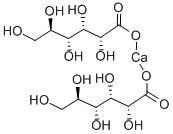
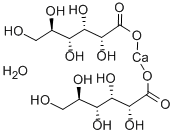
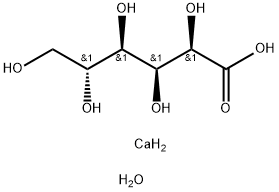
Calcium gluconate
Synonym(s):2,3,4,5,6-Pentahydroxycaproic Acid hemicalcium salt;Calcium D -gluconate;Gluconic acid hemicalcium salt
- CAS NO.:299-28-5
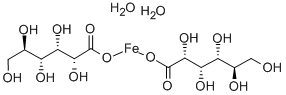
- Empirical Formula: C12H22CaO14
- Molecular Weight: 430.37
- MDL number: MFCD00064209
- EINECS: 206-075-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 13:58:55
What is Calcium gluconate?
Chemical properties
white crystalline powder or granules
The Uses of Calcium gluconate
analgesic, antipyretic
The Uses of Calcium gluconate
In sewage purification; in coffee powders to prevent caking.
The Uses of Calcium gluconate
Calcium Gluconate is used as an inert ingredient in pesticide formulations applied to crops. It is also used as a supplement to fortify beverages and foods lacking a sufficient amount of calcium.
The Uses of Calcium gluconate
Calcium Gluconate is a white crystalline granule or powder that functions as a firming agent, formulation aid, sequestrant, and sta- bilizer. at room temperature the anhydrous form has a solubility of approximately 1 g in 30 ml of water, which improves in boiling water to approximately 1 g in 5 ml of water. it also exists as calcium gluconate (monohydrate). it is used as a source of calcium ions for sodium alginate gels, and as a calcium fortifier in baked goods, pud- dings, and dairy product analogs. it functions as a coagulation aid in milk and instant pudding powders and as a means of masking the bitter aftertaste of some artificial sweeteners.
Indications
Oral calcium salts are used as dietary supplemental therapy for person who may not get enough calcium in their regular diet. Calcium gluconate is used as a cardioprotective agent in high blood potassium. Calcium gluconate is the antidote for magnesium sulfate toxicity.
Background
Calcium gluconate is used as mineral supplement and medication when there is insufficient calcium in the diet. Supplementation may be done to treat or prevent osteoporosis or rickets, consequences of hypocalcemia. It can also be taken by mouth but is not recommended by injection into a muscle. Calcium Gluconate Injection, USP is a sterile, nonpyrogenic supersaturated solution of calcium gluconate for intravenous use only.
Definition
ChEBI: Calcium gluconate is the calcium salt of D-gluconic acid. It has a role as a nutraceutical. It contains a D-gluconate.
brand name
Calglucon (Novartis).
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Industrial uses
calcium gluconate [Ca(C6H11O7)2] is used as a food additive in vitamin pills.injection of a 10% calcium gluconate has been recommended. It has to be kept in mind that the plasma Ca2+ level and any changes to the electrocardiogram (ECG) have to be carefully monitored.
Pharmacokinetics
Calcium Gluconate is the gluconate salt of calcium. An element or mineral necessary for normal nerve, muscle, and cardiac function, calcium as the gluconate salt helps to maintain calcium balance and prevent bone loss when taken orally. This agent may also be chemopreventive for colon and other cancers.
Clinical Use
Hypocalcaemia
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by subcutaneous, intraperitoneal, and intravenous routes. Human systemic effects in infants by intramuscular route: dermatitis and fever. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes. See also CALCIUM COMPOUNDS.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Calcium salts are used for the prevention or treatment of hypocalcemic conditions.
Side Effects
Calcium gluconate side effects include nausea, constipation, and upset stomach. Rapid intravenous injections of calcium gluconate may cause hypercalcemia, which can result in vasodilation, cardiac arrhythmias, decreased blood pressure, and bradycardia. Extravasation of calcium gluconate can lead to cellulitis. Intramuscular injections may lead to local necrosis and abscess formation.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Can impair absorption of some drugs, e.g. iron,
ciprofloxacin.
Absorption
Approximately one-fifth to one-third of orally administered calcium is absorbed in the small intestine, depending on presence of vitamin D metabolites, pH in lumen, and on dietary factors, such as calcium binding to fiber or phytates. Calcium absorption is increased when a calcium deficiency is present or when a patient is on a low-calcium diet. In patients with achlorhydria or hypochlorhydria, calcium absorption, especially with the carbonate salt, may be reduced.
Metabolism
Calcium is absorbed mainly from the small intestine by active transport and passive diffusion. About one-third of ingested calcium is absorbed although this can vary depending upon dietary factors and the state of the small intestine. 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol (calcitriol), a metabolite of vitamin D, enhances the active phase of absorption. Excess calcium is mainly excreted renally. Unabsorbed calcium is eliminated in the faeces, together with that secreted in the bile and pancreatic juice. Minor amounts are lost in the sweat, skin, hair, and nails.
Metabolism
Calcium gluconate does not require hepatic metabolism for the release of Ca++ and is as effective as calcium chloride in treating ionic hypocalcemia in the absence of hepatic function.
Toxicity
Infants : LDLo (Intramuscular ) : 10gm/kg ; Effects - Brain and coverings : meningeal changes Infants : TDLo ( Intramuscular ) : 143 mg/kg ; Effects - Dermatits Mouse: LD50 ( intravenous ) : 950mg/kg Mouse : LDLo (Oral ) : 10gm/kg
Purification Methods
Dissolve it in H2O, filter and precipitate it by adding MeOH. Filter off the solid and dry it in a vacuum at 85o. Alternatively, dissolve it in H2O, filter (from insoluble inorganic Ca) and evaporate it to dryness under vacuum at 85o. [March et al. J Am Pharm Assoc 41 366 1952, Beilstein 3 IV 1255.]
Properties of Calcium gluconate
| Melting point: | 195°C |
| Boiling point: | 400℃[at 101 325 Pa] |
| alpha | 10.2 º (c=1, H2O 22 ºC) |
| Density | 1.677[at 20℃] |
| vapor pressure | 0.004Pa at 20℃ |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Sparingly soluble in water, freely soluble in boiling water. |
| form | Crystals or Crystalline Powder |
| color | White |
| PH | pH;6.0~8.0 |
| Odor | at 100.00?%. odorless |
| Water Solubility | 3.3 g/100mL |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 0: forms stable aqueous solutions |
| Merck | 14,1669 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 299-28-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | D-Gluconic acid, calcium salt (2:1) (299-28-5) |
Safety information for Calcium gluconate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Calcium gluconate
| InChIKey | KYUVBRZSDFBLTH-OSQBQZLYSA-M |
Calcium gluconate manufacturer
Vasa Pharmachem Pvt Ltd. (VPPL)
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Calcium Gluconate 98%View Details
Calcium Gluconate 98%View Details -
 Calcium gluconate 98%View Details
Calcium gluconate 98%View Details -
 299-28-5 Calcium gluconate 98%View Details
299-28-5 Calcium gluconate 98%View Details
299-28-5 -
 Calcium D-gluconate gel CAS 299-28-5View Details
Calcium D-gluconate gel CAS 299-28-5View Details
299-28-5 -
 Calcium gluconate monohydrate 95% CAS 299-28-5View Details
Calcium gluconate monohydrate 95% CAS 299-28-5View Details
299-28-5 -
 Calcium gluconate 98.00% CAS 299-28-5View Details
Calcium gluconate 98.00% CAS 299-28-5View Details
299-28-5 -
 CALCIUM GLUCONATEView Details
CALCIUM GLUCONATEView Details
299-28-5 -
 Calcium Gluconate, Packaging Type: Bottle, Packaging Size: 5LView Details
Calcium Gluconate, Packaging Type: Bottle, Packaging Size: 5LView Details
299-28-5
