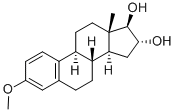
β-Estradiol
Synonym(s):β-Estradiol;17β-Estradiol;17β-Estradiol - CAS 50-28-2 - Calbiochem;3,17β-Dihydroxy-1,3,5(10)-estratriene;Dihydrofolliculin
- CAS NO.:50-28-2
- Empirical Formula: C18H24O2
- Molecular Weight: 272.39
- MDL number: MFCD01074033
- EINECS: 200-023-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-25 12:42:02
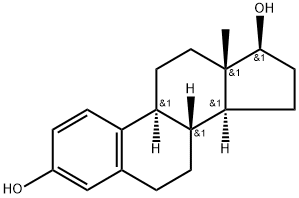
What is β-Estradiol?
Absorption
The absorption of several formulations of estradiol is described below:
Oral tablets and injections
First-pass metabolism in the gastrointestinal tract rapidly breaks down estradiol tablets before entering the systemic circulation. The bioavailability of oral estrogens is said to be 2-10% due to significant first-pass effects. The esterification of estradiol improves the administration (such as with estradiol valerate) or to sustain release from intramuscular depot injections (including estradiol cypionate) via higher lipophilicity. After absorption, the esters are cleaved, which leads to the release of endogenous estradiol, or 17β-estradiol.
Transdermal preparations
The transdermal preparations slowly release estradiol through intact skin, which sustains circulating levels of estradiol during a 1 week period of time. Notably, the bioavailability of estradiol after transdermal administration is about 20 times higher than after oral administration. Transdermal estradiol avoids first pass metabolism effects that reduce bioavailability. Administration via the buttock leads to a Cmax of about 174 pg/mL compared to 147 pg/mL via the abdomen.
Spray preparations
After daily administration, the spray formulations of estradiol reach steady state within 7-8 days. After 3 sprays daily, Cmax is about 54 pg/mL with a Tmax of 20 hours. AUC is about 471 pg?hr/mL.
Vaginal ring and cream preparations
Estradiol is efficiently absorbed through the mucous membranes of the vagina. The vaginal administration of estrogens evades first-pass metabolism. Tmax after vaginal ring delivery ranges from 0.5 to 1 hour. Cmax is about 63 pg/mL. The vaginal cream preparation has a Cmax of estradiol (a component of Premarin vaginal estrogen conjugate cream) was a Cmax of 12.8 ± 16.6 pg/mL, Tmax of 8.5 ± 6.2 hours, with an AUC of 231 ± 285 pg?hr/mL.
Toxicity
The NOAEL (no-observed-adverse-effect-level) oral toxicity of estradiol after 90 day in rats was 0.003 mg/kg/day for blood, female reproductive, and male reproductive, endocrine, and liver toxicity. Oral TDLO of ethinyl estradiol is 21 mg/kg/21D intermittent, woman) with an oral LD50 of 960 mg/kg in the rat.
There is limited information in the literature regarding estrogen overdose. Estradiol overdose likely leads to the occurrence of estrogen-associated adverse effects, including nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, breast tenderness, venous thrombosis, and vaginal bleeding. It is generally recommend to discontinue estradiol treatment and offer supportive care in the case of an overdose.
Description
The Merck Index calls estradiol “the most potent naturally occurring estrogen in mammals”. Females produce it in the ovaries and, during pregnancy, in the placenta. In males, estradiol is a metabolic product of testosterone.
D. W. MacCorquodale and co-workers isolated estradiol from sows’ ovaries in 1936. Soon several researchers prepared it from other steroids. About 40 years later, two research teams reported its total synthesis.
Much research has been devoted to estradiol as a sex hormone, but it recently turned up in a?study of eating disorders. K. L. Klump and co-workers at Michigan State University tracked estradiol levels in twin girls after midpuberty and found that the hormone correlated with eating disorders in identical, but not fraternal, twins. Klump believes that estradiol, a gene transcription factor in the brain, may switch on genes related to the disorders.
?
?
Description
β- Estradiol is an estrogen, or female hormone. It may have neuroprotective effects for Parkinson''s disease patients; however, the mechanism of neuroprotection is unclear. A recent study suggests that age-related decreases in the brain''s sensitivity to estrogens may be linked with certain menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes.
Description
Estradiol, 17-beta- is an odorless white to yellow crystalline substance. Molecular weight = 272.42;Boiling point = (decomposes); Freezing/Meltingpoint = 173 - 179℃. Hazard Identification (based onNFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 2, Flammability 1,Reactivity 0. Insoluble in water.
Chemical properties
White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals.
Chemical properties
Estradiol, 17-β-is an odorless white to yellow crystalline substance.
The Uses of β-Estradiol
17β-Estradiol is the major estrogen secreted by the premenopausal ovary.This compound is a contaminant of emerging concern (CECs). Drinking water contaminant candidate list 3 (CCL 3) compound as per United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), environmental, and food contaminants.
The Uses of β-Estradiol
Estradiol USP (Estrace) is used to treat Breast cancer; prostatic carcinoma.
Indications
Estradiol is indicated in various preparations for the treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms and vulvar and vaginal atrophy due to menopause, for the treatment of hypoestrogenism due to hypogonadism, castration, or primary ovarian failure, and for the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. It is also used for the treatment of breast cancer (only for palliation therapy) in certain men or women with metastatic disease, and for the treatment of androgen-dependent prostate cancer (only for palliation therapy). It is also used in combination with other hormones as a component of oral contraceptive pills for preventing pregnancy (most commonly as Ethinylestradiol, a synthetic form of estradiol).
A note on duration of treatment
Recommendations for treatment of menopausal symptoms changed drastically following the release of results and early termination of the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) studies in 2002 as concerns were raised regarding estrogen use. Specifically, the combined estrogen–progestin group was discontinued after about 5 years of follow up due to a statistically significant increase in invasive breast cancer and in cardiovascular events.
Following extensive critique of the WHI results, Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) is now recommended to be used only for a short period (for 3-5 years postmenopause) in low doses, and in women without a history of breast cancer or increased risk of cardiovascular or thromboembolic disease. Estrogen for postmenopausal symptoms should always be given with a progestin component due to estrogen's stimulatory effects on the endometrium; in women with an intact uterus, unopposed estrogen has been shown to promote the growth of the endometrium which can lead to endometrial hyperplasia and possibly cancer over the long-term.
Background
Estradiol is a naturally occurring hormone circulating endogenously in females. It is commercially available in several hormone therapy products for managing conditions associated with reduced estrogen, such as vulvovaginal atrophy and hot flashes. Some available forms of estradiol include oral tablets, injections, vaginal rings, transdermal patches, sprays, gels, and creams.
When used for oral or IM administration, estradiol is commonly synthesized as a pro-drug ester (such as Estradiol acetate, Estradiol benzoate, Estradiol cypionate, Estradiol dienanthate, and Estradiol valerate). Because it has a low oral bioavailability on its own, estradiol is commonly formulated with an ester side-chain. Ethinylestradiol (EE) is a synthetic form of estradiol commonly used as the estrogenic component of most combination oral contraceptive pills (OCPs). Ethinyl estradiol is different from estradiol due to its higher biovailability and increased resistance to metabolism, rendering it more suitable for oral administration.
What are the applications of Application
β-Estradiol is an ER agonist and activator of PI 3-kinase
Definition
ChEBI: The 17beta-isomer of estradiol.
What are the applications of Application
β-Estradiol has been used:
for the in vitro maturation of bovine cumulus-oocyte complexes (COCs)
as a supplement in in vitro maturation medium (IVM), which is used as a control medium
in estrogen-induction assay
Acquired resistance
Estradiol is the most potent endogenous estrogen, exhibiting high affinity for the ER and high potency when administered parenterally. When administered orally, estradiol is promptly conjugated in the intestine and oxidatively metabolized by the liver, resulting in its low oral bioavailability and therapeutic effectiveness.
General Description
Estradiol, estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol, is the most activeof the natural steroid estrogens. Although its 17β-OHgroup is vulnerable to bacterial and enzymatic oxidation toestrone, it can be temporarily protected as anester at C3 or C17, or permanently protected by adding a17α-alkyl group (e.g., 17α-ethinyl estradiol, the most commonlyused estrogen in oral contraceptives). The increasedoil solubility of the 17β-esters (relative to estradiol) permitsthe esters to remain in oil at the IM injection site for extendedperiods. These derivatives illustrate the principles of steroidmodification. Transdermal estradiolproducts avoid first-pass metabolism, allowing estradiol tobe as effective as oral estrogens for treating menopausalsymptoms. A new transdermal spray, Evamist, was approvedin 2007. Estradiol itself is typically not very effective orallybecause of rapid metabolism, but an oral formulation of micronizedestradiol that allows more rapid absorption of thedrug is available (Estrace). In addition to the oral and transdermalproducts, estradiol is also available in gel, cream, andvaginal ring formulations. The commercially available estradiolesters are the following:
Estradiol 3-acetate, USP (oral; vaginal ring)
Estradiol 17-valerate, USP (IM injection)
Estradiol 17-cypionate, USP (IM injection).
Hazard
A carcinogen (OSHA).
Biological Activity
Endogenous estrogen receptor (ER) agonist (K i values are 0.12 and 0.13 nM for ER α and ER β respectively). Also high affinity ligand at membrane estrogen GPR30 receptors.
Contact allergens
Natural estradiol, used in transdermal systems for hormonal substitution, can induce allergic contact dermatitis, with the risk of systemic contact dermatitis after oral reintroduction.
Biochem/physiol Actions
The major estrogen secreted by the premenopausal ovary. Estrogens direct the development of the female phenotype in embryogenesis and during puberty by regulating gene transcription and, thus, protein synthesis. It also induces the production of gonadotropins which, in turn, induce ovulation. Exposure to estradiol increases breast cancer incidence and proliferation.
Mechanism of action
The most potent naturally occurring estrogen in mammals. It is synthesized primarily in the ovary, and also in the testis, adrenal gland and placenta, and to a limited extent by peripheral tissues (e.g., liver, fat, and skeletal muscle) from androstenedione and testosterone. It is responsible for the development of secondary sex characteristics in the female at puberty (i.e., growth and development of the vagina, uterus and fallopian tubes, enlargement of the breasts, and growth and maturation of long bones).
Pharmacokinetics
Estradiol acts on the on the estrogen receptors to relieve vasomotor systems (such as hot flashes) and urogenital symptoms (such as vaginal dryness and dyspareunia).
Estradiol has also been shown to exert favorable effects on bone density by inhibiting bone resorption. Estrogen appears to inhibit bone resorption and may have beneficial effects on the plasma lipid profile. Estrogens cause an increase in hepatic synthesis of various proteins, which include sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG), and thyroid-binding globulin (TBG). Estrogens are known to suppress the formation of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) in the anterior pituitary gland.
A note on hyper-coagulable state, cardiovascular health, and blood pressure
Estradiol may cause an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, DVT, and stroke, and its use should be avoided in patients at high risk of these conditions. Estrogen induces a hyper-coagulable state, which is also associated with both estrogen-containing oral contraceptive (OC) use and pregnancy. Although estrogen causes an increase in levels of plasma renin and angiotensin. Estrogen-induced increases in angiotensin, causing sodium retention, which is likely to be the mechanism causing hypertension after oral contraceptive treatment.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic, neoplastigenic, tumorigenic, and teratogenic data. A promoter. Human reproductive effects by ingestion: ferthty effects. Experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. A steroid hormone much used in medicine. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Synthesis
Estradiol, estra-1,3,5(10)-trien-3,17|?-diol (28.1.17), is most easily made by reducing the keto-group of estrone by various reducing agents, in particular potassium borohydride.

Potential Exposure
The working environment may be contaminated during sex hormone manufacture, especially during the extraction and purification of natural steroid hormones; grinding of raw materials; handling of powdered products and recrystallization. Airborne particles of sex hormones may be absorbed through the skin, ingested or inhaled. Enteric absorption results in quick inactivation of sex hormones in the liver. The rate of inactivation is decreased for the oral, alkylated steroid hormones (methyl testosterone, anabolic steroids, etc.). Sex hormones may accumulate and reach relatively high levels even if their absorption is intermittent. Consequently, repeated absorption of small amounts may be detrimental to health. Intoxication by sex hormones may occur in almost all the exposed workers if preventive measures are not taken. The effect in the industrial sector is more successful than the agricultural one (chemical caponizing of cockerels by stilbestrol implants and incorporation of estrogens in feed for body weight gain promotion in beef cattle), where measures taken are summary and the number of cases of intoxication is consequently bigger
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Metabolism
Exogenously administered estrogens are metabolized in the same fashion as endogenous estrogens. Metabolic transformation occurs primarily in the liver and intestine. Estradiol is metabolized to estrone, and both are converted to estriol, which is later excreted in the urine. Sulfate and glucuronide conjugation estrogens also take place in the liver. Biliary secretion of metabolic conjugates are released into the intestine, and estrogen hydrolysis in the gut occurs, followed by reabsorption. The CYP3A4 hepatic cytochrome enzyme is heavily involved in the metabolism of estradiol. CYP1A2 also plays a role.
Storage
Room temperature
Shipping
UN3249 Medicine, solid, toxic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials
Purification Methods
17-Estradiol (previously known as -estradiol) is purified by chromatography on SiO2 (toluene/EtOAc 4:1) and recrystallised from CHCl3/hexane or 80% EtOH. It is stable in air, is insoluble in H2O, and is precipitated by digitonin. The UV has max at 225 and 280 nm. The diacetate [3434-88-6] has m 97-98o and forms leaflets from aqueous EtOH. The 3-benzoate crystallises from aqueous MeOH withm 193o and [] D 25 +58o to 63o (c 1, dioxane). [Meischer & Scholz Helv Chim Acta 20 263, 1237 1937, Biochem J 32 1273 1938, Oppolzer & Roberts Helv Chim Acta 63 1703 1980, Inhoffen & Zühlsdorff Chem Ber 7 4 1914 1941, Beilstein 6 IV 6611.]
Properties of β-Estradiol
| Melting point: | 178-179 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 355.44°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D25 +76 to +83° (dioxane) |
| Density | 1.0708 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 80.4 ° (C=1, Dioxane) |
| Flash point: | 2℃ |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, soluble in acetone, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), slightly soluble in methylene chloride. |
| form | powder |
| pka | pKa 10.71±0.02(H2O(0.1% p-dioxane) t=25±0.1 I=0.03(KCl))(Approximate) |
| color | White to off-white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide, ethanol , water, phosphate buffer saline, dimethyl formamide, acetone, dioxane and alkali hydroxides. Slightly soluble in vegetable oils. |
| Merck | 14,3703 |
| BRN | 1914275 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 50-28-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17beta-diol(50-28-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Estradiol (50-28-2) |
Safety information for β-Estradiol
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H351:Carcinogenicity H362:Reproductive toxicity, effects on or via lactation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P263:Avoid contact during pregnancy/while nursing. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for β-Estradiol
| InChIKey | VOXZDWNPVJITMN-ZBRFXRBCSA-N |
β-Estradiol manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 50-28-2 98%View Details
50-28-2 98%View Details
50-28-2 -
 beta-Estradiol CAS 50-28-2View Details
beta-Estradiol CAS 50-28-2View Details
50-28-2 -
 β-Estradiol CAS 50-28-2View Details
β-Estradiol CAS 50-28-2View Details
50-28-2 -
 Beta-estradiol 97% CAS 50-28-2View Details
Beta-estradiol 97% CAS 50-28-2View Details
50-28-2 -
 Estradiol CAS 50-28-2View Details
Estradiol CAS 50-28-2View Details
50-28-2 -
 White Estradiol PowderView Details
White Estradiol PowderView Details
50-28-2 -
 Estraheal Estradiol 2mg TabletView Details
Estraheal Estradiol 2mg TabletView Details
50-28-2 -
 Estrasign Estradiol 2mg TabletsView Details
Estrasign Estradiol 2mg TabletsView Details
50-28-2
