FENCHLORPHOS
- CAS NO.:299-84-3
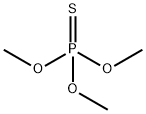
- Empirical Formula: C8H8Cl3O3PS
- Molecular Weight: 321.55
- MDL number: MFCD00055245
- EINECS: 206-082-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
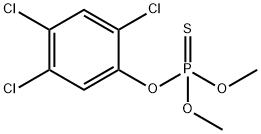
What is FENCHLORPHOS?
Description
Ronnel is a white to light tan crystalline solid.Molecular weight =321.54; Specific gravity (H2O:1) =1.48 at 25℃; Boiling point =(decomposes); Freezing/Melting point= 41℃. Practically insoluble in water;solubility = 0.004% at 25℃.
Chemical properties
Powder or granules. Insoluble in water; soluble in most organic solvents.
Chemical properties
Ronnel is a white to light tan crystalline solid.
The Uses of FENCHLORPHOS
Insecticide.
The Uses of FENCHLORPHOS
Systemic insecticide in livestock
Definition
ChEBI: Fenchlorphos is an organic thiophosphate.
General Description
White to light-tan crystalline solid. Mp: 41° C, Density :1.49 g cm-3 at 25°C. Biocidal (toxic to all animal life in differing degrees) by its action as a cholinesterase inhibitor. Used as an insecticide. Degrades readily in the environment by hydrolysis and oxidation.
Reactivity Profile
FENCHLORPHOS is non-flammable and non-combustible. Decomposes with heating to evolve toxic and corrosive vapors (hydrogen chloride, phosphorus oxides, sulfur oxides). Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation. Cholinesterase inhibitor, use may be restricted. Questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Ronnel is a weak cholinesterase inhibitor and has low toxicity. On both single and repeated doses, ronnel affects the pseudoesterase of the plasma rather than the true acetylcholinesterase of the red blood cells.Ronnel has not been shown to potentiate the effect of other commonly used organophosphorus insecticides.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by skin contact. A cholinesterase inhibitor. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Cl-, POx, and SOx. See also PARATHION and CHLOROPHENOLS.
Potential Exposure
Ronnel is both an organochlorine and organophosphorus compound; potential danger to those involved in manufacture, formulation and application of this insecticide for farm (livestock) and household uses. Degrades readily in the environment by hydrolysis and oxidation .
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Speed in removing material from skinis of extreme importance. Shampoo hair promptly if contaminated. Seek medical attention immediately. If thischemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, beginrescue breathing (using universal precautions, includingresuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Environmental Fate
Chemical/Physical. Though no products were identified, the reported hydrolysis halflife at pH 7.4 and 70°C using a 1:4 ethanol/water mixture is 10.2–10.4 hours (Freed et
al., 1977). Ronnel decomposed at elevated temperatures on five clay surfaces, each treated
with hydrogen, calcium, magnesium, aluminum and iron ions. At temperatures <950°C
(125, 300 and 750°C), bentonite clays impregnated with technical ronnel (18.6 wt %)
decomposed to 2,4,5-trichlorophenol and a rearrangement product tentatively identified
as O-methyl S-methyl-O-(2,4,5-trichlorophenyl) phosphorothioate (Rosenfield and Van
Valkenburg, 1965). At 950°C, only the latter product formed. It was postulated that this
compound resulted from an acid-catalyzed molecular rearrangement reaction. Ronnel also
undergoes base-catalyzed hydrolysis at elevated temperatures. Products include methanol
and a new compound that is formed via cleavage of a methyl group from one of the
methoxy groups, which is then bonded to the sulfur atom (Rosenfield and Van Valkenburg,
1965).
Ronnel is stable to hydrolysis over the pH range of 5–6 (Mortland and Raman, 1967).
However, in the presence of a Cu(II) salt (as cupric chloride) or when present as the
exchangeable Cu(II) cation in montmorillonite clays, ronnel is completely hydrolyzed via
first-order kinetics in <24 hours at 20°C. The calculated half-life of ronnel at 20°C for
this reaction is 6.0 hours. It was suggested that decomposition in the presence of Cu(II)
was a result of coordination of the copper atom through the oxygen or sulfur on the
phosphorus atom resulting in the cleavage of the side chain containing the phosphorus atom forming O,O-ethyl-O-phosphorothioate and 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene (Mortland and
Raman, 1967).
Emits very toxic fumes of chlorides, sulfur and phosphorus oxides when heated to
decomposition (Lewis, 1990).
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, wellventilated area away from strong oxidizers. Where possible,automatically transfer material from drums or other storagecontainers to process containers. Sources of ignition, suchas smoking and open flames, are prohibited where thischemical is handled, used, or stored. Metal containersinvolving the transfer of this chemical should be groundedand bonded. Wherever this chemical is used, handled, manufactured, or stored, use explosion-proof electrical equipment and fittings.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN2783 Organophosphorus pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explo- sions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, and epoxides. Store at temperatures <25-30℃. Organothiophosphates are susceptible to formation of highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrideds and active metals. Partial oxidation by oxidizing agents may result in the release of toxic phosphorus oxides
Waste Disposal
Incineration with added flam- mable solvent in furnace equipped with afterburner and alkali scrubber . In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesti- cide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or fed- eral environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of FENCHLORPHOS
| Melting point: | 41.0℃ |
| Boiling point: | 97℃ |
| Density | 1.485 g/cm3 (25 ºC) |
| vapor pressure | 5.29 at 20 °C, 18.6 at 30 °C (Freed et al., 1977) |
| refractive index | 1.5585 (589.3 nm 20℃) |
| Flash point: | -18 °C |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C
|
| solubility | Soluble in acetone, carbon tetrachloride, ether, kerosene, methylene chloride, and toluene
(Windholz et al., 1983) |
| form | solid |
| color | White to light brown, waxy solid |
| Water Solubility | 40mg/L(room temperature) |
| Merck | 13,8337 |
| BRN | 1885571 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 8.46 at 25 °C (approximate - calculated from water solubility and vapor pressure) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 10 mg/m3, IDLH 300 mg/m3; OSHA PEL: TWA
15 mg/m3; ACGIH TLV: TWA 10 mg/m3. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ronnel (299-84-3) |
Safety information for FENCHLORPHOS
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H311:Acute toxicity,dermal H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. |
Computed Descriptors for FENCHLORPHOS
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Fenchlorphos CAS 299-84-3View Details
Fenchlorphos CAS 299-84-3View Details
299-84-3 -
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4