Cuprous oxide
Synonym(s):Cuprous oxide
- CAS NO.:1317-39-1
- Empirical Formula: Cu2O
- Molecular Weight: 143.09
- MDL number: MFCD00010974
- EINECS: 215-270-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
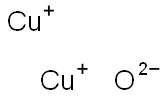
What is Cuprous oxide?
Chemical properties
Copper(I) oxide, Cu2O, occurs in nature as the red or reddish brown mineral cuprite in a cubic or octahedral crystalline morphology. Synthetic materials variously appear as yellow (somewhat pyrophoric), orange, red, or purple powders, depending on particle size. Copper(I) oxide is stable in dry air, but slowly oxidizes to copper(II) oxide, [1317-38-0], in moist air. It is virtually insoluble in water but dissolves in complexing acids such as HCl and in aqueous ammonia to form copper(I) complexes. In dilute sulfuric and nitric acids, disproportionation to the soluble copper(II) salts and copper powder obtains.
The Uses of Cuprous oxide
Fungicide; antiseptic for fishnets; in antifouling paints for marine use; in photoelectric cells; as red pigment for glass, ceramic glazes; in brazing pastes; in rectifiers; as catalyst.
The Uses of Cuprous oxide
Copper (I) oxide is used as red pigment for glass; in antifouling paints; fungicide.
The Uses of Cuprous oxide
Red pigment for glass and ceramic glazes, and as a catalystCopper(I) oxide is used in antifouling, marine paint, brazing paste, antifungal treatment for plant seeds. Used as a hydrogen scavenger in copper brass and bronze and high grade lubricants. Finds uses in glass and ceramic pigments, ferrite magnets, catalyst in organic synthesis, dyes and dye intermediates and as catalysts.
Definition
For the native ore see cuprite.
Definition
An insoluble red powder prepared by the heating of copper with copper(II) oxide or the reduction of an alkaline solution of copper(II) sulfate. Copper(I) oxide is easily reduced by hydrogen when heated; it is oxidized to copper(II) oxide when heated in air. It is used in the glass industry. Copper( I) oxide undergoes disproportionation in acid solutions, producing copper(II) ions and copper. The oxide will dissolve in concentrated hydrochloric acid due to the formation of the complex ion [CuCl2]-. Copper(I) oxide is a covalent solid.
Preparation
Copper(I) oxide decomposes above 1800°C but can be prepared by heating copper metal in air above 1030°C. To prevent further oxidation, the material must be cooled in an inert atmosphere. Lower temperatures may be used to produce the oxide if the material is blended with a reducing agent such as carbon and heated to 750°C in an inert atmosphere. The product must be stabilized with isophthalic acid or pine oil (Ayers, 1953). A particularly stable copper(I) oxide can be prepared by blending copper powder and cupric oxide in stoichiometric amounts and heating to 800-900°C. Lower temperatures can be used if ammonia or certain ammonium salts are added to the blend (Day, 1969; Drapeau and Johnson, 1956; Drapeau and Johnson, 1959).
General Description
Copper(I) oxide is a weak inorganic base that can be used to activate halides for nucleophilic substitution reaction. It is also used in decarboxylation and cyclo condensation reactions.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion. Experimental reproductive effects. A fungicide. Violent, potentially explosive reaction with concentrated peroxyformic acid. Violent reaction when heated with aluminum. See also COPPER COMPOUNDS.
Properties of Cuprous oxide
| Melting point: | 1232 °C |
| Boiling point: | 1800 °C |
| Density | 6 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| refractive index | 2.705 |
| Flash point: | 1800°C |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O |
| form | powder |
| color | red |
| Specific Gravity | 6. |
| Water Solubility | practically insoluble |
| Sensitive | Air & Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,2664 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 1 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 100 mg/m3; TWA 1 mg/m3 |
| Dielectric constant | 18.1(Ambient) |
| Stability: | Stable. May be air or light sensitive. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1317-39-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Copper(i) oxide(1317-39-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cuprous oxide (1317-39-1) |
Safety information for Cuprous oxide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P241:Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/…/equipment. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Cuprous oxide
Cuprous oxide manufacturer
Related products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Cuprous Oxide Red 98%View Details
Cuprous Oxide Red 98%View Details -
 Copper(I) oxide CAS 1317-39-1View Details
Copper(I) oxide CAS 1317-39-1View Details
1317-39-1 -
 Copper(I) oxide CAS 1317-39-1View Details
Copper(I) oxide CAS 1317-39-1View Details
1317-39-1 -
 Copper(I) oxide CAS 1317-39-1View Details
Copper(I) oxide CAS 1317-39-1View Details
1317-39-1 -
 Copper(I) oxide CAS 1317-39-1View Details
Copper(I) oxide CAS 1317-39-1View Details
1317-39-1 -
 Copper(I) oxide CAS 1317-39-1View Details
Copper(I) oxide CAS 1317-39-1View Details
1317-39-1 -
 Copper(I) oxide CAS 1317-39-1View Details
Copper(I) oxide CAS 1317-39-1View Details
1317-39-1 -
 Copper(I) oxide CAS 1317-39-1View Details
Copper(I) oxide CAS 1317-39-1View Details
1317-39-1