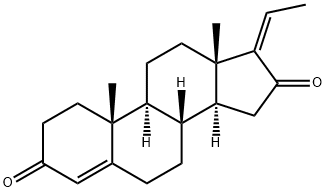
Gestrinone
- CAS NO.:16320-04-0
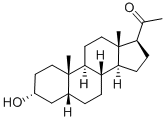
- Empirical Formula: C21H24O2
- Molecular Weight: 308.41
- MDL number: MFCD00865561
- EINECS: 685-143-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
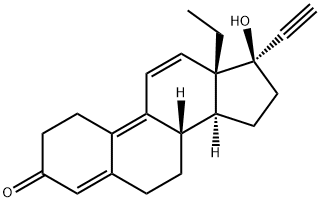
What is Gestrinone?
Absorption
The oral absorption of gestrinone is 30% ±30 .
Toxicity
Many of gestrinone's adverse effects occur due to its androgenic activity. These effects include acne, seborrhea, hirsutism, weight gain and deepening of the voice. Most patients develop at least one adverse event while taking this drug. This is because the drug is embryotoxic in some animals and may also cause masculinization of a female fetus. Gestrinone significantly reduces HDL concentrations .
It is advisable to monitor liver transaminases and cholesterol levels in hyperlipidemic patients, as well as glucose in diabetic patients. Gestrinone has shown to decrease in the concentration of thyroid-binding globulin. Therefore, a decrease in serum total thyroxine levels is commonly observed. This is without clinical significance as free thyroxine levels and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels remain within the normal reference range .
Description
Gestrinone is a synthetic steroid with antiprogesterone and antiestrogenic activities. It is reported to be useful in the treatment of endometriosis and uterine leiom yomas.
Chemical properties
Light Yellow Solid
Originator
Roussel UCLAF (France)
The Uses of Gestrinone
Steroidal antiestrogen, antiprogestogen, analog of Norgestrienone. Antigonadotropin. Controlled substance.
Indications
Endometriosis with or without accompanying sterility. Treatment is limited to a single course of 6 months duration per lifetime .
Background
Gestrinone, also known as ethylnorgestrienone, is a synthetic steroid of the 19-nortestosterone group that is marketed in Europe, Australia, and Latin America, though not the United States or Canada, and is used primarily in the treatment of endometriosis.
Gestrinone was developed in the early 1970s and was tested clinically as a weekly oral contraceptive in Europe and North America. Without significant advantages over other oral contraceptives and with its high cost, gestrinone was no longer used after the Stage II clinical trials. However, from 1982 this drug attracted increased interest due to significant therapeutic effects in the treatment endometriosis. Under different endocrine conditions, gestrinone possesses estrogenic, progestational, androgenic, antiestrogenic and antiprogesterone actions .
What are the applications of Application
Gestrinone is a synthetic steroid that acts centrally on the hypothalamic-pituitary system
Definition
ChEBI: Gestrinone is an oxo steroid.
brand name
DIMETROSE
Pharmacokinetics
Gestrinone is a synthetic steroidal hormone which has androgenic, anti-estrogenic and anti-progestogenic properties . The findings of several studies suggest that gestrinone is as effective as danazol in the treatment of infertility associated with endometriosis and is better tolerated, in terms of adverse effects .
Gestrinone has moderate anti-estrogen, and anti-gonadal properties, which can lead to increased concentrations of free testosterone, and decrease the level of sex hormone-binding globulin, suppress the FSH and LH hormone peak levels and decrease the LH mean to reduce estrogen levels. In addition, gestrinone has a direct effect on the endometrium and ectopic endometrial receptors, which have the roles of anti-progesterone and anti-estrogen effects lead to endometrial and ectopic endometrial atrophy to achieve therapeutic effects .
Gestrinone inhibits the release of pituitary gonadotropins. The effect on ovarian hormone secretion results in the atrophy of endometrial tissue, resulting in the regression of endometriosis. Gestrinone is structurally related to norgestrel and possesses some androgenic and progestogenic activity. However, the gestrinone has an antiprogesterone effect on endometrial tissue .
The effect of oral gestrinone, 2.5 mg biweekly for 6 months, was studied in a group of 11 women with mild or moderate endometriosis laparoscopically confirmed. Painful symptoms were alleviated in all patients within 8 weeks from the start of treatment. Gonadotropins, prolactin (PRL) 17 beta-estradiol (17 beta-E2), estrone (E1), progesterone (P), androstenedione (A), and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S) remained in the physiological follicular phase range .
Total testosterone (TT) and sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) decreased, and free testosterone (FT) slightly increased. Metabolic studies showed a decrease in total triglyceride level, very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) triglycerides, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and VLDL cholesterol .
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and apoprotein B were found to be increased during gestrinone therapy. It can be extrapolated that gestrinone possesses antiestrogenic, androgenic, and progestogenic effects at therapeutic dosages both by acting on both central and peripheral steroid receptors .
Side Effects
Gestrinone, like danazol, inhibits the synthesis of estrogens and progestogens and has been used mainly to prepare patients with an endometrial disorder for hysterectomy. Its most common adverse effects are nausea, headache, mood changes, rash, hot flushes, weight gain, and discomfort in the joints and muscles. In some cases, there is evidence of masculinization.
Metabolism
Gestrinone undergoes hydroxylation in the liver. Gestrinone is actively metabolized in the liver, mainly by hydroxylation, to conjugated metabolites 16b-hydroxy,13-ethyl (1-OH) and D-homo gestrinone. In vitro studies have shown that the metabolites are active but weaker than the unchanged drug .
Mode of action
The primary action of gestrinone is on the hypothalamic-pituitary axis, where it inhibits gonadotrophin release with a weak inhibitory effect on its synthesis. It also possesses anti-estrogen activity. The mode of action of gestrinone used for EC is probably inhibition of implantation by acting on the endometrium rather than inhibiting ovulation[1].
References
[1] Xuefeng Gao, Guian Chen, Erruo Wu . “Mechanism of emergency contraception with gestrinone: a preliminary investigation.” Contraception 76 3 (2007): Pages 221-227.
Properties of Gestrinone
| Melting point: | 150-152°C |
| Boiling point: | 388.8°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D20 +84.6° (c = 0.41 in methanol) |
| Density | 1.1040 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4900 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | DMF:20.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);64.85(Max Conc. mM) DMSO:35.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);113.48(Max Conc. mM) Ethanol:20.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);64.85(Max Conc. mM) Ethanol:PBS (pH 7.2) (1:5):0.25(Max Conc. mg/mL);81.06(Max Conc. mM) Water:1.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);3.24(Max Conc. mM) |
| form | A crystalline solid |
| pka | 12.76±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | Off-white to light yellow |
| Merck | 14,4415 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C21H24O2/c1-3-20-11-9-17-16-8-6-15(22)13-14(16)5-7-18(17)19(20)10-12-21(20,23)4-2/h2,9,11,13,18-19,23H,3,5-8,10,12H2,1H3/t18-,19+,20+,21+/m1/s1 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 16320-04-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Gestrinone
Computed Descriptors for Gestrinone
| InChIKey | BJJXHLWLUDYTGC-ANULTFPQSA-N |
| SMILES | C1C2C(CC[C@]3([H])C=2C=C[C@@]2(CC)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]2(C#C)O)=CC(=O)C1 |
Gestrinone manufacturer
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Gestrinone CAS 16320-04-0View Details
Gestrinone CAS 16320-04-0View Details
16320-04-0 -
 17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 -
 131987-69-4 98+View Details
131987-69-4 98+View Details
131987-69-4 -
 Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
67967-07-1 -
 764-60-3 2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
764-60-3 2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
764-60-3 -
 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
5968-21-8 -
 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
1878-69-9 -
 132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6
