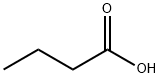
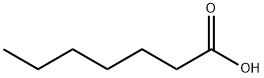
Hexanoic acid
Synonym(s):Acid C6;Caproic acid;Hexanoic acid
- CAS NO.:142-62-1
- Empirical Formula: C6H12O2
- Molecular Weight: 116.16
- MDL number: MFCD00004421
- EINECS: 205-550-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:38
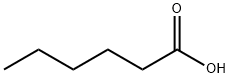
What is Hexanoic acid?
Description
Hexanoic acid (also known as Caproci acid), is the carboxylic acid derived from hexane with the general formula C5H11COOH. It is a colorless oily liquid with an odor that is fatty, cheesy, waxy, and like that of goats or other barnyard animals. It is a fatty acid found naturally in various animal fats and oils, and is one of the chemicals that give the decomposing fleshy seed coat of the ginkgo its characteristic unpleasant odor. The primary use of hexanoic acid is in the manufacture of its esters for artificial flavors, and in the manufacture of hexyl derivatives, such as hexylphenols. Hexanoic acid belongs to medium chain triglycerides (MCT) that are widely used as a nutrition supplement that added to foods, drugs and cosmetics.
Chemical properties
Hexanoic acid is a colourless liquid that has a sickening, sweaty, rancid, sour, sharp, pungent, cheesy, fatty, unpleasant odor reminiscent of copra oil. It exhibits an acrid taste. Hexanoic acid may be prepared by fractionation of the volatile fatty acids of coconut oil.
Physical properties
Hexanoic acid is oily, colorless or slightly yellow, and liquid at room temperature. Odor is that of Limburger cheese. Soluble in alcohol and ether; slightly soluble in water. It is derived from the crude fermentation of butyric acid; or by fractional distillation of natural fatty acids.
Occurrence
Hexanoic acid is found in many foods, some of which are tapioca pearl, meat bouillon, pecan nut, and oval-leaf huckleberry. A secondary product of butyric fermentation; reported found in the essential oils of lavender, camphor, palmarosa, lemongrass and Juniperus phoenicea; in a few fruital aromas: apple, currant and strawberry; also identified among the constituents of petitgrain lime oil.
The Uses of Hexanoic acid
Hexanoic acid is used to prepare esters by reacting with alcohols, which finds application in artificial flavors. It is also involved in the production of hexylphenols, hexanoates and caproates. Further, it is used as non-viral gene carrier as well as to protect tomato plants from Botrytis cinerea.
What are the applications of Application
Hexanoic acid is a carboxylic acid used as a building block for biochemical research
Definition
ChEBI: Hexanoic acid is a C6, straight-chain saturated fatty acid. It has a role as a human metabolite and a plant metabolite. It is a straight-chain saturated fatty acid and a medium-chain fatty acid. It is a conjugate acid of a hexanoate.
Preparation
hexanoic acid is produced by fractionation of the volatile fatty acids of coconut oil.
Aroma threshold values
Detection: 93 ppb to 10 ppm
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 99, p. 3184, 1977 DOI: 10.1021/ja00451a064
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 57, p. 6173, 1992 DOI: 10.1021/jo00049a024
Tetrahedron Letters, 11, p. 2679, 1970
General Description
Hexanoic acid is an oily carboxylic acid found (as glycerides) in cow’s milk and some vegetable oils. It is a white crystalline solid or colorless to light yellow solution with an unpleasant odor. Insoluble to slightly soluble in water and less dense than water. Contact may severely irritate skin, eyes and mucous membranes. May be toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. Used to make perfumes.
Air & Water Reactions
Slightly water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Hexanoic acid is a carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acids donate hydrogen ions if a base is present to accept them. They react in this way with all bases, both organic (for example, the amines) and inorganic. Their reactions with bases, called "neutralizations", are accompanied by the evolution of substantial amounts of heat. Neutralization between an acid and a base produces water plus a salt. Carboxylic acids with six or fewer carbon atoms are freely or moderately soluble in water; those with more than six carbons are slightly soluble in water. Soluble carboxylic acid dissociate to an extent in water to yield hydrogen ions. The pH of solutions of carboxylic acids is therefore less than 7.0. Many insoluble carboxylic acids react rapidly with aqueous solutions containing a chemical base and dissolve as the neutralization generates a soluble salt. Carboxylic acids in aqueous solution and liquid or molten carboxylic acids can react with active metals to form gaseous hydrogen and a metal salt. Such reactions occur in principle for solid carboxylic acids as well, but are slow if the solid acid remains dry. Even "insoluble" carboxylic acids may absorb enough water from the air and dissolve sufficiently in Hexanoic acid to corrode or dissolve iron, steel, and aluminum parts and containers. Carboxylic acids, like other acids, react with cyanide salts to generate gaseous hydrogen cyanide. The reaction is slower for dry, solid carboxylic acids. Insoluble carboxylic acids react with solutions of cyanides to cause the release of gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases and heat are generated by the reaction of carboxylic acids with diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides. Carboxylic acids, especially in aqueous solution, also react with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), to generate flammable and/or toxic gases and heat. Their reaction with carbonates and bicarbonates generates a harmless gas (carbon dioxide) but still heat. Like other organic compounds, carboxylic acids can be oxidized by strong oxidizing agents and reduced by strong reducing agents. These reactions generate heat. A wide variety of products is possible. Like other acids, carboxylic acids may initiate polymerization reactions; like other acids, they often catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions. Hexanoic acid reacts with bases, oxidizing agents and reducing agents.
Hazard
Strong irritant to tissue.
Health Hazard
Harmful if swallowed, inhaled, or absorbed through skin. Material is extremely destructive to tissue of mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract, eyes and skin. Inhalation may be fatal as a result of spasm, inflammation and edema of the larynx and bronchia, chemical pneumonitis and pulmonary edema. Symptoms of exposure may include burning sensation, coughing, wheezing, laryngitis, shortness of breath, headache, nausea and vomiting.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Irritating vapor may be generated.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Purification Methods
Dry the acid with MgSO4 and fractionally distil it from CaSO4. [Beilstein 2 IV 917.]
References
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/hexanoic_acid#section=Toxicological-Information
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hexanoic_acid
Properties of Hexanoic acid
| Melting point: | -4 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 202-203 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.927 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 4 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.18 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 2559 | HEXANOIC ACID |
| Flash point: | 220 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | water: slightly soluble1.082g/100g(lit.) |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 4.85(at 25℃) |
| Specific Gravity | 0.929 (20/4℃) |
| color | Clear colorless to light yellow |
| PH | 3.95(1 mM solution);3.43(10 mM solution);2.93(100 mM solution); |
| Odor | at 10.00 % in propylene glycol. sour fatty sweat cheese |
| Odor Threshold | 0.0006ppm |
| Water Solubility | 1.1 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,1759 |
| JECFA Number | 93 |
| BRN | 773837 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.6(71℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with bases, reducing agents and oxidizing agents. Flammable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 142-62-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Hexanoic acid(142-62-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Hexanoic acid (142-62-1) |
Safety information for Hexanoic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H311:Acute toxicity,dermal H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Hexanoic acid
| InChIKey | FUZZWVXGSFPDMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Hexanoic acid manufacturer
Madhu Chemicals
Triveni Interchem Private Limited (Group Of Triveni Chemicals)
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 CAPROIC ACID 99%View Details
CAPROIC ACID 99%View Details -
 Hexanoic Acid 98%View Details
Hexanoic Acid 98%View Details -
 Hexanoic acid 98.00% CAS 142-62-1View Details
Hexanoic acid 98.00% CAS 142-62-1View Details
142-62-1 -
 Hexanoic acid 95% CAS 142-62-1View Details
Hexanoic acid 95% CAS 142-62-1View Details
142-62-1 -
 Caproic Acid CASView Details
Caproic Acid CASView Details -
 Caproic Acid extrapure CAS 142-62-1View Details
Caproic Acid extrapure CAS 142-62-1View Details
142-62-1 -
 N-Caproic Acid (142-62-1)View Details
N-Caproic Acid (142-62-1)View Details
142-62-1 -
 Caproic Acid /Hexanoic Acid, CAS Number: 142-62-1, Packaging Size: 180 KgsView Details
Caproic Acid /Hexanoic Acid, CAS Number: 142-62-1, Packaging Size: 180 KgsView Details
142-62-1