FUMING SULFURIC ACID
Synonym(s):Oleum
- CAS NO.:8014-95-7
- Empirical Formula: H2O7S2
- Molecular Weight: 178.14
- MDL number: MFCD00137792
- EINECS: 616-954-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
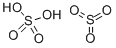
What is FUMING SULFURIC ACID?
Description
Fuming sulfuric acid is also called oleum, which is a trade name. It is a heavy, oily liquid, colorless to dark brown depending on purity, and fumes strongly in moist air and is extremely hygroscopic. Fuming sulfuric acid is a solution of sulfur trioxide in sulfuric acid. Sulfur trioxide is forced into solution with sulfuric acid to the point that the solution cannot hold any more. As soon as the solution is exposed to air, the fuming begins, forming dense vapor clouds. It is violently water reactive, as are most acids. Oleum is also a strong irritant to tissue. The four-digit UN identification number is 1831.
Chemical properties
viscous liquid, is a mixture of sulfur trioxide dissolved in sulfuric acid. The SO3 content may range between 15 and 30%.
Chemical properties
Sulfuric acid is a colorless to dark brown, odorless, oily liquid which is commercially sold @ 93% to 98% H2SO4, the remainder being water.
Physical properties
Dithionic acid, H2S2O6, is a chemical compound known only in solution. This acid is dibasic and salts called dithionates are known. All dithionates are readily soluble in water. They are mild oxidizing and mild reducing agents.
The Uses of FUMING SULFURIC ACID
In manufacture of fertilizers, explosives, dyestuffs, other acids, parchment paper, glue, purification of petroleum, pickling of metal.
The Uses of FUMING SULFURIC ACID
65% Sulfur Trioxide (Fuming) in Sulfuric Acid is a useful reagent that is widely used in the preparation of various compounds. It has been used for processing sulfonated polyoxadizole into ion-conducting films.
General Description
Thick fuming yellow liquid. Density 16.5 lb / gal. Very toxic by inhalation. Corrosive to metals and tissue, quickly causing severe burns. Used to make chemicals, dyes, explosives and in petroleum refining.
Air & Water Reactions
Fumes in air. Soluble in water; dissolution generates dangerous amounts of heat that can cause localized boiling and spattering of the acidic mixture and generate heavy fumes. During sulfonation of mononitrobenzene with fuming sulfuric acid, a leak from an internal cooling coil permitted water to enter the reaction tank. A violent eruption occurred due to the heat of solution [MCA Case History 944(1963)].
Reactivity Profile
SULFURIC ACID reacts as a strong acid, as an oxidizing agent and as a dehydrating agent. Chars wood, sugar and many other organic materials on contact. The heat from these reactions may ignite the wood, sugar or organic matter. May react explosively with acetic acid, acetic anhydride, acetonitrile, acrolein, acrylic acid, acrylonitrile, allyl alcohol, allyl chloride, ammonium hydroxide, aniline, cresol, butyraldehyde, cumene, ethyl acetate, ethylene diamine, ethylene glycol, glyoxal, isoprene, isopropyl alcohol, methyl ethyl ketone, propylene oxide, pyridine, styrene, vinyl acetate; strong bases (sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide) or mineral acids (nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, hydrofluoric acid) [Lewis, 3rd ed., 1993, p. 1195]. Mixing in equal molar portions with any of the following substances in a closed container caused the temperature and pressure to increase: 2-aminoethanol, ammonium hydroxide (28%), chlorosulfonic acid, ethylenediamine, ethyleneimine, ethylene cyanohydrin, hydrochloric acid (36%), hydrofluoric acid (48.7%), isopropyl alcohol, nitric acid (70%), 2-nitropropane, propiolactone, propylene oxide, pyridine, styrene monomer, sodium hydroxide, sulfolane, vinyl acetate, vinylidene chloride [NFPA 1991]. Extremely hazardous in contact with carbides, bromates, chlorates, fulminates, picrates, and powdered metals. May induce violent polymerization in polymerizable organic compounds such as allyl chloride. Reacts exothermically with sodium hypochlorite to produce chlorine gas.
Hazard
Reacts violently with water. Strong irritant to tissue.
Health Hazard
Acid mist is irritating to eyes, nose and throat. Liquid causes severe burns of skin and eyes.
Health Hazard
Oleum is an extremely corrosive substance. It emits suffocating fumes of sulfur trioxide that can cause severe lung damage. Skin contact can cause severe burns.
LC50 value, inhalation (rats): 347 ppm/L/h.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic and irritating vapors are generated.
Safety Profile
Confirmed human carcinogen. A poison. Moderately toxic by inhalation. A corrosive irritant to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. A very dangerous fire hazard by chemical reaction with reducing agents and carbohydrates. A severe explosion hazard by chemical reaction with acetic acid, acetic anhydride, acetonitrile, acrolein, acrylic acid, acrylonitrile, allylalcohol, allyl chloride, 2-amino ethanol, NH4OH, aniline, cresol, n-butyraldehyde, cumene, dichloroethyl ether, diethylene glycol monomethyl ether, diisobutylene, epichlorohydrin, ethyl acetate, ethylene cyanohydrin, ethylene diamine, ethylene glycol, ethylene glycol monoethyl ether acetate, ethylene imine, glyoxal, HCl, HF, isoprene, isopropyl alcohol, mesityl oxide, methyl ethyl ketone, HNO3, 2-nitropropane7 p-propiolacetone, propylene oxide, pyridine, NaOH, styrene monomer, vinylidene chloride, sulfolane, vinyl acetate. Will react with water or steam to produce heat and toxic and corrosive fumes. Can react vigorously with reducing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of SOx. See also SULFUROUS ACID.
Potential Exposure
Used as a chemical feedstock in the manufacture of acetic acid, hydrochloric acid; citric acid; phosphoric acid; aluminum sulfate; ammonium sulfate;barium sulfate; copper sulfate; phenol, superphosphates, titanium dioxide; as well as synthetic fertilizers, nitrate explosives; artificial fibers; dyes, pharmaceuticals, detergents, glue, paint, and paper. It finds use as a dehydrating agent for esters and ethers due to its high affinity for water; as an electrolyte in storage batteries; for the hydrolysis of cellulose to obtain glucose; in the refining of mineral and vegetable oil; and in the leather industry. Other uses include fur and food processing; carbonization of wool fabrics; gas drying; uranium extraction from pitchblende; and laboratory analysis. Sulfuric acid is among the highestvolume produced chemical in the United States.
Shipping
UN1830 Sulfuric acid with >51% acid or sulfuric acid with not >51% acid, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material. UN1831 Sulfuric acid, fuming with 30% or more free sulfur trioxide and Sulfuric acid, fuming, with <30% free sulfur trioxide, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material. UN1832 Sulfuric acid, spent, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
Incompatibilities
A strong acid and oxidizer. Reacts violently with water with dangerous spattering and evolution of heat. Reacts violently with combustible and reducing materials; bases, organic materials; chlorates, carbides, picrates, fulminates, water, powdered metals. Corrosive to most common metals forming explosive hydrogen gas.
Waste Disposal
Add slowly to solution of soda ash and slaked lime with stirring; flush to drain with large volumes of water. Recovery and reuse of spent sulfuric acid may be a viable alternative to disposal, and processes are available.
Properties of FUMING SULFURIC ACID
| Melting point: | 2 °C |
| Boiling point: | ~290 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.925 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | <0.3 (25 °C, vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 146 °C) |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 1.92(at 25℃) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.925 |
| color | Colorless |
| PH | <1 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | Miscible with water. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,8974 |
| BRN | 2037554 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.2 mg/m3 OSHA: TWA 1 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 15 mg/m3; TWA 1 mg/m3 |
| Dielectric constant | 84(20.0℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with organic materials, powdered metals, bases, halides. Reacts violently with water. Very hygroscopic. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 8014-95-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Fuming sulfuric acid (8014-95-7) |
Safety information for FUMING SULFURIC ACID
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for FUMING SULFURIC ACID
FUMING SULFURIC ACID manufacturer
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Sulfuric Acid CAS 8014-95-7View Details
Sulfuric Acid CAS 8014-95-7View Details
8014-95-7 -
![Cis-2-(Bromomethyl)-2-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1,3-Dioxolane-4-Ylmethyl Benzoate [CBB] 61397-56-6 99%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) Cis-2-(Bromomethyl)-2-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1,3-Dioxolane-4-Ylmethyl Benzoate [CBB] 61397-56-6 99%View Details
Cis-2-(Bromomethyl)-2-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1,3-Dioxolane-4-Ylmethyl Benzoate [CBB] 61397-56-6 99%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 287930-77-2 / 142569-70-8 99%View Details
287930-77-2 / 142569-70-8 99%View Details
287930-77-2 / 142569-70-8 -
 Ethyl-2-Chloroacetoacetate 609-15-4View Details
Ethyl-2-Chloroacetoacetate 609-15-4View Details
609-15-4 -
 CIS- BROMO BENZOATEView Details
CIS- BROMO BENZOATEView Details
61397-56-6 -
 609-15-4View Details
609-15-4View Details
609-15-4 -
![1-(6-Methylpyridin-3-Yl)-2-[4-(Methylsulfonyl)Phenyl]Ethanone [Ketosulfone] 99%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) 1-(6-Methylpyridin-3-Yl)-2-[4-(Methylsulfonyl)Phenyl]Ethanone [Ketosulfone] 99%View Details
1-(6-Methylpyridin-3-Yl)-2-[4-(Methylsulfonyl)Phenyl]Ethanone [Ketosulfone] 99%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 27143-07-3View Details
27143-07-3View Details
27143-07-3
