Fenbutatin oxide
Synonym(s):Bis[tris-(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)tin] oxide
- CAS NO.:13356-08-6
- Empirical Formula: C60H78OSn2
- Molecular Weight: 1052.68
- MDL number: MFCD00072480
- EINECS: 236-407-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
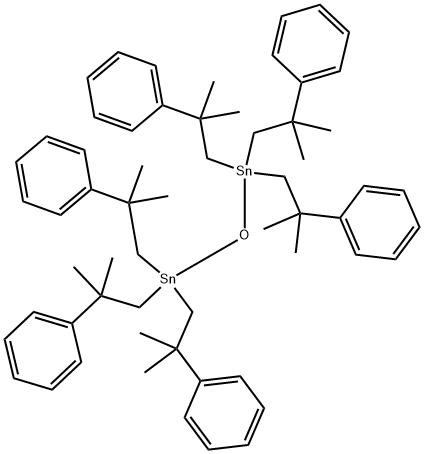
What is Fenbutatin oxide?
Chemical properties
White crystalline solid or powder. Mild odor
The Uses of Fenbutatin oxide
Fenbutatin Oxide is an organotin pesticide. Fenbutatin Oxide is widely used as an aracacide in the control of mites, in particular spider mites.
The Uses of Fenbutatin oxide
Acaricide.
The Uses of Fenbutatin oxide
Fenbutatin oxide is a non-systemic acaricide used to control a wide range of phytophagous mites on deciduous fruits, citrus, vines, selected nut crops, bananas, glasshouse crops and ornamentals.
What are the applications of Application
Fenbutatin oxide is an organotin pesticide
Definition
ChEBI: Fenbutatin oxide is an organotin acaricide.
General Description
White crystalline solid with a mild odor.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Fenbutatin oxide is in the family of tin compounds widely used as stabilizers for plastics, additives to paint(as antifouling agents). Some have catalytic properties. Examples include butyl tin, dibutyl tin oxide. Their main hazard is associated with their high toxicity, in skin adsorption or inhalation.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide, Miticide: A U.S. EPA restricted Use Pesticide (RUP). A selective miticide for deciduous pome and stone fruits, citrus fruits, grapes, vegetables, berry fruit, nut crops (selected), ornamentals and greenhouse crops.
Trade name
BENDEX®; NEOSTANOX®; OSDARAN®; SD-14114®; SHELL SD-14114®; TORQUE®; VENDEX®
Potential Exposure
Organotin/phenyltin insecticide and selective miticide for deciduous pome and stone fruits, citrus fruits, grapes, vegetables, berry fruit, nut crops (selected), ornamentals, and greenhouse crops. A United States Environmental Protection Agency Restricted Use Pesticide (RUP)
Environmental Fate
Chemical/Physical. Reacts with moisture forming tris(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)tin hydroxide (Worthing and Hance, 1991).
Metabolic pathway
Fenbutatin oxide is quite stable to hydrolytic degradation. Metabolism in soils, plants and animals is minimal. The extensive and irreversible adsorption/binding to cationic and organic matter is the primary dissipation mechanism in the soil environment. Cleavage of the neophenyl-tin linkages is the primary degradation and metabolic pathway (Scheme 1). Transformation of the neophenyl moiety has not been observed. Most of the information reported below was obtained from experiments using 119mSlna belhg conducted by DuPont.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required
Degradation
Fenbutatin oxide (1) dissociates slowly in water to the corresponding
hydroxide [tris(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)tin hydroxide 21. The neophenyl
moiety of fenbutatin oxide was stable at pH 5, 7, and 9 at 25 °C
with minimal degradation occurring after 30 days (Home, 1987a).
The photodegradation of fenbutatin oxide in pH 7 buffer solution was a
significant degradation process with a DT50 of approximately 51 days
following continuous exposure to simulated sunlight at 25 °C (Home,
1987b). Fenbutatin oxide underwent hydrolysis with a loss of two moles
of the 2-methyl-2-phenylprop yl moiety, yielding dlhydroxy-bis(2-methyl-
2-phenylpropyl)stannane (3), accounting for ca. 23% of the initial
concentration after 15 days of continuous irradiation. Fenbutatin oxide
and its metabolites react reversibly with water to form the analogous
oxide/hydroxide compounds (Gray et a1 ., 1995).
Incompatibilities
May form explosive mixture with air. Decomposes above 230C. Contact with water causes slow decomposition. Orgotin oxides can be strongly basic and will react, possibly dangerously, with acidic compounds and mixtures
Waste Disposal
Organic tin compounds may be disposed of in sealed containers in secured sanitary landfill. Chemical Treatability of tin; Concentration Process: Chemical precipitation; Chemical Classification: Metals; Scale of Study: Pilot scale; Type of Wastewater Used: Synthetic wastewater; Results of Study: At 600 ppm, 95.3% reduction with alum. At 500 ppm, 98% reduction with ferric chloride, 92% reduction with lime (three coagulants used: 200 mg of alum at pH = 6.4, 40 ppm of ferric chloride @ pH = 6.2, 41 ppm of lime @ pH = 11.5 Chemical coagulation was followed by dual media filtration). Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Incineration with effluent gas scrubbing is recommended. Containers must be disposed of properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of Fenbutatin oxide
| Melting point: | 142-145°C |
| Boiling point: | 235-240 °C(Press: 0.05 Torr) |
| Density | 0.42 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | 8.5×10-8 Pa (20 °C) |
| Flash point: | 100 °C |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Very Slightly, Heated, Sonicated) |
| form | solid |
| Water Solubility | 0.005 mg l-1 (23 °C) |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 4: no reaction with water under neutral conditions |
| Merck | 13,3991 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Fenbutatin oxide (13356-08-6) |
Safety information for Fenbutatin oxide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Fenbutatin oxide
Related products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Fenbutatin oxide 95.00% CAS 13356-08-6View Details
Fenbutatin oxide 95.00% CAS 13356-08-6View Details
13356-08-6 -
 Fenbutatin oxide CAS 13356-08-6View Details
Fenbutatin oxide CAS 13356-08-6View Details
13356-08-6 -
 106-43-4 Para Chloro Toluene (PCT) 99.00%View Details
106-43-4 Para Chloro Toluene (PCT) 99.00%View Details
106-43-4 -
 Pyrrolidine 99.00%View Details
Pyrrolidine 99.00%View Details
123-75-1 -
 88-82-4 2,3,5-Triiodobenzoic Acid 99.00%View Details
88-82-4 2,3,5-Triiodobenzoic Acid 99.00%View Details
88-82-4 -
 Methyl-2-Methoxy-5-Sulfamoyl Benzoate 99.00%View Details
Methyl-2-Methoxy-5-Sulfamoyl Benzoate 99.00%View Details
33045-52-2 -
 Orthochlorobenzaldehyde (2-Chlorobenzaldehyde) 89-98-5 99.00%View Details
Orthochlorobenzaldehyde (2-Chlorobenzaldehyde) 89-98-5 99.00%View Details
89-98-5 -
 12029-98-0 99.00%View Details
12029-98-0 99.00%View Details
12029-98-0