Ethyl oleate
Synonym(s):Ethylis oleas;Ethyloleate;Oleic acid ethyl ester
- CAS NO.:111-62-6
- Empirical Formula: C20H38O2
- Molecular Weight: 310.51
- MDL number: MFCD00009579
- EINECS: 203-889-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-25 11:31:46
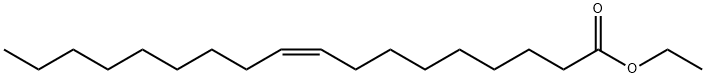
What is Ethyl oleate?
Description
Ethyl oleate is a fatty acid ester formed by the condensation of oleic acid and ethanol. It is a colorless to light yellow liquid. Ethyl oleate is produced by the body during ethanol intoxication.
Ethyl oleate is used as a solvent for pharmaceutical drug preparations involving lipophilic substances such as steroids. It also finds use as a lubricant and a plasticizer.
Ethyl oleate is regulated as a food additive by the Food and Drug Administration under "Food Additives Permitted for Direct Addition to Food for Human Consumption", 21CFR172.515.
Ethyl oleate has been identified as a primer pheromone in honeybees.
Ethyl oleate is one of the fatty acid ethyl esters (FAEE) that is formed in the body after ingestion of ethanol. There is a growing body of research literature that implicates FAEEs such as ethyl oleate as the toxic mediators of ethanol in the body (pancreas, liver, heart, and brain). Among the speculations is that ethyl oleate may be the toxic mediator of alcohol in fetal alcohol syndrome. The oral ingestion of ethyl oleate has been carefully studied and due to rapid degradation in the digestive tract it appears safe for oral ingestion. Ethyl oleate is not currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for any injectable use. However, it is used by compounding pharmacies as a vehicle for intramuscular drug delivery, in some cases to prepare the daily doses of progesterone in support of pregnancy. Studies which document the safe use of ethyl oleate in pregnancy for both the mother and the fetus have never been performed.
Chemical properties
Ethyl oleate is a pale yellow to almost colorless, mobile, oily liquid with a taste similar to olive oil and a slight odor that is not rancid. In the USP32-NF27, Ethyl oleate is described as consisting of esters of ethyl alcohol and high molecular weight fatty acids, principally oleic acid. It may contain a suitable antioxidant.
Occurrence
Reported found in cocoa, buckwheat, elderberry and babaco fruit (Carica pentagona Heilborn).
The Uses of Ethyl oleate
Ethyl oleate is a flavoring and fragrance agent. Usually used to prepare the oily phase of self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) for tacrolimus (Tac). It was obtained by the hydrolysis of various animal and vegetable fats and oils.
What are the applications of Application
Oleic Acid ethyl ester is a neutral, more lipid-soluble form of oleic acid
Definition
ChEBI: Ethyl oleate is a long-chain fatty acid ethyl ester resulting from the formal condensation of the carboxy group of oleic acid with the hydroxy group of ethanol. It has a role as a plant metabolite and an acaricide. It is functionally related to an oleic acid.
Preparation
Ethyl oleate is prepared by the reaction of ethanol with oleoyl chloride in the presence of a suitable hydrogen chloride acceptor. Or by direct esterification of oleic acid with ethyl alcohol in the presence of HCl at the boil; in the presence of Twitchell’s reagent or chlorosulfonic acid.
Aroma threshold values
Detection: 130 to 610 ppm
General Description
Ethyl oleate is a colourless to pale yellow oily liquid that has a faint, floral note. It is neutral and is a more lipid-soluble form of oleic acid. The compound contributed to approximately 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine in porcine platelets. The compound is one of the fatty acid ethyl esters that is generated after the breakdown of ethanol in the body. Moreover, ethyl oleate usually acts as a toxic mediator of ethanol in the heart, liver, pancreas, and brain.
Health effects
Ethyl oleate is one of the fatty acid ethyl esters (FAEE) that is formed in the body after ingestion of ethanol. There is a growing body of research literature that implicates FAEEs such as ethyl oleate as the toxic mediators of ethanol in the body (pancreas, liver, heart, and brain). Among the speculations is that ethyl oleate may be the toxic mediator of alcohol in fetal alcohol syndrome. The oral ingestion of ethyl oleate has been carefully studied and due to rapid degradation in the digestive tract it appears safe for oral ingestion. Ethyl oleate is not currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for any injectable use. However, it is used by compounding pharmacies as a vehicle for intramuscular drug delivery, in some cases to prepare the daily doses of progesterone in support of pregnancy. Studies which document the safe use of ethyl oleate in pregnancy for both the mother and the fetus have never been performed.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Ethyl oleate is primarily used as a vehicle in certain parenteral
preparations intended for intramuscular administration. It has also
been used as a solvent for drugs formulated as biodegradable
capsules for subdermal implantation) and in the preparation of
microemulsions containing cyclosporinand norcantharidin.
Microemulsion formulations containing ethyl oleate have also been
proposed for topical and ocular delivery, and for liver targeting
following parenteral administration. Ethyl oleate has been used in
topical gel formulations, and in self-microemulsifying drug
delivery systems for oral administration.
Ethyl oleate is a suitable solvent for steroids and other lipophilic
drugs. Its properties are similar to those of almond oil and peanut
oil. However, it has the advantage that it is less viscous than fixed
oils and is more rapidly absorbed by body tissues.
Ethyl oleate has also been evaluated as a vehicle for subcutaneous
injection.
Clinical Use
Ethyl oleate is used by compounding pharmacies as a vehicle for intramuscular administration and in some cases to formulate daily doses of progesterone to support pregnancy. There are no studies to prove that the use of ethyl oleate during pregnancy is safe for both mother and foetus.
Safety
Ethyl oleate is generally considered to be of low toxicity but ingestion should be avoided. Ethyl oleate has been found to cause minimal tissue irritation. No reports of intramuscular irritation during use have been recorded.
Carcinogenicity
Not listed by ACGIH, California Proposition 65, IARC, NTP, or OSHA.
Storage
Ethyl oleate should be stored in a cool, dry place in a small, wellfilled,
well-closed container, protected from light. When a partially
filled container is used, the air should be replaced by nitrogen or
another inert gas. Ethyl oleate oxidizes on exposure to air, resulting
in an increase in the peroxide value. It remains clear at 5°C, but
darkens in color on standing. Antioxidants are frequently used to
extend the shelf life of ethyl oleate. Protection from oxidation for
over 2 years has been achieved by storage in amber glass bottles
with the addition of combinations of propyl gallate, butylated
hydroxyanisole, butylated hydroxytoluene, and citric or ascorbic
acid. A concentration of 0.03% w/v of a mixture of propyl
gallate (37.5%), butylated hydroxytoluene (37.5%), and butylated
hydroxyanisole (25%) was found to be the best antioxidant for
ethyl oleate.
Ethyl oleate may be sterilized by heating at 150°C for 1 hour.
Incompatibilities
Ethyl oleate dissolves certain types of rubber and causes others to swell. It may also react with oxidizing agents.
Regulatory Status
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (transdermal preparation). Included in parenteral (intramuscular injection) and nonparenteral (transdermal patches) medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Ethyl oleate
| Melting point: | −32 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 216-218 °C15 mm Hg |
| Density | 0.87 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 2450 | ETHYL OLEATE |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | chloroform: soluble10% |
| form | Oily Liquid |
| color | Clear |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. fatty oily dairy milky waxy tallow |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,6828 |
| JECFA Number | 345 |
| BRN | 1727318 |
| Dielectric constant | 3.2(28℃) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 111-62-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 9-Octadecenoic acid (Z)-, ethyl ester(111-62-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ethyl oleate (111-62-6) |
Safety information for Ethyl oleate
Computed Descriptors for Ethyl oleate
| InChIKey | LVGKNOAMLMIIKO-VAWYXSNFSA-N |
Ethyl oleate manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 111-62-6 98%View Details
111-62-6 98%View Details
111-62-6 -
 111-62-6 Ethyl oleate 98%View Details
111-62-6 Ethyl oleate 98%View Details
111-62-6 -
 Ethyl oleate CAS 111-62-6View Details
Ethyl oleate CAS 111-62-6View Details
111-62-6 -
 Ethyl Oleate pure CAS 111-62-6View Details
Ethyl Oleate pure CAS 111-62-6View Details
111-62-6 -
 Ethyl Oleate CAS 111-62-6View Details
Ethyl Oleate CAS 111-62-6View Details
111-62-6 -
 ETHYL OLEATE For Synthesis CAS 111-62-6View Details
ETHYL OLEATE For Synthesis CAS 111-62-6View Details
111-62-6 -
 Ethyl oleate CAS 111-62-6View Details
Ethyl oleate CAS 111-62-6View Details
111-62-6 -
 Grade: Ip Ethyl Oleate Bp, Purity: Above 99%View Details
Grade: Ip Ethyl Oleate Bp, Purity: Above 99%View Details
111-62-6
