EPROSARTAN
- CAS NO.:133040-01-4
- Empirical Formula: C23H24N2O4S
- Molecular Weight: 424.51
- MDL number: MFCD00897872
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-13 18:13:23
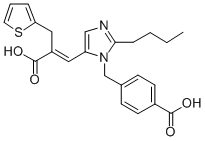
What is EPROSARTAN?
Absorption
Absolute bioavailability following a single 300 mg oral dose of eprosartan is approximately 13%. Administering eprosartan with food delays absorption.
Toxicity
There was no mortality in rats and mice receiving oral doses of up to 3000 mg eprosartan/kg and in dogs receiving oral doses of up to 1000 mg eprosartan/kg.
Description
Teveten was launched in Germany for the treatment of hypertension. There are several ways in which it has been prepared, the shortest of which is four steps; beginning with displacement of 2-butyl-4-chloroimidazole-5-carboxaldehyde with methyl 4-(bromomethyl)benzoate. Teveten is an angiotensin Ⅱ antagonist selective for the AT, subtype receptor. It is a potent, highly selective, competitve antagonist with no agonist activity. Duration of action is similar to Enalapril (greater than 12 hr) but Teveten had a faster onset. While it is orally active, it rapidly dissociates from the receptor. This is contrary to its prolonged duration of action, which presumably results from slow removal from compartments within tissue, cells or matrix around the AT, receptor. It is not bound by BSA.
Chemical properties
Light-Yellow Solid
Originator
SmithKline Beecham (UK)
The Uses of EPROSARTAN
Eprosartan (E590100) impurity.
The Uses of EPROSARTAN
Prototype of the imidazoleacrylic acid angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Antihypertensive
The Uses of EPROSARTAN
Eprosartan is a prototype of the imidazoleacrylic acid angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Eprosartan is an antihypertensive.
Indications
For the management of hypertension alone or in combination with other classes of antihypertensive agents. Also used as a first-line agent in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy, as well as a second-line agent in the treatment of congestive heart failure (only in those intolerant of ACE inhibitors).
Background
Eprosartan is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist used to treat hypertension. It performs 2 actions on the renin angiotensin system. By preventing the binding of angiotensin II to AT1, vascular smooth muscle relaxes and vasodilation occurs. By inhibiting norepinephrine production, blood pressure is further reduced.
What are the applications of Application
Eprosartan is a prototype of the imidazoleacrylic acid angiotensin II receptor antagonist
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of imidazoles and thiophenes that is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist used for the treatment of high blood pressure.
brand name
Teveten
Pharmacokinetics
Angiotensin II, the principal pressor agent of the renin-angiotensin system, is formed from angiotensin I in a reaction catalyzed by angiotensin-converting enzyme [kininase II]. It is responsible for effects such as vasoconstriction, stimulation of synthesis and release of aldosterone, cardiac stimulation, and renal reabsorption of sodium. Eprosartan selectively blocks the binding of angiotensin II to the AT1 receptor, which in turn leads to multiple effects including vasodilation, a reduction in the secretion of vasopressin, and reduction in the production and secretion of aldosterone. The resulting effect is a decrease in blood pressure.
Clinical Use
Angiotensin-II antagonistHypertension
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.Analgesics: antagonism of hypotensive effect and increased risk of renal impairment with NSAIDs; hyperkalaemia with ketorolac and other NSAIDs.Antihypertensives: increased risk of hyperkalaemia hypotension and renal impairment with ACE inhibitors and aliskiren.Ciclosporin: increased risk of hyperkalaemia and nephrotoxicity.Diuretics: enhanced hypotensive effect; hyperkalaemia with potassium-sparing diuretics.Epoetin: increased risk of hyperkalaemia; antagonism of hypotensive effect.Lithium: reduced excretion, possibility of enhanced lithium toxicity.Potassium salts: increased risk of hyperkalaemia.Tacrolimus: increased risk of hyperkalaemia and nephrotoxicity.
Metabolism
Eprosartan is not metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system. It is mainly eliminated as unchanged drug. Less than 2% of an oral dose is excreted in the urine as a glucuronide.
Metabolism
Following oral and intravenous dosing with [14C] eprosartan in human subjects, eprosartan was the only drug-related compound found in the plasma and faeces. In the urine, approximately 20% of the radioactivity excreted was an acyl glucuronide of eprosartan with the remaining 80% being unchanged eprosartanEprosartan is eliminated by both biliary and renal excretion. Following intravenous [14C] eprosartan, about 61% of radioactivity is recovered in the faeces and about 37% in the urine. Following an oral dose of [14C] eprosartan, about 90% of radioactivity is recovered in the faeces and about 7% in the urine.
Properties of EPROSARTAN
| Melting point: | 250-253°C |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Dichloromethane (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Pale Yellow to Light Yellow |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 133040-01-4 |
Safety information for EPROSARTAN
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for EPROSARTAN
EPROSARTAN manufacturer
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
![133040-01-4 Eprosartan
(E)-3-[2-Butyl-1-[(4-carboxyphenyl)methyl]-imidazol-5-yl]-2-(2- thienyl methyl)-2-propenoic acid 96%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//ProductImageIndia/2024-03/Raw/9f47841d-3633-4fe4-8639-9b1392d40602.png) 133040-01-4 Eprosartan (E)-3-[2-Butyl-1-[(4-carboxyphenyl)methyl]-imidazol-5-yl]-2-(2- thienyl methyl)-2-propenoic acid 96%View Details
133040-01-4 Eprosartan (E)-3-[2-Butyl-1-[(4-carboxyphenyl)methyl]-imidazol-5-yl]-2-(2- thienyl methyl)-2-propenoic acid 96%View Details
133040-01-4 -
 Eprosartan 98% CAS 133040-01-4View Details
Eprosartan 98% CAS 133040-01-4View Details
133040-01-4 -
 55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1