Pregabalin
Synonym(s):(S)-3-(Aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid;(S)-3-(Aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid; (S)-3-Isobutyl-γ-aminobutyric acid;3-Isobutyl GABA;, ;
- CAS NO.:148553-50-8
- Empirical Formula: C8H17NO2
- Molecular Weight: 159.23
- MDL number: MFCD00917044
- EINECS: 604-639-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-11-26 13:53:03
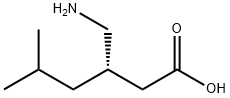
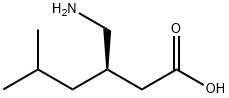
What is Pregabalin?
Absorption
After oral dosing administered in the fasted state, pregabalin absorption is rapid, and extensive. Pregabalin oral bioavailability is reported to be ≥90% regardless of the dose. Cmax is attained within 1.5 hours after single or multiple doses, and steady state is attained within 24-48 hours with repeated administration. Both Cmax and AUC appear to be dose proportional.
Food decreases the rate of pregabalin absorption and as a result, lowers the Cmax by an estimated 25-30% and increases the Tmax to approximately 3 hours. However, the effect of food does not appear to impact the total absorption of pregabalin in a way that is clinically relevant. As a result, pregabalin can be administered with or without food.
Toxicity
The most common symptoms of pregabalin toxicity (dose range includes 800 mg/day and single doses up to 11,500 mg) include somnolence, confusion, restlessness, agitation, depression, affective disorder and seizures.
Since there is no antidote for pregabalin overdose, patients should receive general supportive care. If appropriate, gastric lavage or emesis may help eliminate unabsorbed pregabalin (healthcare providers should take standard precautions to maintain the airway).
Description
Pregabalin is structurally similar to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) - an inhibitory neurotransmitter. It may be used to manage neuropathic pain, postherpetic neuralgia, and fibromyalgia among other conditions. Although as per the FDA Label the mechanism of action has not been definitively defined, there is evidence that pregabalin exerts its effects by binding to the α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels. Pregabalin is marketed by Pfizer under the trade name Lyrica and Lyrica Cr (extended release). It may have dependence liability if misused but the risk appears to be highest in patients with current or past substance use disorders.
The Uses of Pregabalin
Pregabalin was originally FDA approved in 2004 as an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It works by slowing down impulses in the brain that cause seizures. Pregabalin is used to treat pain caused by fibromyalgia, or nerve pain in people with diabetes (diabetic neuropathy), herpes zoster (post-herpetic neuralgia), or spinal cord injury.
Indications
Pregabalin is indicated for the management of neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, fibromyalgia, neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury, and as adjunctive therapy for the treatment of partial-onset seizures in patients 1 month of age and older.
Definition
ChEBI: Pregabalin is a gamma-amino acid that is gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) carrying an isobutyl substitutent at the beta-position (the S-enantiomer). Binds with high affinity to the alpha2-delta site (an auxiliary subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels) in central nervous system tissues. It has a role as an anticonvulsant and a calcium channel blocker. It is functionally related to a gamma-aminobutyric acid.
brand name
Lyrica (CP).
Pharmacokinetics
Although the structure of pregabalin is similar to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), it does not bind to GABA receptors. Instead, it binds the alpha2-delta subunit of presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system. Pregabalin does not modulate dopamine receptors, serotonin receptors, opiate receptors, sodium channels or cyclooxygenase activity.
Clinical Use
Antiepileptic
Neuropathic pain
Generalised anxiety disorder
Synthesis
Several syntheses of pregabalin (X) have been disclosed in the literature, including process scale-up comparison of
several different routes. The most cost efficient route
as described in the publication is shown in the Scheme.
Condensation of diethyl malonate 69 in the presense of
diisopropyl amine in acetic acid gave a,b-unsaturated diester
70 in high yield. Reaction of the enone diester with
potassium cyanide gave cyano diester 71 in 95% yield. In a
remarkable three step, one pot process, the nitrile in 71 was
hydrolyzed followed by decarboxylation of one of the esters
to provide 72 in 73% yield. Resolution of the two
enantiomers was achieved using (S)-(+)-mandellic acid, one
of the best acid found after many salt screening, to give, after
two recrystallization, a 99:1 ratio of the desired diastereomer.Removal of the acid was done with wet THF instead of base
separation, to avoid salt impurities, and one recrystallization
in ethanol gave 100% ee diastereomer in 25 ¨C 29% overall
yield.
It?ˉs worth noting that the Pfizer group have come up
with a new process of preparing pregabalin (X) via
enantioselective reduction, that promises to further reduce
cost and waste associated with the manufacture of this drug.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions of Pregabalin with other drugs
Antidepressants: anticonvulsant effect antagonised.
Antimalarials: anticonvulsant effect antagonised by
mefloquine.
Antipsychotics: anticonvulsant effect antagonised.
Orlistat: possible increased risk of convulsions.
Metabolism
Less than 2% of pregabalin is metabolized and it is excreted virtually unchanged in the urine.
Properties of Pregabalin
| Melting point: | 194-196°C |
| Boiling point: | 274.0±23.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D23 +10.52° (c = 1.06 in water) |
| Density | 0.997±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | deionized water: ≥10mg/mL |
| pka | 4.23±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | white powder |
| Water Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C8H17NO2/c1-6(2)3-7(5-9)4-8(10)11/h6-7H,3-5,9H2,1-2H3,(H,10,11)/t7-/m0/s1 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 148553-50-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Pregabalin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects H361:Reproductive toxicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Pregabalin
| InChIKey | AYXYPKUFHZROOJ-ZETCQYMHSA-N |
| SMILES | C(O)(=O)C[C@@H](CN)CC(C)C |
Pregabalin manufacturer
SRINI PHARMACEUTICALS PVT LTD
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Pregabalin 99%View Details
Pregabalin 99%View Details -
 Pregabalin 98%View Details
Pregabalin 98%View Details -
 Pregabalin 98%View Details
Pregabalin 98%View Details -
 Pregabalin 99%View Details
Pregabalin 99%View Details -
 Pregabalin 98%View Details
Pregabalin 98%View Details -
 Pregabalin 98%View Details
Pregabalin 98%View Details -
 Pregabalin 98%View Details
Pregabalin 98%View Details -
 Pregabalin 98%View Details
Pregabalin 98%View Details
