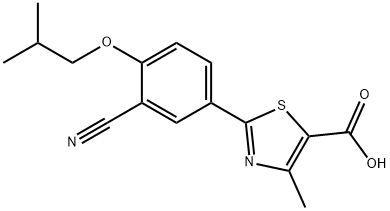
Febuxostat
Synonym(s):2-(3-Cyano-4-isobutoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxylic acid;Adenuric;Atenuri;Uloric
- CAS NO.:144060-53-7
- Empirical Formula: C16H16N2O3S
- Molecular Weight: 316.37
- MDL number: MFCD00871598
- EINECS: 682-158-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-19 17:28:17
What is Febuxostat?
Absorption
After oral administration, about 85% of febuxostat is absorbed rapidly. Tmax ranges from 1 to 1.5 hours. Following once-daily oral administration, Cmax was approximately 1.6 ± 0.6 mcg/mL at a dose of 40 mg febuxostat and 2.6 ± 1.7 mcg/mL at a dose of 80 mg febuxostat.
A high-fat meal decreased Cmax by 49% and AUC by 18%, but there were no clinically significant changes in the ability of febuxostat to decrease serum uric acid concentrations.
Toxicity
Oral lowest published toxic dose (TDLO) in humans is 1.82 mg/kg/14D (intermittent). Oral LD50 is 300 mg/kg in mice, 3200 mg/kg in rabbits, and 980 mg/kg in rats.
No dose-limiting toxicities were observed with febuxostat administered at doses up to 300 mg daily for seven days in healthy subjects. There are no reports of overdose of febuxostat in clinical studies and there is no known antidote. Overdose should be managed by symptomatic and supportive care.
Description
Febuxostat is a selective xanthine oxidase inhibitor used in the chronic treatment of hyperuricaemia in patients with gout. Febuxostat is a non-purine derivative with higher potency and selectivity than allopurinol in inhibiting xanthine oxidase. It completely inhibited the activity of human xanthine oxidase in lung cancer cell line A549, whereas its effect on the activity of other enzymes involved in purine or pyrimidine metabolism (e.g., purine nucleoside phosphatases, adenosine deaminases, and pyrimidine nucleoside phosphatases) was less than 4%.
Chemical properties
Crystalline Solid
Physical properties
Febuxostat has low solubility. It is almost insoluble in acidic conditions, slightly soluble in neutral conditions, and slightly more soluble in alkaline conditions. It is not suitable for making injections, but it can be taken orally because of its high oil-water partition coefficient and strong ability to cross cell membranes.
Originator
Teijin (Japan)
The Uses of Febuxostat
Xanthine oxidase/xanthine dehydrogenase inhibitor. Used for treatment of hyperuricemia and chronic gout. 40-120 mg/day febuxostat was proven effective in lowering serum urate levels when administered to manage hyperuricemia in patients with gout.
Background
Febuxostat is a non-purine xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibitor. In early 2008, febuxostat was granted marketing authorization by the European Commission for the treatment of chronic hyperuricemia and gout. In the following year, the FDA for approved febuxostat for use in the chronic management of hyperuricemia in adult patients with gout who have an inadequate response or intolerance to allopurinol. Gout is a form of arthritis that is caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystal in or around a joint, leading to inflammation and further deposition of uric acid crystal deposition in bones, joints, tissues, and other organs in the long term. Gout is closely associated with hyperuricemia. Febuxostat works by inhibiting the activity of an enzyme that is responsible for the synthesis of uric acid, thereby reducing serum uric acid levels.
In February 2019, a black box warning for febuxostat was added, based on the findings of a post-market clinical study (the CARES trial) where there was an increased risk of cardiovascular (CV) fatal outcomes in patients with gout and known cardiovascular disease treated with febuxostat, when compared to those treated with allopurinol. The manufacturer and the FDA advise health professionals to limit the use of febuxostat to second-line therapy in patients who have inadequate response or intolerance to allopurinol, and to avoid the use of febuxostat in patients with cardiovascular diseases.
Indications
Febuxostat is indicated for the chronic management of hyperuricemia in adult patients with gout who have an inadequate response to a maximally titrated dose of allopurinol, who are intolerant to allopurinol, or for whom treatment with allopurinol is not advisable. It is not recommended for the treatment of asymptomatic hyperuricemia or secondary hyperuricemia.
What are the applications of Application
Febuxostat is an inhibitor xanthine oxidase and xanthine dehydrogenase
Definition
ChEBI: Febuxostat is a 1,3-thiazolemonocarboxylic acid that is 4-methyl-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxylic acid which is substituted by a 3-cyano-4-(2-methylpropoxy)phenyl group at position 2. It is an orally-active, potent, and selective xanthine oxidase inhibitor used for the treatment of chronic hyperuricaemia in patients with gout. It has a role as an EC 1.17.3.2 (xanthine oxidase) inhibitor. It is an aromatic ether, a nitrile and a 1,3-thiazolemonocarboxylic acid.
Preparation
Febuxostat can be synthesized in a multistep sequence from 2,4-dicyanophenol, starting with the alkylation of the phenolic hydroxyl group with isobutyl bromide and potassium carbonate, followed by treatment with thioacetamide in hot dimethyl formamide to yield 3-cyano-4-isobutoxythiobenzamide. Cyclization of the thioamide group with 2-chloroacetoacetic acid ethyl ester in refluxing ethanol affords 2-(3-cyano-4-isoutoxyphenyl)-4-methylthiazole-5-carboxylic acid ethyl ester, which is hydrolyzed with sodium hydroxide to produce febuxostat.
brand name
Uloric, Adenuric
General Description
Febuxostat is a potent, non-purine compound, which inhibits the expression of cytokines/chemokines. It has also been reported to inhibit LPS-induced TNF-α, VCAM-1, MMP9 and MCP-1 expression.
Mechanism of action
Febuxostat works by non-competitively blocking the molybdopterin centre (the active site of xanthine oxidase). Xanthine oxidase is required to oxidise hypoxanthine and xanthine sequentially to uric acid. Therefore, febuxostat inhibits xanthine oxidase, thereby reducing uric acid production.
Biological Activity
Febuxostat is an antihyperuricemic nonpurine inhibitor of both the oxidized and reduced forms of xanthine oxidase. It inhibits bovine milk xanthine oxidase as well as mouse and rat liver xanthine oxidase/xanthine dehydrogenase (IC50s = 1.4, 1.8, and 2.2 nM, respectively). It is 10-30 times more potent than the hypoxanthine analog allopurinol (; Kis = 0.7 nM and 0.7 μM, respectively). Febuxostat decreases the serum level of urate in a potassium oxonate rat model of hyperuricemia (ED50 = 1.5 mg/kg). It reduces hepatic macrovesicular steatosis in mice fed a high-fat diet containing trans fatty acids when administered at a dose of 1 mg/kg per day. Febuxostat (0.75 mg/kg) also increases CNS expression of glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase 2 (GOT2) and improves neurological symptoms in a mouse model of secondary progressive experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Formulations containing febuxostat have been used in the treatment of symptomatic hyperuricemia in patients with gout.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Febuxostat is a potent non-purine xanithine oxidase inhibitor. Febuxostat is used in urate lowering therapies (ULTs) for the treatment of gout.
Pharmacokinetics
Febuxostat is a novel, selective xanthine oxidase/dehydrogenase inhibitor that works by decreasing serum uric acid in a dose-dependent manner. In healthy subjects, febuxostat decreased the mean serum uric acid and serum xanthine concentrations, as well as the total urinary uric acid excretion. Febuxostat at daily doses of 40-80 mg reduced the 24-hour mean serum uric acid concentrations by 40 to 55%. Closely related to the drug-induced reduction of serum uric acid levels and mobilization of urate crystals in tissue deposits, febuxostat is associated with gout flares.
Unlike allopurinol and oxypurinol, febuxostat has no inhibitory actions against other enzymes involved in purine and pyrimidine synthesis and metabolism, because it does not structurally resemble purines or pyrimidines.
Clinical Use
Fabuxostat was discovered by Teijin Pharmaceuticals and licensed to TAP Pharmaceuticals (which is currently part of Takeda Pharmaceuticals) and was approved in the U.S. for the treatment of hyperuricemia in patients with gout. It is a once-daily non-purine based agent with potent inhibitory activity against xanthine oxidase. The safety profile of the drug also does not require dose adjustment for patients with mild to moderate renal or hepatic impairment. Febuxostat is the first new agent cleared for this indication in 40 years.
Side Effects
The incidence of adverse events such as dizziness, diarrhea, headache, and nausea with febuxostat was similar to allopurinol. Febuxostat is contraindicated in patients being treated with the xanthine oxidase substrates such as azathioprine, mercaptopurine, and theophylline.
Synthesis
There are a number of routes available to prepare this agent as discussed in recent publications. The synthesis shown in Scheme 10 is a short and concise route and does not require the use of toxic reagents. Thus the commercially available and easily prepared 4-hydroxythiobenzamide (52) was reacted with ethyl bromoacetoacetate (53) in refluxing ethanol to provide the thiazole ester 54 in ??60% yield after crystallization. The phenolic ester 54 was then treated with hexamethylenetetramine (HMTA) in polyphosphoric acid at 80 ??C to provide the crude aldehyde 55 (74% conversion by HPLC). Reaction of phenol 55 and isobutyl bromide (56) in the presence of potassium carbonate with catalytic potassium iodide in DMF gave isobutyl ether 57 (64%, two steps). This ether was then converted in one pot to nitrile 58 in 93% by reacting the aldehyde with hydroxylamine hydrochloride and sodium formate in refluxing formic acid. Saponification of the ester 58 with aqueous sodium hydroxide provided fabuxostat (X).

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Azathioprine: avoid concomitant use, increased risk of neutropenia. Cytotoxics: avoid concomitant use with mercaptopurine. Theophylline: use with caution
Metabolism
Febuxostat is metabolized in the liver by UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) and Cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, with the relative contribution of each enzyme isoform in the metabolism of febuxostat not fully elucidated. UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A9, and UGT2B7 mediate conjugation of febuxostat, which approximately accounts for 22–44% of the metabolism of the total dose administered, to produce the acyl-glucuronide metabolite. CYP1A2, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and non-P450 enzymes are responsible for the oxidation reaction, which accounts for 2-8% of the metabolism of the dose. Oxidation reaction produces 67M-1, 67M-2, and 67M-4, which are pharmacologically active metabolites. 67M-1, 67M-2, and 67M-4 can further undergo glucuronidation and sulfation. Hydroxy metabolites are present in human plasma at much lower concentrations than the parent drug.
Metabolism
Extensively metabolised by conjugation via the uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (UDPGT) enzyme system, and by oxidation via the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme system to form active metabolites. About 49% of a dose is excreted via the urine, and 45% via the faeces (12% as unchanged drug)
Side Effects
Common side effects of Febuxostat include: diarrhoea, nausea, headache, oedema (localised swelling due to fluid retention in the tissues), muscle pain, joint pain. Most of these effects tend to go away on their own. Rare but more serious side effects include: difficulty or difficulty breathing, inability to speak, severe or sudden headache, sunken eyes, temporary blindness, fainting, vomiting of blood or material that looks like coffee grounds, pain or difficulty urinating, and allergic reactions. Seek medical attention if any serious adverse symptoms occur.
Storage
Store at RT
Mode of action
Xanthine oxidase is the main enzyme promoting uric acid production. It works by non-competitively blocking the molybdenum pterin center, which is the active site of xanthine oxidase. Through highly selective inhibition of oxidized and reduced xanthine oxidase, Febuxostat can reduce the synthesis of uric acid, decreasing its concentration and effectively treating gout. Through liver metabolism, Xanthine oxidase does not rely on renal excretion, so patients with moderate to severe liver and kidney dysfunction do not need to reduce dosages. Febuxostat is a non-purine XOR inhibitor, so it is very safe.
Properties of Febuxostat
| Melting point: | 238-239°(dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 536.6±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.31±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | powder |
| pka | 2.48±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Merck | 14,3948 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C16H16N2O3S/c1-9(2)8-21-13-5-4-11(6-12(13)7-17)15-18-10(3)14(22-15)16(19)20/h4-6,9H,8H2,1-3H3,(H,19,20) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 144060-53-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Febuxostat
Computed Descriptors for Febuxostat
| InChIKey | BQSJTQLCZDPROO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | S1C(C(O)=O)=C(C)N=C1C1=CC=C(OCC(C)C)C(C#N)=C1 |
Febuxostat manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![2-[2-(2-AMINO-9H-PURIN-9-YL)ETHYL]-1,3-PROPANEDIOL](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/104227-86-3.gif)

You may like
-
 Febuxostat 99%View Details
Febuxostat 99%View Details -
 Febuxostat 98%View Details
Febuxostat 98%View Details -
 Febuxostat 98%View Details
Febuxostat 98%View Details -
 Febuxostat 98% (HPLC) CAS 144060-53-7View Details
Febuxostat 98% (HPLC) CAS 144060-53-7View Details
144060-53-7 -
 Febuxostat 98% CAS 144060-53-7View Details
Febuxostat 98% CAS 144060-53-7View Details
144060-53-7 -
 Febuxostat Api, 25Kg BagView Details
Febuxostat Api, 25Kg BagView Details
144060-53-7 -
 Febuxostat IHRSView Details
Febuxostat IHRSView Details
144060-53-7 -
 Febuxostat Powder ApIView Details
Febuxostat Powder ApIView Details
144060-53-7
