Zinc gluconate
- CAS NO.:4468-02-4
- Empirical Formula: C12H22O14Zn
- Molecular Weight: 455.68
- MDL number: MFCD00868110
- EINECS: 224-736-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:59
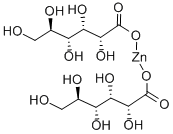
What is Zinc gluconate?
Absorption
Please refer to DrugBank entry Zinc
Toxicity
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and mouth irritation have been reported in patients ingesting zinc gluconate tablets that were dissolved in the mouth for management the common cold .
Zinc crosses the placenta and is found the cord blood and placenta. Fetal concentrations are regulated by the placenta .
For more information, refer to Please refer to DrugBank entry Zinc.
Acute: 1290 mg/kg in mouse
Chemical properties
White or almost white, hygroscopic, crystalline powder.
The Uses of Zinc gluconate
zinc gluconate helps maintain the skin in good condition and acts as a deodorant by preventing the growth of micro-organisms, such as bacteria, fungi or yeast, in a formulation. Zinc gluconate could also be effectively used in anti-acne products.
The Uses of Zinc gluconate
Chelating agent. In high alkalinity bottle washes and other cleansers; in finish removers; in the tanning and textile industry.
The Uses of Zinc gluconate
Zinc gluconate hydrate is used as a food additive, a pharmaceutical intermediate.
Background
Zinc gluconate is a zinc salt of gluconic acid comprised of two gluconic acid molecules for each zinc cation (2+). Zinc gluconate is a generally recognized as safe (GRAS) substance by FDA . It is available as a trace mineral supplement and over the counter as a lozenge form for a reduced duration of common colds and with decreased symptom severity.
Although it has been nasally administered for treating the common cold, this route of administration has been associated with some cases of anosmia , , , .
Studies show that zinc may be better absorbed in humans in the gluconate form , , however, results from other studies may vary.
Interestingly, zinc supplementation has become a critical intervention for treating diarrheal episodes in children. Studies suggest that administration of zinc along with new low osmolarity oral rehydration solutions/salts (oral rehydration solution), may reduce both the duration and severity of diarrheal episodes for up to 12 weeks .
More information about Zinc (in its natural form) is available at Zinc.
Indications
Zinc gluconate is mainly indicated in conditions like zinc deficiency, and can also be administered in adjunctive therapy as an alternative drug of choice in diarrhea .
Definition
ChEBI: Zinc gluconate is a L-alpha-D-Hepp-(1->7)-L-alpha-D-Hepp-(1->3)-L-alpha-D-Hepp-(1->5)-alpha-Kdo.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Biotechnological Applications
Zinc gluconate is the most common standalone zinc supplement and is used in zinc lozenges, which are discussed later. In one study, the use of a zinc tolerance test shows zinc gluconate to be better absorbed than zinc sulfate. It can also be noted that zinc gluconate has given positive results in a number of supplementation studies, including some done for malnutrition situations. On the other hand, in a small unpublished study from this author, zinc gluconate was very ineffective at raising plasma zinc, while a zinc amino acid chelate raised plasma zinc in all subjects tested. In addition, in a rat supplementation study, neither zinc gluconate nor zinc sulfate was as effective as a zinc–amino acid chelate in protecting against chemically induced oxidant damage. Thus, zinc gluconate seems to be a good source of zinc for many purposes, though in some applications, it may not be the absolute best source.
Pharmacokinetics
Zinc is an important mineral found in almost every cell in the human body. It promotes the activity of about 100 enzymes. Zinc deficiency is often associated with an increased risk of infection. When they are used to treat the common cold, zinc supplements may interfere with rhinovirus cleavage or adhesion and may play a role in protecting plasma membranes from microbial toxins and complement .
Safety Profile
Experimental reproductive effects. W'hen heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of ZnO.
Metabolism
Please refer to DrugBank entry Zinc
Properties of Zinc gluconate
| Melting point: | 172-175 °C |
| Boiling point: | 319°C |
| Density | 1.44[at 20℃] |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 20℃ |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in water, practically insoluble in anhydrous ethanol and in methylene chloride. |
| form | powder to crystal |
| color | White to Almost white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water 100g/ l. |
| Merck | 14,4456 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 4468-02-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Zinc, bis(D-gluconato-.kappa.O1,.kappa.O2)-, (T-4)- (4468-02-4) |
Safety information for Zinc gluconate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. |
Computed Descriptors for Zinc gluconate
Zinc gluconate manufacturer
Vasa Pharmachem Pvt Ltd. (VPPL)
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
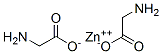

You may like
-
 Zinc Gluconate 98%View Details
Zinc Gluconate 98%View Details -
 Zinc gluconate 98%View Details
Zinc gluconate 98%View Details -
 4468-02-4 99%View Details
4468-02-4 99%View Details
4468-02-4 -
 Zinc gluconate 99%View Details
Zinc gluconate 99%View Details
4468-02-4 -
 Zinc gluconate 4468-02-4 98%View Details
Zinc gluconate 4468-02-4 98%View Details
4468-02-4 -
 4468-02-4 Zinc gluconate 98%View Details
4468-02-4 Zinc gluconate 98%View Details
4468-02-4 -
 Zinc gluconate 98%View Details
Zinc gluconate 98%View Details
4468-02-4 -
 Zinc(II) Gluconate CAS 4468-02-4View Details
Zinc(II) Gluconate CAS 4468-02-4View Details
4468-02-4
