Ethyl silicate
Synonym(s):TEOS;Tetraethyl orthosilicate;Tetraethoxysilane;Tetraethyl silicate;Tetraethoxysilicon(IV)
- CAS NO.:78-10-4
- Empirical Formula: C8H20O4Si
- Molecular Weight: 208.33
- MDL number: MFCD00009062
- EINECS: 201-083-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:40
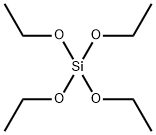
What is Ethyl silicate?
Description
Tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) is an ester of orthosilicic acid, which exists in small amounts in nature wherever silica is in contact with water. The ester is also known by several other names, including ethyl silicate (which is somewhat ambiguous), silicon tetraethoxide, and tetraethoxysilane.
In a landmark paper published in 1928, A. W. Dearing and E. Emmet Reid* at Johns Hopkins University (Baltimore) reported improved syntheses of various alkyl orthosilicates. TEOS was obtained in 70% yield by slowly adding silicon tetrachloride (SiCl4) to cold anhydrous ethanol, followed by removing byproduct hydrogen chloride with a stream of dry air. The reaction system must be rigorously free of water because even though TEOS is only slightly soluble in water, it hydrolyzes to form silica and ethanol. The reaction is the basis of modern TEOS production.
TEOS has multiple specialty uses, including stone hardening (which arrests the decay of structures and art objects), mortar and cement manufacture, and cross-linking silicone polymers. Its 2020 global market is valued at US$245 million for an estimated production of ≈120,000 t.
Chemical properties
Ethyl silicate is a flammable, colourless liquid with a mild, sweet, alcohol-like odour. Exposure to ethyl silicate can occur through inhalation, ingestion, and eye or skin contact. It is practically insoluble in water, soluble in alcohol, and slightly soluble in benzene.
The Uses of Ethyl silicate
Tetraethyl Orthosilicate is used in the preparation of antidreflective coatings on silicate glass via silicon dioxide. Crosslinking reagent.
The Uses of Ethyl silicate
Commonly used as a precursor to prepare xerogel1,2
The Uses of Ethyl silicate
In weatherproofing and hardening stone, arresting decay and disintegration; manufacture of weatherproof and acidproof mortars and cements. In the "lost wax" process for casting of high-melting alloys.
What are the applications of Application
Tetraethyl orthosilicate is a commonly used precursor to prepare xerogel & study of mixed-metal bioactive glasses
Production Methods
Prepared from absolute alcohol and silicon tetrachloride.
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with a faint odor. Flash point 125°F. Less dense than water. Vapors are heavier than air.
Air & Water Reactions
Flammable. Practically insoluble in water. Reacts slowly with water to form silica and ethyl alcohol [Merck].
Reactivity Profile
Tetraethyl orthosilicate reacts exothermically with acids Strong oxidizing acids may cause a reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. May generate with caustic solutions. May generate flammable hydrogen with alkali metals and hydrides.
Hazard
Moderate fire risk. Strong irritant to eyes, nose, throat.
Health Hazard
Exposures to ethyl silicate cause adverse health effects. The symptoms of poisoning include, but are not limited to, irritation of the eye, mucous membrane, respiratory tract, respiratory difficulty, tremor, fatigue, narcosis, nausea, and vomiting. Prolonged periods of skin contact may produce drying, cracking, inflammation, and dermatitis. As observed in laboratory animals, occupational workers exposed to the chemical substance may suffer from liver and kidney damage, CNS depression, and anemia. At concentrations of 3000 ppm, ethyl silicate causes extreme and intolerable irritation of the eyes and mucous membranes; at 1200 ppm, it produces tearing of the eyes; at 700 ppm, it causes mild stinging of the eyes and nose; and at 250 ppm, it produces slight irritation of the eyes and nose.
Fire Hazard
HIGHLY FLAMMABLE: Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route. Moderately toxic by other routes. A skin,mucous membrane, and severe eye irritant. Narcotic in high concentrations. Flammable liquid when exposed to heat or flame; can react vigorously with oxidzing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes. See also ESTERS.
Potential Exposure
Ethyl silicate is used as a binder in production of cases and molds for investment casting of metals. The next largest application is in corrosion-resistant coatings; primarily as a binder for zinc dust paints. Miscellaneous uses include the protection of white-light bulbs; the preparation of soluble silicas; catalyst preparation and regeneration; and as a crosslinker and intermediate in the production of silicones
Shipping
UN1292 Tetraethyl acetate, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid.
Purification Methods
Fractionate it through an 80cm Podbielniak type column (p 11) with a heated jacket and partial take-off head. It is slowly decomposed by H2O-and is soluble in EtOH. It is flammable-it irritates the eyes and mucous membranes. [Sumrell & Ham J Am Chem Soc 78 5573 1956, Bradley et al. J Chem Soc 5020 1952, Beilstein 1 IV 1360.]
Incompatibilities
May form explosive mixture with air. Strong oxidizers; strong acids; water.
Waste Disposal
Incineration in admixture with a more flammable solvent.
Precautions
Occupational workers should avoid contact between ethyl silicate and strong oxidizers, water, mineral acids, and alkalis. Workers should use appropriate personal protective clothing and equipment that must be carefully selected, used, and maintained to be effective in preventing skin contact with ethyl silicate. The selection of the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) (e.g., gloves, sleeves, encapsulating suits) should be based on the extent of the worker’s potential exposure to ethyl silicate. There are no published reports on the resistance of various materials to permeation by ethyl silicate.
Properties of Ethyl silicate
| Melting point: | -77 °C |
| Boiling point: | 168 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.933 g/mL at 20 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 7.2 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | <1 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 116 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | Soluble in ethanol and 2-propanol. |
| form | Liquid |
| appearance | colorless liquid |
| color | Colorless |
| Specific Gravity | 0.934 |
| explosive limit | 1.3-23%(V) |
| Water Solubility | Hydrolysis |
| FreezingPoint | -77℃ |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 7: reacts slowly with moisture/water |
| Merck | 14,3851 |
| BRN | 1422225 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 10 ppm OSHA: TWA 100 ppm(850 mg/m3) NIOSH: IDLH 700 ppm; TWA 10 ppm(85 mg/m3) |
| Dielectric constant | 4.1(20℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, water, alkalies, mineral acids. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 78-10-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Silicic acid (H4sio4), tetraethyl ester(78-10-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tetraethyl silicate (78-10-4) |
Safety information for Ethyl silicate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H226:Flammable liquids H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P241:Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/…/equipment. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Ethyl silicate
| InChIKey | BOTDANWDWHJENH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Ethyl silicate manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Triveni Interchem Private Limited (Group Of Triveni Chemicals)
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

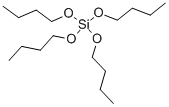
You may like
-
 Tetraethoxysilane CAS 78-10-4View Details
Tetraethoxysilane CAS 78-10-4View Details
78-10-4 -
 Tetraethoxysilane CAS 78-10-4View Details
Tetraethoxysilane CAS 78-10-4View Details
78-10-4 -
 Tetraethoxysilane CAS 78-10-4View Details
Tetraethoxysilane CAS 78-10-4View Details
78-10-4 -
 Tetraethoxysilane CAS 78-10-4View Details
Tetraethoxysilane CAS 78-10-4View Details
78-10-4 -
 Tetraethoxysilane CAS 78-10-4View Details
Tetraethoxysilane CAS 78-10-4View Details
78-10-4 -
 Tetraethoxysilane CAS 78-10-4View Details
Tetraethoxysilane CAS 78-10-4View Details
78-10-4 -
 Tetraethyl Orthosilicate (TEOS) extrapure CAS 78-10-4View Details
Tetraethyl Orthosilicate (TEOS) extrapure CAS 78-10-4View Details
78-10-4 -
 Ethyl Silicate 40, 200 Kg, Technical GradeView Details
Ethyl Silicate 40, 200 Kg, Technical GradeView Details
78-10-4
