Moxifloxacin hydrochloride
Synonym(s):12-8039;1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-[(4aS,7aS)-octahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl]-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid hydrochloride;Avalox;BAY12-8039;Moxifloxacin hydrochloride
- CAS NO.:186826-86-8
- Empirical Formula: C21H25ClFN3O4
- Molecular Weight: 437.8923032
- MDL number: MFCD00949117
- EINECS: 641-756-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-16 16:15:04
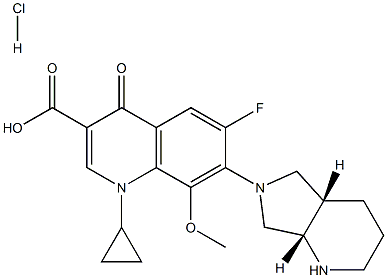
What is Moxifloxacin hydrochloride?
Description
Moxifioxacin hydrochlodde is one of the two new fluoroquinolonecarboxylic acid antibiotics introduced in 1999 for the treatment of respiratory tract infections such as community-acquired pneumonia, acute exacerbations of bronchitis or acute sinusitis. Moxifloxacin can be synthesized through a 12 step sequence from the classical 4-quinolone-3-carboxylic acid template. Some advantages of Moxifloxacin over Ciprofloxacin, another of Bayer's launched quinolones, have been shown, i.e. an enhanced activity against Gram-positive bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae, Clostndium pneumoniae), a favorable pharmacokinetic profile (good tissue penetration and plasma concentrations above MICs) and a lack of phototoxicity (UVA irradiation).
Description
Moxifloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic. It is active against 390 clinical isolates of aerobic and anaerobic Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria (MIC90s = ≤0.25 μg/ml), as well as clinical isolates of methicillin-susceptible and -resistant S. aureus (MIC90s = 0.12 and 2 μg/ml, respectively). Moxifloxacin is an inhibitor of E. coli DNA gyrase that is selective for DNA gyrase over E. coli topoisomerase IV (IC50s = 0.51 and 38.8 mg/L, respectively, in cell-free assays). It prevents S. aureus- or P. aeruginosa-induced increases in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) neutrophil infiltration and reduces S. aureus- or P. aeruginosa-induced increases in lung chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (CXCL1) and IL-1β levels in mouse models of bacterial pneumonia when administered at a dose of 100 mg/kg twice per day for two days. Moxifloxacin (100 mg/kg) decreases the number of lung and spleen colony forming units (CFUs) in a mouse model of systemic M. tuberculosis infection. Formulations containing moxifloxacin have been used in the treatment of various bacterial infections.
Chemical properties
Light yellow to yellow crystalline powder
Originator
Bayer (Germany)
The Uses of Moxifloxacin hydrochloride
Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride is an antibacterial agent that inhibits the activities of Topo II (DNA gyrase) and topoisomerase IV.
The Uses of Moxifloxacin hydrochloride
acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (reversible), cognitive enhancer
Definition
ChEBI: A hydrochloride comprising equimolar amounts of moxifloxacin and hydrogen chloride.
Manufacturing Process
Manufacturing process for Moxifloxacin hydrochloride includes 3 steps: Synthesis of intermidate octahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine (2,8- diazabicyclo[4.3.0]nonane);Synthesis of intermidate 1-cyclopropyl-6,7-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-4- oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid;Syntesis of 1-cyclopropyl-7-(2,8-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-8-yl)-6-fluoro-1,4- dihydro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid hydrochloride (moxifloxacin hydrochloride)
brand name
Avelox (Bayer); Vigamox (Alcon.
Therapeutic Function
Antibacterial
General Description
Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride is an anti-infectious compound that belongs to the class of fluoroquinolone antibiotics. It is a well-known broad-spectrum antibiotic prescription medicine effective against a variety of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria including the anaerobic type. It is an S,S-isomer with two chiral centers. It works by preventing the activity of various crucial enzymes involved in the replication, transcription, recombination, and repair of deoxyribonucleic acid in the bacteria such as DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II), topoisomerase IV. It finds its application in the treatment of various ocular and respiratory tract infections.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Moxifloxacin has proved to be effective in treating sinusitis, community-acquired respiratory tract infection, pneumonia and acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis. It has improved anti-gram positive activity compared to other fluoroquinolone such as ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin. Moxifloxacin is useful in treating skin infections that is of bacterial origin. It is known to have proper penetration into peripheral tissues and inflammatory fluids. Fluoroquinolones stabilize DNA strand breaks created by DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV by binding to the enzyme-DNA complex. Compared to mammalian DNA gyrase, moxifloxacin has 100 times higher affinity for bacterial DNA gyrase. Moxifloxacin is an antibiotic and works against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Moxifloxacin is being investigated for the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis.
Side Effects
The possible serious side effects of moxifloxacin hydrochloride including: unusual bruising/bleeding, signs of a new infection (such as sore throat that doesn't go away, fever), signs of kidney problems (such as change in the amount of urine), signs of liver problems (such as nausea/vomiting that doesn't stop, unusual tiredness, stomach/abdominal pain, yellowing eyes/skin, dark urine).
Precautions
Before taking moxifloxacin hydrochloride, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or to other quinolone antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin); or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.
References
[1]. cruz la, hall r: enantiomeric purity assay of moxifloxacin hydrochloride by capillary electrophoresis. j pharm biomed anal 2005, 38(1):8-13.
[2]. kamruzzaman m, alam am, lee sh, ragupathy d, kim yh, park sr, kim sh: spectrofluorimetric study of the interaction between europium(iii) and moxifloxacin in micellar solution and its analytical application. spectrochim acta a mol biomol spectrosc 2012, 86:375-380.
[3]. culley cm, lacy mk, klutman n, edwards b: moxifloxacin: clinical efficacy and safety. am j health syst pharm 2001, 58(5):379-388.
[4]. turkes c, soyut h, beydemir s: human serum paraoxonase-1 (hpon1): in vitro inhibition effects of moxifloxacin hydrochloride, levofloxacin hemihidrate, cefepime hydrochloride, cefotaxime sodium and ceftizoxime sodium. j enzyme inhib med chem 2014:1-7.
Properties of Moxifloxacin hydrochloride
| Melting point: | Slightly yellow to yellow crystalline powder, mp 324-325° |
| Boiling point: | 636℃ |
| alpha | 25D -256° (c = 0.5 in water) |
| RTECS | VB1983750 |
| Flash point: | >110°(230°F) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: soluble5mg/mL, clear (warmed) |
| form | powder |
| color | white to beige |
| Water Solubility | Sparingly soluble in water. Soluble in DMSO |
| BRN | 8377447 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 186826-86-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Moxifloxacin hydrochloride
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Moxifloxacin hydrochloride
| InChIKey | IDIIJJHBXUESQI-DFIJPDEKSA-N |
| SMILES | N1(C2CC2)C2=C(C=C(F)C(N3C[C@]4([H])CCCN[C@]4([H])C3)=C2OC)C(=O)C(C(O)=O)=C1.[H]Cl |&1:12,18,r| |
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride manufacturer
Vinayak Group
The Bangalore Sales Corporation
Global Chemie
Pharma Links
Cns Chemicals
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![(4aS,7aS)-1-methyloctahydro-1H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180629/GIF/CB03345928.gif)
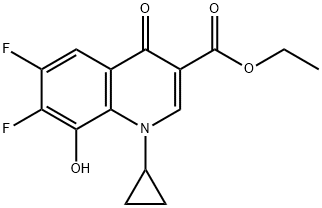
You may like
-
 Moxifloxacin hydrochloride 99%View Details
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride 99%View Details -
 Moxifloxacin hydrochloride 98%View Details
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride 98%View Details -
 Moxifloxacin hydrochloride 98%View Details
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride 98%View Details -
 Moxifloxacin Hcl 99%View Details
Moxifloxacin Hcl 99%View Details -
 Moxifloxacin HCl 98% (HPLC) CAS 186826-86-8View Details
Moxifloxacin HCl 98% (HPLC) CAS 186826-86-8View Details
186826-86-8 -
 Moxifloxacin CAS 186826-86-8View Details
Moxifloxacin CAS 186826-86-8View Details
186826-86-8 -
 Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride Powder, Grade Standard: IPView Details
Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride Powder, Grade Standard: IPView Details
186826-86-8 -
 Moxifloxacin HCL Powder, Grade Standard: USPView Details
Moxifloxacin HCL Powder, Grade Standard: USPView Details
186826-86-8
