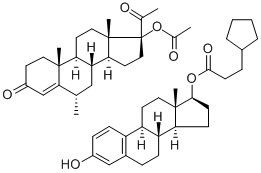
Estradiol Cypionate
Synonym(s):β-Estradiol 17-cypionate;1,3,5(10)-Estratriene-3,17β-diol 17-cyclopentylpropionate;3,17β-Hydroxy-1,3,5(10)-estratriene 17-cyclopentylpropionate;Depoestradiol
- CAS NO.:313-06-4
- Empirical Formula: C26H36O3
- Molecular Weight: 396.57
- MDL number: MFCD00056558
- EINECS: 206-237-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-03-06 08:32:39

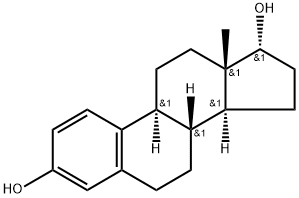
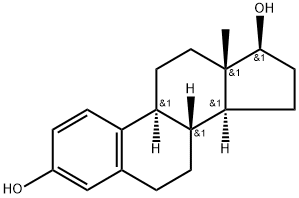
What is Estradiol Cypionate?
Absorption
When conjugated with aryl and alkyl groups for parenteral administration, the rate of absorption of oily preparations is slowed with a prolonged duration of action, such that a single intramuscular injection of estradiol valerate or estradiol cypionate is absorbed over several weeks .
Chemical properties
Estradiol cypionate is a White to Off-White Solid. It is soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, DMSO, and dimethyl formamide (DMF). The solubility of estradiol cypionate in ethanol is approximately 20 mg/ml and approximately 15 mg/ml in DMSO and DMF.
Originator
Depo-Estradiol,Upjohn,US,1952
The Uses of Estradiol Cypionate
Estradiol Cypionate is the cypionate salt form of estradiol, the most potent, naturally produced estrogen. Estradiol Cypionate is present in injectable contraceptive formulations. Used in hormone replacement therapy with potential for improving cognition in post-menopausal women.
Background
Estradiol Cypionate is a pro-drug ester of Estradiol, a naturally occurring hormone that circulates endogenously within the human body. Estradiol is the most potent form of all mammalian estrogenic steroids and acts as the major female sex hormone. As a pro-drug of estradiol, estradiol cypionate therefore has the same downstream effects within the body through binding to the Estrogen Receptor (ER) including ERα and ERβ subtypes, which are located in various tissues and organs such as the breasts, uterus, ovaries, skin, prostate, bone, fat, and brain.
Estradiol is commonly produced with an ester side-chain as endogenous estradiol has very low oral bioavailability on its own (2-10%). First-pass metabolism by the gut and the liver quickly degrades the estradiol molecule before it gets a chance to enter systemic circulation and exert its estrogenic effects . Esterification of estradiol aims to improve absorption and bioavailability after oral administration (such as with Estradiol Valerate) or to sustain release from depot intramuscular injections (such as with Estradiol Cypionate) through improved lipophilicity. Following absorption, the esters are cleaved, resulting in the release of endogenous estradiol, or 17β-estradiol. Ester pro-drugs of estradiol are therefore considered to be bioidentical forms of estrogen .
Estradiol cypionate is commercially available as Depo-Estradiol, an intramuscular depot injection used for the treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause and for the treatment of hypoestrogenism due to hypogonadism .
The primary source of estrogen in normally cycling adult women is the ovarian follicle, which secretes 70 to 500 mcg of estradiol daily, depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. However, after menopause, most endogenous estrogen is produced by conversion of androstenedione, secreted by the adrenal cortex, to estrone by peripheral tissues. Thus, estrone and the sulfate conjugated form, estrone sulfate, are the most abundant circulating estrogens in postmenopausal women . Although circulating estrogens exist in a dynamic equilibrium of metabolic interconversions, estradiol is the principal intracellular human estrogen and is substantially more potent than its metabolites, estrone and estriol at the receptor level. Because of the difference in potency between estradiol and estrone, menopause (and a change in primary hormone from estradiol to estrone) is associated with a number of symptoms associated with this reduction in potency and in estrogenic effects. These include hot flashes, vaginal dryness, mood changes, irregular menses, chills, and sleeping problems. Administration of synthetic and bioidentical forms of estrogen, such as estradiol cypionate, has shown to improve these menopausal symptoms.
Indications
Depo-Estradiol intramuscular depot injection is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms and hypoestrogenism due to hypogonadism.
Definition
ChEBI: Estradiol 17beta-cyclopentylpropionate is a steroid ester. It inhibits ET-1 synthesis via estrogen receptor.
Manufacturing Process
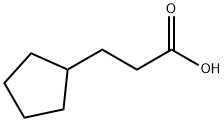
A solution of 80.0 grams (0.294 mol) of estradiol-17β in 860 ml of pyridine
was cooled in an ice-bath and 130.0 grams (0.81 mol) of
cyclopentanepropionyl chloride was added dropwise with stirring during a
period of about 20 minutes. The ice-bath was removed, stirring was continued
for 1 hour and the reaction mixture was allowed to stand at room temperature
overnight. The mixture was warmed on a steam bath and stirred for about 45
minutes, cooled and poured slowly onto about 1,000 grams of ice to which
had been added 330 ml of concentrated sulfuric acid. The precipitated product
was extracted with 400 to 500 mi of ether, and the extract was washed
successively with two 100-ml portions of cold 1 N sulfuric acid, two 100-ml
portions of saturated sodium carbonate solution and water until the pH was 7
and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. After removal of the drying agent,
the solution was concentrated to a volume of about 250 ml and an equal
volume of methanol was added.
After chilling overnight a total of 120.0 grams (78.5%) of estradiol 3,17β-
dicyclopentanepropionate was obtained which melted at 87° to 90°C. A
sample recrystallized from ether methanol for analysis melted at 90.5° to
91.5°C.
To a solution of 2.5 grams (18.1 mmol) of potassium carbonate in 25 ml of
water was added 225 ml of methanol followed by 5.0 grams (9.6 mmol) of
estradiol 3,17β-dicyclopentanepropionate. The mixture was stirred for 2?
hours at 202°C during which time some precipitation occurred. The mixture was poured into 700 ml of water with efficient stirring and the precipitated
solid was removed by filtration, washed with water and dried.
Recrystallization of the crude product from 80% methanol gave 3.16 grams
(83%) of estradiol 17β-cyclopentanepropionate melting at 148° to 151°C.
Recrystallization from benzenepetroleum ether raised the MP to 151° to
152°C.
brand name
depGynogen(Forest); Depo (Pharmacia & Upjohn).
Therapeutic Function
Estrogen
Biological Activity
estradiol cypionate is the 17 β-cyclopentylpropinate ester of estradiol, which inhibits et-1 synthesis via estrogen receptor.
Pharmacokinetics
Estrogen mediates its effects across the body through potent agonism of the Estrogen Receptor (ER), which is located in various tissues including in the breasts, uterus, ovaries, skin, prostate, bone, fat, and brain. Estradiol binds to both subtypes of the Estrogen Receptor: Estrogen Receptor Alpha (ERα) and Estrogen Receptor Beta (ERβ). Estradiol also acts as a potent agonist of G Protein-coupled Estrogen Receptor (GPER), which has recently been recognized as a major mediator of estradiol's rapid cellular effects .
Pharmacokinetics
Estradiol cypionate/medroxyprogesterone acetate is a combined injectable contraceptive containing 5 mg estradiol cypionate and 25 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate in microcrystalline aqueous suspension for once-monthly intramuscular administration. With this formulations, estradiol levels peak 2 to 3 days post-injection with average maximal circulating levels of about 250 pg/mL. The elimination half-life of estradiol with these formulations is 8.4 to 10.1 days, and circulating estradiol levels return to a baseline of about 50 pg/mL approximately 14 to 24 days post-injection
Side Effects
The side effects of estradiol cypionate are the same as those of estradiol. The side effects of Estradiol Cypionate include breast tenderness and enlargement, nausea, vomiting, bloating, edema, headache, migraine, and melasma. High-dose estrogen therapy with estradiol cypionate injections may also cause an increased risk of thromboembolism, changes in blood lipid profile, increased insulin resistance, and increased levels of prolactin.
Safety Profile
An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. A steroid. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes.
Metabolism
Exogenous estrogens are metabolized in the same manner as endogenous estrogens. Circulating estrogens exist in a dynamic equilibrium of metabolic interconversions. These transformations take place mainly in the liver. Estradiol is converted reversibly to estrone, and both can be converted to estriol, which is the major urinary metabolite. Estrogens also undergo enterohepatic recirculation via sulfate and glucuronide conjugation in the liver, biliary secretion of conjugates into the intestine, and hydrolysis in the gut followed by reabsorption. In postmenopausal women, a significant proportion of the circulating estrogens exist as sulfate conjugates, especially estrone sulfate, which serves as a circulating reservoir for the formation of more active estrogens .
Mode of action
Estradiol cypionate diffuses through the cell membrane and binds to and subsequently activates the nuclear estrogen receptor found in the reproductive tract, breast, pituitary, hypothalamus, liver, and bone. The activated complex binds to the estrogen response element on the DNA and activates the transcription of genes involved in the functioning of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics.
Properties of Estradiol Cypionate
| Melting point: | 151-152° |
| Boiling point: | 460.24°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D25 +45° (chloroform) |
| Density | 1.0828 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4700 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | 10.25±0.60(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 313-06-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Estradiol cypionate(313-06-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17-diol (17.beta.)-, 17-cyclopentanepropanoate (313-06-4) |
Safety information for Estradiol Cypionate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H350:Carcinogenicity H360:Reproductive toxicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Estradiol Cypionate
| InChIKey | UOACKFBJUYNSLK-JCRQLOERNA-N |
| SMILES | C[C@]12CC[C@]3([H])C4C=CC(O)=CC=4CC[C@@]3([H])[C@]1([H])CC[C@@H]2OC(=O)CCC1CCCC1 |&1:1,4,15,17,21,r| |
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 313-06-4 Estradiol 17-cypionate 98%View Details
313-06-4 Estradiol 17-cypionate 98%View Details
313-06-4 -
 313-06-4 98%View Details
313-06-4 98%View Details
313-06-4 -
 Estradiol cypionate 98% (HPLC) CAS 313-06-4View Details
Estradiol cypionate 98% (HPLC) CAS 313-06-4View Details
313-06-4 -
 Estradiol cypionate CAS 313-06-4View Details
Estradiol cypionate CAS 313-06-4View Details
313-06-4 -
 Ethyl-2-Chloroacetoacetate 609-15-4View Details
Ethyl-2-Chloroacetoacetate 609-15-4View Details
609-15-4 -
 609-15-4View Details
609-15-4View Details
609-15-4 -
![1-(6-Methylpyridin-3-Yl)-2-[4-(Methylsulfonyl)Phenyl]Ethanone [Ketosulfone] 99%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) 1-(6-Methylpyridin-3-Yl)-2-[4-(Methylsulfonyl)Phenyl]Ethanone [Ketosulfone] 99%View Details
1-(6-Methylpyridin-3-Yl)-2-[4-(Methylsulfonyl)Phenyl]Ethanone [Ketosulfone] 99%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 27143-07-3View Details
27143-07-3View Details
27143-07-3
