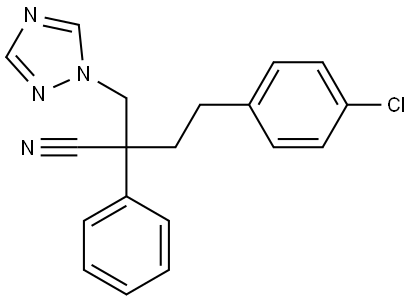
FENBUCONAZOLE
- CAS NO.:114369-43-6
- Empirical Formula: C19H17ClN4
- Molecular Weight: 336.82
- MDL number: MFCD01632336
- EINECS: 406-140-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
What is FENBUCONAZOLE?
The Uses of FENBUCONAZOLE
Fenbuconazole is a conazole based fungicide used as a spray for the control of leaf spot, yellow and brown rust, powdery mildew and net blotch on wheat and barley and apple scab, pear scab and apple p owdery mildew on apples and pears.
The Uses of FENBUCONAZOLE
Agricultural fungicide.
The Uses of FENBUCONAZOLE
Fenbuconazole is used for control of Septoria, Puccinia rusts, bunt, smut and Rhyncosporium secalis on cereals; powdery mildew and scab on pome fruit; brown rot and powdery mildew on stone fruit; powdery mildew, black rot and grey mould on vines, rust on beans and bean leaf spot on sugar beet. It is also used for control of a wide range of diseases on field crops, rice, bananas, tree nuts, vegetables and ornamentals. It can also be used in foliar, post-harvest and seed treatments.
Definition
ChEBI: 4-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-phenyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)butanenitrile is a member of the class of triazoles that is 1-chloro-4-(3-phenylpropyl)benzene substituted at position 3 of the propyl moiety by cyano and 1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl groups. It is a member of triazoles, a nitrile and a member of monochlorobenzenes.
Metabolic pathway
A number of sites in the fenbuconazole molecule are susceptible to
enzymic attack. Consequently, a large variety of metabolites may be
formed by oxidative attack on the phenolic rings or the aliphatic benzylic
carbon atom adjacent to the 4-chlorophenyl ring. In mammals, oxidation
at the benzylic carbon atom is an important pathway, which gives rise to
the corresponding alcohol or ketone. This pathway also leads to lactone
formation via hydrolysis of the nitrile group and elimination of a molecule
of water. The alcohol may also form conjugates with glucuronic or sulfuric
acid. Additional reactions in mammals involve hydroxylation of the
phenolic rings.
In plants, oxidation at the benzylic carbon is an important step to
further metabolites and cleavage of the linkage to the triazole ring generates
triazole, which is subsequently incorporated in a number of metabolic
products. Information presented in this entry is based on the PSD
Evaluation (PSD, 1995).
Degradation
Fenbuconazole is thermally stable up to 150 °C and there was no observed
degradation when fenbuconazole was incubated in the dark in aqueous
solutions at pH 5,7 and 9 for up to 30 days at 25 °C.
When an aqueous solution of fenbuconazole (concentration 1.5μg ml-1,
pH 7) was irradiated with a xenon arc lamp (filtered to remove wavelengths
below 290 nm), the overall radioactivity was 105% of the original
amount and the only compound detected was fenbuconazole.
Properties of FENBUCONAZOLE
| Melting point: | 125.0℃ |
| Boiling point: | 507.14°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1288 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 5 x l0-6 Pa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6110 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly) |
| pka | 2.34±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 0.2 mg l-1 (25 °C) |
| BRN | 8333667 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Fenbuconazole (114369-43-6) |
Safety information for FENBUCONAZOLE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for FENBUCONAZOLE
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Fenbuconazol CAS 114369-43-6View Details
Fenbuconazol CAS 114369-43-6View Details
114369-43-6 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1