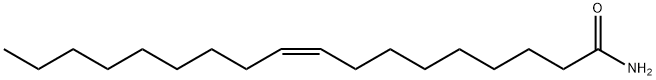
Oleic acid
Synonym(s):Oleic acid;OlAc;cis-9-Octadecenoic acid;cis-9-Octadecenoic Acid, 18:1;Elainic acid
- CAS NO.:112-80-1
- Empirical Formula: C18H34O2
- Molecular Weight: 282.46
- MDL number: MFCD00064242
- EINECS: 204-007-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
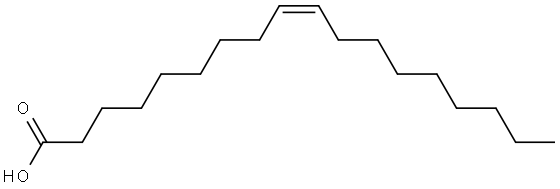
What is Oleic acid?
Absorption
Fatty acid uptake by different tissues may be mediated via passive diffusion to facilitated diffusion or a combination of both . Fatty acids taken up by tissues are then stored in the form of triglycerides or oxidized . Oleic acid was shown to penetrate rat skin . Following oral administration of Brucea javanica oil emulsion in rats, the time of oleic acid to reach peak plasma concentration was approximately 15.6 hours .
Toxicity
In rat, oral LD50 74 g/kg and intravenous LD50 is 2.4 mg/kg . Dermal LD50 in guinea pig was >3000 mg/kg .
Description
Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and a major component of membrane phospholipids that has been found in human plasma, cell membranes, and adipose tissue. It contributes approximately 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets. Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 μg/ml. It also inhibits fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation by 55 and 68%, respectively, when used at a concentration of 5 μM, similar to arachidonic acid ( | 90010.1 | 10006607). Oleic acid (60 μM) induces release of intracellular calcium in human platelets. In vivo, oleic acid increases TNF-α, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-1β production, neutrophil accumulation, and apoptotic and necrotic cell death in mouse lung and has been used to induce lung injury in a mouse model of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Chemical properties
Oleic acid, C17H33COOH, also known as red oil, elaine oil, and octadecenoic acid, is a yellowish unsaturated fatty acid with an aroma similar to lard. Oleic acid consists chiefly of (Ζ)-9-octadecenoic acid together with varying amounts of saturated and other unsaturated acids. It is insoluble in water, but soluble in most organic solvents. Oleic acid is the main component in cooking and olive oils.It is used for making aluminum oleate, which thickens lubricating oil, and in the preparation of soaps and cosmetics.
Occurrence
Reported found in apple, banana, cranberry, guava, grapes, melon, papaya, ginger, hop oil, ginger, beef fat, beer, rum, whiskies, cider, sherry, tea, goat milk, butterfat, celery, cheese, blue cheese, munster cheese, other cheeses, cognac, country cured ham, pork fat, potato, raspberry oil, tomato, peanut oil, coconut meat, avocado, mushroom, fenugreek, tamarind, kelp, cardamom, rice, dill seed, sake, buckwheat, malt, wort, roasted chicory root and cape gooseberry.
The Uses of Oleic acid
Oleic acid is a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid. Oleic Acid is obtained by the hydrolysis of various animal and vegetable fats and oils. Oleic Acid is used as an emulsifying or solubilizing agent i n aerosol products.
The Uses of Oleic acid
oleic acid is also known as omega-9. oleic acid can improve the skinpenetration abilities of a preparation’s other components. An essential fatty acid, it is obtained from various animal and vegetable fats and oils, and may be mildly irritating to the skin.
The Uses of Oleic acid
Oleic Acid is an unsaturated fatty acid that functions as a lubricant, binder, and defoamer.
Background
An unsaturated fatty acid that is the most widely distributed and abundant fatty acid in nature. It is used commercially in the preparation of oleates and lotions, and as a pharmaceutical solvent. (Stedman, 26th ed)
What are the applications of Application
Oleic Acid is an anti-proliferative agent and activator of PKC and CaMKII
Definition
ChEBI: Oleic acid is an octadec-9-enoic acid in which the double bond at C-9 has Z (cis) stereochemistry. It has a role as an EC 3.1.1.1 (carboxylesterase) inhibitor, an Escherichia coli metabolite, a plant metabolite, a Daphnia galeata metabolite, a solvent, an antioxidant and a mouse metabolite. It is a conjugate acid of an oleate. It derives from a hydride of a cis-octadec-9-ene.
Production Methods
Oleic acid is obtained by the hydrolysis of various animal and vegetable fats or oils, such as olive oil, followed by separation of the liquid acids. It consists chiefly of (Ζ)-9-octadecenoic acid. Oleic acid that is to be used systemically should be prepared from edible sources.
General Description
Colorless to pale yellow liquid with a mild odor. Floats on water.
Air & Water Reactions
Keep cis-9-Octadecenoic acid well closed; protect cis-9-Octadecenoic acid from air and light. . May form peroxides upon exposure to air. This is taken to account for an explosion that occurred, by the mixing of the acid with aluminum, [J. Chem. Educ., 1956, 36, 308]. Water Insoluble.
Reactivity Profile
cis-9-Octadecenoic acid is a carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acids donate hydrogen ions if a base is present to accept them. They react in this way with all bases, both organic (for example, the amines) and inorganic. Their reactions with bases, called "neutralizations", are accompanied by the evolution of substantial amounts of heat. Neutralization between an acid and a base produces water plus a salt. Carboxylic acids with six or fewer carbon atoms are freely or moderately soluble in water; those with more than six carbons are slightly soluble in water. Soluble carboxylic acid dissociate to an extent in water to yield hydrogen ions. The pH of solutions of carboxylic acids is therefore less than 7.0. Many insoluble carboxylic acids react rapidly with aqueous solutions containing a chemical base and dissolve as the neutralization generates a soluble salt. Carboxylic acids in aqueous solution and liquid or molten carboxylic acids can react with active metals to form gaseous hydrogen and a metal salt. Such reactions occur in principle for solid carboxylic acids as well, but are slow if the solid acid remains dry. Even "insoluble" carboxylic acids may absorb enough water from the air and dissolve sufficiently in cis-9-Octadecenoic acid to corrode or dissolve iron, steel, and aluminum parts and containers. Carboxylic acids, like other acids, react with cyanide salts to generate gaseous hydrogen cyanide. The reaction is slower for dry, solid carboxylic acids. Insoluble carboxylic acids react with solutions of cyanides to cause the release of gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases and heat are generated by the reaction of carboxylic acids with diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides. Carboxylic acids, especially in aqueous solution, also react with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), to generate flammable and/or toxic gases and heat. Their reaction with carbonates and bicarbonates generates a harmless gas (carbon dioxide) but still heat. Like other organic compounds, carboxylic acids can be oxidized by strong oxidizing agents and reduced by strong reducing agents. These reactions generate heat. A wide variety of products is possible. Like other acids, carboxylic acids may initiate polymerization reactions; like other acids, they often catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions.
Health Hazard
Industrial use of compound involves no known hazards. Ingestion causes mild irritation of mouth and stomach. Contact with eyes or skin causes mild irritation.
Fire Hazard
cis-9-Octadecenoic acid is combustible.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Oleic acid is used as an emulsifying agent in foods and topical
pharmaceutical formulations. It has also been used as a penetration enhancer in transdermal formulations,to improve the bioavailability
of poorly water-soluble drugs in tablet formulations,
and as part of a vehicle in soft gelatin capsules, in topical
microemulsion formulations,in oral self-emulsifying drug
delivery systems,in oral mucoadhesive patches,and in a
metered dose inhaler.Oleic acid was shown to be an important
factor in the hypoglycemic effect produced by multiple emulsions
containing insulin intended for intestinal delivery of insulin.
The phase behavior of sonicated dispersions of oleic acid has
been described,and mechanisms for the topical penetrationenhancing
actions of oleic acid have been presented.
Oleic acid has been reported to act as an ileal ‘brake’ that slows
down the transit of luminal contents through the distal portion of
the small bowel.
Oleic acid labeled with 131I and 3H is used in medical imaging.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Oleic acid is a colourless, odourless fatty acid that blocks the glucose production and food intake when administered intracerebroventricularly.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route. Mildly toxic by ingestion. Mutation data reported. A human skin and eye irritant. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. To fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical. The peroxidzed acid explodes on contact with aluminum. Potentially dangerous reaction with perchloric acid + heat. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Safety
Oleic acid is used in oral and topical pharmaceutical formulations.
In vitro tests have shown that oleic acid causes rupture of red
blood cells (hemolysis), and intravenous injection or ingestion of a
large quantity of oleic acid can therefore be harmful. The effects of
oleic acid on alveolar and buccal epithelial cells in vitro have
also been studied; the in vitro and in vivo effects of oleic acid on rat
skin have been reported. Oleic acid is a moderate skin irritant; it
should not be used in eye preparations.
An acceptable daily intake for the calcium, sodium, and
potassium salts of oleic acid was not specified by the WHO since
the total daily intake of these materials in foods was such that they
did not pose a hazard to health.
LD50 (mouse, IV): 0.23 g/kg
LD50 (rat, IV): 2.4 mg/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 74 g/kg
Carcinogenicity
Some recent studies suggested that oleic acid may decrease the incidence of mammary gland tumors of some rodent species. In a reviewof several fatty acids, Ip concludes that there is little evidence for the protective effect of oleic acid on the development of cancer.
Metabolism
Like most fatty acids, oleic acid may undergo oxidation via beta-oxidation and tricarboxylic acid cycle pathways of catabolism, where an additional isomerization reaction is required for the complete catabolism of oleic acid. Via a series of elongation and desaturation steps, oleic acid may be converted into longer chain eicosatrienoic and nervonic acid .
storage
On exposure to air, oleic acid gradually absorbs oxygen, darkens in
color, and develops a more pronounced odor. At atmospheric
pressure, it decomposes when heated at 80–100°C.
Oleic acid should be stored in a well-filled, well-closed container,
protected from light, in a cool, dry place.
Purification Methods
Purify the acid by fractional crystallisation from its melt, followed by molecular distillation at 10 -3mm, or by conversion to its methyl ester, the free acid can be crystallised from acetone at -40o to -45o (12mL/g). For purification by the use of lead and lithium salts, see Keffler and McLean [J Soc Chem Ind (London) 54 176T 1935]. Purification based on direct crystallisation from acetone is described by Brown and Shinowara [J Am Chem Soc 59 6 1937, pK White J Am Chem Soc 72 1857 1950]. [Beilstein 2 H 463, 2 I 198, 2 II 429, 2 III 1387, 2 IV 1641.]
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with aluminum, calcium, heavy metals, iodine solutions, perchloric acid, and oxidizing agents. Oleic acid reacts with alkalis to form soaps.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (inhalation and nasal aerosols, tablets, topical and transdermal preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines (metered dose inhalers; oral capsules; oral prolonged release granules; topical creams and gels) licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Oleic acid
| Melting point: | 13-14 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 360 °C |
| Density | 0.89 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 1.03 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 52 mm Hg ( 37 °C) |
| FEMA | 2815 | OLEIC ACID |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 133 °F |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Miscible with ethanol, ether, acetone, chloroform, dimethyl formamide and dimethyl sulfoxide. |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | pKa 5.35(H2O,t =25) (Uncertain) |
| Specific Gravity | 0.892 (20/4℃) |
| color | Colorless to pale yellow |
| Odor | Peculiar Lard-Like |
| Water Solubility | negligible |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| JECFA Number | 333 |
| Merck | 14,6828 |
| BRN | 1726542 |
| Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance (HLB) | 1 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.5(20℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, aluminium. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 112-80-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 9-Octadecenoic acid (Z)-(112-80-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Oleic acid (112-80-1) |
Safety information for Oleic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H320:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P321:Specific treatment (see … on this label). P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Oleic acid
| InChIKey | ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-KTKRTIGZSA-N |
Oleic acid manufacturer
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 Oleic acid 112-80-1 98%View Details
Oleic acid 112-80-1 98%View Details
112-80-1 -
 Oleic acid CAS 112-80-1View Details
Oleic acid CAS 112-80-1View Details
112-80-1 -
 Oleic acid CAS 112-80-1View Details
Oleic acid CAS 112-80-1View Details
112-80-1 -
 Oleic Acid pure CAS 112-80-1View Details
Oleic Acid pure CAS 112-80-1View Details
112-80-1 -
 Oleic acid 94% (GC) CAS 112-80-1View Details
Oleic acid 94% (GC) CAS 112-80-1View Details
112-80-1 -
 Oleic acid, ≥99% CAS 112-80-1View Details
Oleic acid, ≥99% CAS 112-80-1View Details
112-80-1 -
 Oleic acid 95% CAS 112-80-1View Details
Oleic acid 95% CAS 112-80-1View Details
112-80-1 -
 Oleic acid CAS 112-80-1View Details
Oleic acid CAS 112-80-1View Details
112-80-1
