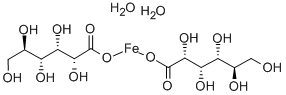
Gluconic acid
Synonym(s):2,3,4,5,6-Pentahydroxycaproic acid
- CAS NO.:526-95-4
- Empirical Formula: C6H12O7
- Molecular Weight: 196.16
- MDL number: MFCD00004240
- EINECS: 208-401-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 08:32:17
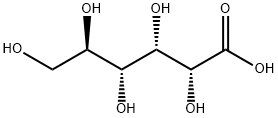
What is Gluconic acid?
Description
Gluconic acid is an organic compound with molecular formula C6H12O7 and condensed structural formula HOCH2(CHOH)4COOH. It is one of the 16 stereoisomers of 2,3,4,5,6-penta hydroxy hexanoic acid.
In aqueous solution at neutral pH, gluconic acid forms the gluconate ion. The salts of gluconic acid are known as "gluconates". Gluconic acid, gluconate salts, and gluconate esters occur widely in nature because such species arise from the oxidation of glucose. Some drugs are injected in the form of gluconates.
Description
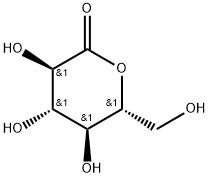
D-Gluconic acid is the oxidized form of D-glucose (or dextrose), one of the fundamental building blocks for sugars, polysaccharides, and cellulose. Like glucose, it cyclizes in solution, in this case to form an ester (glucono-δ-lactone) rather than a hemiacetal.
Gluconic acid widely exists in nature, especially in fruits and in sucrose-containing substances such as honey. Early methods of synthesizing gluconic acid from glucose included hypobromite oxidation and alkaline hydrolysis. Now it is commercially produced by using microbes such as Aspergillus niger to oxidize glucose enzymatically.
Gluconate, gluconic acid’s conjugate base, is useful as a metal-chelating agent in alkaline solutions. It is a component of many cleaning products; and it is used to prevent formation of solids in dairy processing and beer brewing.
More recently, gluconic acid has been investigated as a chelating agent for extracting rare earths (lanthanides) from the fertilizer waste phosphogypsum.1 An estimated 100,000 t per year of valuable lanthanides are discarded in this waste product worldwide. Sulfuric acid is highly effective for recovering the rare earths, but a team led by Richard E. Riman of Rutgers University (New Brunswick, NJ) showed that gluconic acid and other bioacids are promising alternatives and would be considerably easier than sulfuric acid to treat for disposal.
1. Phosphogypsum does not contain phosphorus; it is a mostly gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O) waste product of phosphoric acid plants.
Chemical properties
clear yellow to brownish-yellow solution
Chemical properties
d-Gluconic acid is an acid sugar composed of white crystals with
a milk-acidic taste. In aqueous solutions, it is in equilibrium with gamma- and delta-gluconolactones. It is prepared by enzymatic
oxidation of glucose and strains of the microorganisms used to
supply the enzyme action are nonpathogenic and nontoxicogenic
to man or other animals. This substance is used as a component
of bottle rinsing formulations, at levels not to exceed good manufacturing
practice.
An FDA letter to a trade association revoking affirmation of general
recognition of safety in dietary supplements was dated April
9, 1970.
Physical properties
The chemical structure of gluconic acid consists of a six-carbon chain with five hydroxyl groups terminating in a carboxylic acid group. In aqueous solution, gluconic acid exists in equilibrium with the cyclic ester glucono delta-lactone.
Occurrence
Gluconic acid occurs naturally in fruit, honey, kombucha tea, and wine. As a food additive ( E574 ), it is an acidity regulator. It is also used in cleaning products where it dissolves mineral deposits especially in alkaline solution. The gluconate anion chelates Ca2+,Fe2+, Al3+, and other metals. In 1929 Horace Terhune Herrick developed a process for producing the salt by fermentation.
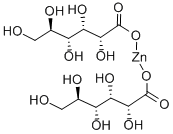
Calcium gluconate, in the form of a gel, is used to treat burns from hydrofluoric acid; calcium gluconate injections may be used for more severe cases to avoid necrosis of deep tissues. Quinine gluconate is a salt between gluconic acid and quinine, which is used for intramuscular injection in the treatment of malaria. Zinc gluconate injections are used to neuter male dogs. Iron gluconate injections have been proposed in the past to treat anemia.
The Uses of Gluconic acid
Gluconic Acid is an acidulant that is a mild organic acid which is the hydrolyzed form of glucono-delta-lactone. it is prepared by the fermentation of dextrose, whereby the physiological d-form is produced. it is soluble in water with a solubility of 100 g/100 ml at 20°c. it has a mild taste and at 1% has a ph of 2.8. it functions as an antioxidant and enhances the function of other antioxidants. in beverages, syrups, and wine, it can eliminate calcium turbidities. it is used as a leavening component in cake mixes, and as an acid component in dry-mix desserts and dry beverage mixes.
The Uses of Gluconic acid
A chemical used in glycolytic pathway studies.
The Uses of Gluconic acid
Gluconic acid occurs naturally in fruit, honey, and wine. As a food additive it is an acidity regulator. It is also used in cleaning products.
What are the applications of Application
D-Gluconic acid solution is a chemical used in glycolytic pathway studies
Background
Commonly found in salts with sodium and calcium. Gluconic acid or gluconate is used to maintain the cation-anion balance on electrolyte solutions.
Indications
For use as part of electrolyte supplementation in total parenteral nutrition [FDA Label].
Definition
A soluble crystalline organic acid made by the oxidation of glucose (using specific molds). It is used in paint strippers.
Definition
gluconic acid: An opticallyactive hydroxycarboxylic acid,CH2(OH)(CHOH)4COOH. It is the carboxylicacid corresponding to the aldosesugar glucose, and can be madeby the action of certain moulds.
brand name
Calglucon (Novartis).
Biotechnological Production
Currently, gluconic acid is commercially produced by submerged fed-batch cultivations
of Aspergillus niger using glucose as substrate. A. niger produces
citric acid and gluconic acid growing on glucose. The product concentration and
yields of the product depend on the fermentation conditions. For optimal gluconic
acid production, high glucose concentrations (110–250 g.L-1), low concentrations
of nitrogen and phosphorus in the medium, a limitation of metal ion concentrations,
a pH value in the range of 4.5–6.5, and high aeration rates for the oxygen
supply are needed.
Much research has been carried out to find new ways for cheaper production.
Different microorganisms have been studied (e.g. G. oxydans, Z. mobilis, A.
methanolicous, and P. fluorescence. Moreover, new microbial strains
have been developed by mutagenesis or genetic engineering. Additionally,
the fermentation process and recovery have been optimized. New inexpensive
substrates (e.g. cornstarch, grape or banana must, figs, and cheese whey)
have been tested.
One example of a new and efficient production process of gluconic acid is the
cultivation of Aureobasidium pullulans growing on glucose. Using a
continuous process with biomass retention by crossover filtration, a product concentration of 375 g.L-1, a yield of 0.83 g of gluconic acid per gram of glucose, and
a productivity of 17 g.L-1.h-1 could be achieved at a residence time of 22 h. In
this process, 100 % of the glucose is converted. This process might be
interesting for industrial applications. In continuous gluconic acid production with
immobilized mycelia of A. niger, product concentrations of 120–140 g.L-1 have
been achieved.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Pharmacokinetics
Used as part of electrolyte salts to maintain cation-anion balance in solutions.
Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of Gluconic acid
| Melting point: | 15 °C |
| Boiling point: | 102 °C |
| alpha | D20 -6.7° (c = 1) |
| Density | 1.23 |
| refractive index | 1.4161 |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly), Water |
| appearance | colorless or white crystals |
| form | Crystalline Powder or Crystals |
| pka | pK (25°) 3.60 |
| color | White to light yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 1.234 |
| Odor | commercial 50 aq. soln. lt. amber, faint odor of vinegar |
| optical activity | [α]/D +9.0 to 15.5° |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Merck | 14,4456 |
| BRN | 1726055 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 526-95-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Gluconic acid(526-95-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | D-Gluconic acid (526-95-4) |
Safety information for Gluconic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P330+P331:IF SWALLOWED: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Gluconic acid
Gluconic acid manufacturer
Gandhi Chemicals
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 GLUCONIC ACID 50%View Details
GLUCONIC ACID 50%View Details -
 Gluconic Acid CASView Details
Gluconic Acid CASView Details -
 Gluconic acid CAS 526-95-4View Details
Gluconic acid CAS 526-95-4View Details
526-95-4 -
 Gluconic Acid (contains Gluconolactone) (45-50% in Water) CAS 526-95-4View Details
Gluconic Acid (contains Gluconolactone) (45-50% in Water) CAS 526-95-4View Details
526-95-4 -
 D-Gluconic acid 50%, solution CAS 526-95-4View Details
D-Gluconic acid 50%, solution CAS 526-95-4View Details
526-95-4 -
 Gluconic acid CASView Details
Gluconic acid CASView Details -
 Liquid Gluconic Acid, Packaging Type: Drum Packing, Packaging Size: 250 Kgs DrumView Details
Liquid Gluconic Acid, Packaging Type: Drum Packing, Packaging Size: 250 Kgs DrumView Details
526-95-4 -
 Gluconic Acid cas no : 526-95-4, For Industrial, LiquidView Details
Gluconic Acid cas no : 526-95-4, For Industrial, LiquidView Details
526-95-4
