INDIUM ARSENIDE
- CAS NO.:1303-11-3
- Empirical Formula: AsIn
- Molecular Weight: 189.74
- MDL number: MFCD00016144
- EINECS: 215-115-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
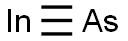
What is INDIUM ARSENIDE?
Chemical properties
Crystals.Insoluble in acids.
The Uses of INDIUM ARSENIDE
Indium arsenide is used in semiconductor devices.
The Uses of INDIUM ARSENIDE
In semiconductor electronics.
The Uses of INDIUM ARSENIDE
Indium arsenide is used in semiconductor electronics, construction of infrared detectors, terahertz radiation source, as it is a strong Photo-dember emitter, superior electron mobility and velocity, in high-power applications detector, diode lasers.
Production Methods
In and As are put into a silica boat at the stoichiometric ratio. The materials are put into a silica
tube together with a small amount of As. The small amount of As is heated to about 300℃ to
eliminate O2 under evacuation followed by sealing off the tube. The boat is zone-refined at the speed of 2 cm/h in the first run and 5 cm/h in the following several runs. The obtained ingot is
pulled out and cut by half to use as a single crystal source. Loading the source into the silica boat
with roughened inner wall, the boat is put into a horizontal silica tube together with a small amount
of As followed by vacuum sealing in the same manner as the first run. A single crystal is obtained
by putting the silica tube into the horizontal Stockbarger furnace with three zones: A (560℃),
B (1000℃) and C (900℃), and by traveling the tube to the direction A→B→C with the speed of
2–5 cm/h. The n-type samples with about 1016 cm-3are grown using this method. The
Czochralski method is also available.
The vapor phase method is available to deposit the thin films. For instance, InAs is grown on the
low temperature area by heating the closed tube loaded with In+AsCl3
together with Cl2
, which
works as a carrier gas. By using this method, we can grow the epitaxial layer.
Hazard
See indium; arsenic.
Structure and conformation
The space lattice of InAs belongs to the cubic system, and its zinc-blend structure has a lattice constant of a=0.6058 nm and the nearest neighbor distance of 0.262 nm.
Properties of INDIUM ARSENIDE
| Melting point: | 936°C |
| Density | 5.69 g/cm3 |
| refractive index | 3.51 |
| solubility | insoluble in acid solutions |
| form | 1.5 To 9.5mm Polycrystalline Pieces |
| color | Gray |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water. |
| Crystal Structure | Cubic, Sphalerite Structure - Space Group F(-4)3m |
| Merck | 14,4949 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.01 mg/m3; TWA 0.1 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 5 mg/m3; TWA 0.1 mg/m3; Ceiling 0.002 mg/m3 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Indium arsenide (InAs) (1303-11-3) |
Safety information for INDIUM ARSENIDE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for INDIUM ARSENIDE
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
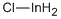
You may like
-
 Indium arsenide CAS 1303-11-3View Details
Indium arsenide CAS 1303-11-3View Details
1303-11-3 -
 Indium arsenide CAS 1303-11-3View Details
Indium arsenide CAS 1303-11-3View Details
1303-11-3 -
 Indium arsenide, Hardly attacked by mineral acids CAS 1303-11-3View Details
Indium arsenide, Hardly attacked by mineral acids CAS 1303-11-3View Details
1303-11-3 -
 Indium arsenide, Hardly attacked by mineral acids CAS 1303-11-3View Details
Indium arsenide, Hardly attacked by mineral acids CAS 1303-11-3View Details
1303-11-3 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
