid:
5I2 + 4HCl + 3Cl2 → 10ICl + 2H2
Alternatively, iodine monochloride may be made by oxidation of iodine withiodic acid in strong hydrochloric acid solution:
2I2 + HIO3 + 2HCl → 2ICl + 3HIO
General Description
Iodine monochloride is a black crystals or a reddish brown oily liquid with a pungent odor. Melting point 27°C (alpha form) or 14°C (beta form). Corrosive to metals and tissue. It is a useful synthetic reagent and source of I+.
Air & Water Reactions
Reacts with air to form iodine pentaoxide (I2O5), which decomposes into iodine (I2) and oxygen (O2) with heat beginning at 275°C and proceeding rapidly at 350°C. Soluble in water; reacts with water or steam to produce toxic and corrosive fumes [Lewis].
Reactivity Profile
Iodine monochloride is moderately explosive when heated [Lewis]. Reacts with rubber and many organic materials. Enflames (after a period of delay) with aluminum foil [Mellor 2:119(1946-1947)]. Reacts dangerously with other active metals. Reacts vigorously with cadmium sulfide, lead sulfide, silver sulfide, and zinc sulfide [Mellor 2, Supp. 1:502(1956)]. Combines very exothermically with phosphorus trichloride [Mellor 2, Supp. 1:502(1956)]. Forms Iodine pentaoxide in air which reacts explosively when warmed with carbon, sulfur, sugar, resin, or powdered combustible elements [Mellor 8: 841(1946-1947)].
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation, strong irritant to eyes and skin. Reaction with water or moist air will release toxic, corrosive or flammable gases. Reaction with water may generate much heat that will increase the concentration of fumes in the air. Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Health Hazard
Iodine monochloride is highly corrosive tothe skin. Contact with the skin causes burns and dark patches. Upon contact, washimmediately with 15-20% HCl. Vapors areirritating to the skin, eyes, and mucous mem branes. The compound is moderate to highlytoxic by an oral route. The lethal dose in ratsis 59 mg/kg (NIOSH 1986).
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Vapors may accumulate in confined areas (basement, tanks, hopper/tank cars etc.). Substance will react with water (some violently), releasing corrosive and/or toxic gases and runoff. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated or if contaminated with water.
Purification Methods
Purify it by repeated fractional crystallisation from its melt at low temperatures. The black crystals melt to a red-brown liquid. [Cornog & Karges Inorg Synth I 165 1939.]
Properties of Iodine monochloride
| Melting point: | 25-27°C |
| Boiling point: | 97.4 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 3.24 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 5.5 (vs air) |
| Flash point: | 96-98°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | acetic acid: soluble(lit.) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Red-brown |
| PH | <1 (H2O, 20°C) |
| Water Solubility | decomposes |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,5017 |
| BRN | 3902972 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 50 ppm OSHA: TWA 25 ppm; STEL 125 ppm NIOSH: IDLH 2300 ppm |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with organic materials, strong bases, metals. Air, light and moisture sensitive. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7790-99-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Iodine monochloride(7790-99-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Iodine chloride (ICl) (7790-99-0) |
Safety information for Iodine monochloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Iodine monochloride
Iodine monochloride manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
SAKEM LLP
Triveni Interchem Private Limited (Group Of Triveni Chemicals)
ASM Organics
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Iodine monochloride CAS 7790-99-0View Details
Iodine monochloride CAS 7790-99-0View Details
7790-99-0 -
 Iodine monochloride CAS 7790-99-0View Details
Iodine monochloride CAS 7790-99-0View Details
7790-99-0 -
 Iodine Chloride CAS 7790-99-0View Details
Iodine Chloride CAS 7790-99-0View Details
7790-99-0 -
 Iodine monochloride CAS 7790-99-0View Details
Iodine monochloride CAS 7790-99-0View Details
7790-99-0 -
 Iodine monochloride CAS 7790-99-0View Details
Iodine monochloride CAS 7790-99-0View Details
7790-99-0 -
 Iodine chloride, 98% 99%View Details
Iodine chloride, 98% 99%View Details -
 Wij's solution CASView Details
Wij's solution CASView Details -
 Wijs solution CASView Details
Wijs solution CASView Details
