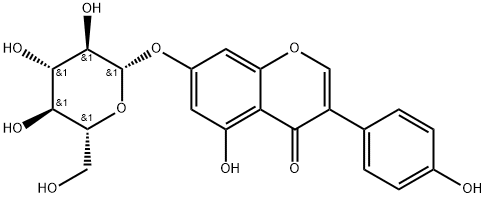
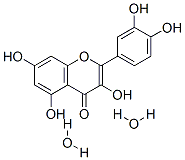
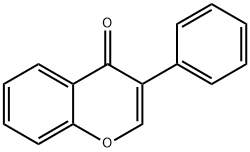
Genistein
Synonym(s):4ʹ,5,7-Trihydroxyisoflavone;4′,5,7-Trihydroxyisoflavone;5,7-Dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one;Genistein;Genistein, Soybean - CAS 446-72-0 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:446-72-0
- Empirical Formula: C15H10O5
- Molecular Weight: 270.24
- MDL number: MFCD00016952
- EINECS: 207-174-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:56
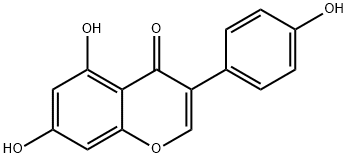
What is Genistein?
Description
Genistein (446-72-0) is a naturally occurring flavonoid with a wide range of biological actions. Inhibits protein tyrosine kinases including epidermal growth factor receptor kinase.1,2?Phytoestrogen3?and agonist at GPR304. Displays cancer chemopreventive activity.5
Chemical properties
Yellow Crystalline Solid
The Uses of Genistein
Exhibits specific inhibitory activity against tyrosine kinases,including autophosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor kinase (IC50 - 2.6uM). Also inhibits other protein kinases through competitive inhibition of ATP. Inhibits tumor cell proliferation and induces tumor cell differentiation. Produces cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in Jurat T-leukemia cells. However, it prevents anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody-induced thymic apoptosis. Genistein also inhibits topoisomerase II activity in vitro. Genistein has also been shown to inhibit the action of GABA on recombinant GABAA receptors 2. uv(max)ethanol: 262.5 nm (e= 138). moderately sol. in hot alcohol
The Uses of Genistein
Genistein, a phytoestrogen found in soy products, is a highly specific inhibitor of protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) which blocks the mitogenic effect mediated by EGF on NIH-3T3 cells with IC50 of 12μM or by insulin with IC50 of 19 μM.
The Uses of Genistein
cytotoxic inhibitor of tyrosine kinase and topoisomerase II kinase
The Uses of Genistein
genistein is an isoflavone commonly found in soy. It has demonstrated uV-protection properties through anti-oxidant activity. Studies indicate genistein can promote collagen synthesis, making it applicable in anti-aging cosmetics.
What are the applications of Application
Genistein is naturally occurring isoflavone, phytoestrogen, and highly specific inhibitor of protein tyrosine kinase (PTK).
Definition
ChEBI: 7-Hydroxyisoflavone with additional hydroxy groups at positions 5 and 4'. It is a phytoestrogenic isoflavone with antioxidant properties.
General Description
Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards
Biological Activity
Phytoestrogen with a wide range of biological actions. Inhibits protein tyrosine kinases including epidermal growth factor receptor kinase. Also binds to PPAR γ and estrogen receptors and acts as an agonist at GPR30. Also available as part of the MAPK Cascade Inhibitor Tocriset™ .
Biochem/physiol Actions
Inhibitor of tyrosine protein kinase; competitive inhibitor of ATP in other protein kinase reactions. Antiangiogenic agent, down-regulates the transcription of genes involved in controlling angiogenesis.
Mechanism of action
Genistein, an isoflavone isolated from soybeans, exhibits anticarcinogenic and antioxidant properties. Particularly, genistein has been shown to inhibit production of IL-6 and MAPK. Modulation to these cellular events may help regulate and attenuate UVB-induced inflammatory damage to the skin. Moreover, genistein inhibits UV-induced oxidative DNA damage and blocks UV-induced expression of c-fos and c-jun proto-oncogenes.
Anticancer Research
It is an isoflavone and is obtained from a variety of plants like psoralea (Psoraleacorylifolia), kudzu (Pueraria lobata), faba beans (Vicia faba), and soybeans(Glycine max). It exhibits anticancer effect by inhibiting NF-κB and protein kinaseB (Akt) signaling pathways (Singh et al. 2016b). It blocks the proliferation of cancercells via the inhibition of cell growth enzymes and survival like tyrosine kinase andtopoisomerase II; hence it is used to treat leukemia. Genistein increases the growthrate of some estrogen receptors in breast cancer cells and the rate of proliferation of estrogen-dependent breast cancer by competitive binding to the estrogen-β receptors.It may be involved in JNK pathway in inducing activator protein-1(AP-1) activity(Wang et al. 2012; Dixon and Ferreira 2002).
Safety Profile
Experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Storage
-20°C (desiccate)
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from EtOH or aqueous EtOH. It has UV: max at 290nm (EtOH). The S(-)-enantiomer (natural form) has m 255-256o (from EtOH) and [] D 20 -28.0o (c 2, EtOH), [ ] D 20 -35.2o (c 1, pyridine).[Beilstein 18 H 503, 18 II 164, 18 III/IV 2630.] Genistein (4',5,7-trihydroxyisoflavone) [446-72-0]M 270.2 crystallises from 60% aqueous EtOH or water with m 297-298o and [] D 20 -28o (c 0.6, 20mM NaOH). [Beilstein 18/4 V 594.]For Naringin (naringenin 7-rhamnoglucoside) See “Carbohydrates” in Chapter 6.
References
1) Akiyama?et al.?(1987),?Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases; J. Biol. Chem.,?262?5592 2) Linassier?et al.?(1990),?Mechanisms of action in NIH-3T3 cells of genistein, an inhibitor if EGF receptor tyrosine kinase?Biochem. Pharmacol.,?39?187 3) Dang?et al.?(2003),?Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) as a molecular target for the soy phytoestrogen genistein; J. Biol. Chem.,?278?962 4) Vivacqua?et al.?(2006),?17beta-estradiol, genistein, and 4-hydroxytamoxifen induce the proliferation of thyroid cancer cells through the g protein-coupled receptor GPR30; Mol. Pharmacol., 70?1414 5) Sarker and Li (2002),?Mechanisms of cancer chemoprevention by soy isoflavone genistein; Cancer Metastasis Rev.,?21?265
Properties of Genistein
| Melting point: | 297-298 °C |
| Boiling point: | 333.35°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2319 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6000 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble |
| form | powder |
| pka | 6.51±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | off-white |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Merck | 14,4391 |
| BRN | 263823 |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 446-72-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)- (446-72-0) |
Safety information for Genistein
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Genistein
| InChIKey | TZBJGXHYKVUXJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Genistein 98% CAS 446-72-0View Details
Genistein 98% CAS 446-72-0View Details
446-72-0 -
 Genistein, 95% CAS 446-72-0View Details
Genistein, 95% CAS 446-72-0View Details
446-72-0 -
 Genistein CAS 446-72-0View Details
Genistein CAS 446-72-0View Details
446-72-0 -
 Genistein, 98% CAS 446-72-0View Details
Genistein, 98% CAS 446-72-0View Details
446-72-0 -
 Genistein CAS 446-72-0View Details
Genistein CAS 446-72-0View Details
446-72-0 -
 Genistein CAS 446-72-0View Details
Genistein CAS 446-72-0View Details
446-72-0 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details