Ephedrine
Synonym(s):(−)-Ephedrine;(1R,2S)-(−)-α-(1-Methylaminoethyl)benzyl alcohol;(1R,2S)-(−)-2-Methylamino-1-phenyl-1-propanol;L -α-(1-Methylaminoethyl)benzyl alcohol
- CAS NO.:299-42-3
- Empirical Formula: C10H15NO
- Molecular Weight: 165.24
- MDL number: MFCD00064257
- EINECS: 206-080-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
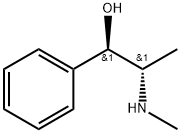
What is Ephedrine?
Absorption
Oral ephedrine reaches an average Cmax of 79.5ng/mL, with a Tmax of 1.81h, and a bioavailability of 88%.
Toxicity
Patients experiencing an overdose of ephedrine will present with rapidly increasing blood pressure. Manage overdose with blood pressure monitoring, and possibly the administration of parenteral antihypertensives. The LD50 in mice after oral administration is 785mg/kg, after intraperitoneal administration if 248mg/kg, and after subcutaneous administration is 425mg/kg.
Description
Use of the bronchodilator and stimulant ephedrine [(1R,2S)-2-(methylamino-1-phenylpropan-1-ol] by athletes is banned at the Olympic Games. Its 1S,2S?isomer is the common nasal decongestant pseudoephedrine, so the sniffling at award ceremonies might not just be emotional.
Description
Ephedrine is a naturally occurring alkaloid drug (→Alkaloids) derived from Ephedra equistina and Ephedra vulgaris. It can be prepared synthetically. It is used mainly in combination with other agents.
Chemical properties
white crystals or powder
Originator
CAM,Rybar-UK
The Uses of Ephedrine
Ephedrine, 1-phenyl-2-methylaminopropanol, C6H5 CH(OH)CH(NHCH3)CH3, is a white-to-colorless granular substance, unctuous (greasy) to the touch, and hygroscopic. The compound gradually decomposes upon exposure to light. Soluble in water, alcohol, ether, chloroform, and oils, and decomposes above this temperature. Ephedrine is isolated from stems or leaves of Ephedra, especially Ma huang (found in China and India). Medically, it is usually offered as the hydrochloride. In the treatment of bronchial asthma, ephedrine is known as a beta agonist. Compounds of this type reduce obstruction by activating the enzyme adenylate cyclase. This increases intracellular concentrations of cAMP (cyclic 3 5 -adenosine monophosphate) in bronchial smooth muscle and mast cells. Ephedrine is most useful for the treatment of mild asthma. In severe asthma, ephedrine rarely maintains completely normal airway dynamics over long periods. Ephedrine also has been used in the treatment of cerebral transient ischemic attacks, particularly with patients with vertabrobasilar artery insufficiency who have symptoms associated with relatively low blood pressure, or with postural changes in blood pressure. Ephedrine sulfate also has been used in drug therapy in connection with urticaria (hives).
The Uses of Ephedrine
Medicine (bronchodilator).
Background
Ephedrine was first described in western literature in 1888, as a naturally occurring component of the ephedra plant, along with pseudoephedrine. Ephedrine acts as both a direct and indirect sympathomimetic. It is an alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptor agonist; however, it also causes the indirect release of norepinephrine from sympathetic neurons, inhibiting norepinephrine reuptake and displacing more norepinephrine from storage vesicles. Ephedrine is used for its vasoconstrictive, positive chronotropic, and positive inotropic effects. Ephedrine and phenylephrine are still used to treat hypotension, but their use in other indications has decreased due to the development of more selective adrenergic agonists. Ephedrine was granted a type 7 FDA Approval on 29 April 2016.
Indications
Ephedrine intravenous injections are indicated to treat hypotension under anesthesia, ephedrine injections by multiple routes are indicated to treat allergic conditions such as bronchial asthma, ephedrine nasal spray is and OTC medication used as a decongestant.
Definition
ChEBI: A phenethylamine alkaloid that is 2-phenylethanamine substituted by a methyl group at the amino nitrogen and a methyl and a hydroxy group at position 2 and 1 respectively.
Definition
ephedrine: An alkaloid,C6H5CH(OH)CH(CH3)NHCH3 found inplants of the genus Ephedra, onceused as a bronchodilator in the treatmentof asthma. It is also used as astimulant and appetite suppressant.Structurally, it is a phenylethylamineand is similar to amphetamines, althoughless active. It is, however,widely used in the illegal synthesis ofmethamphetamine. The moleculehas two chiral centres. If the stereo- chemical conformations are opposite(i.e. 1R,2S or 1S,1R) the nameephedrine is used. If the conformationsare the same (1R,2R or 1S,2S)then the compound is called pseudoephedrine.
Manufacturing Process
120 grams of the fermentation product containing phenylpropanolone obtained
by extraction with ether (Biochemische Zeit-schrift Vol. 115, 1921, page 282
et seq.) are allowed to run, without further purification, in for about two hours
into a solution of 10 g of methylamine in 500 ml of ether in presence of 20 g
of activated aluminum, for example of the type described in British Patent No.
336,412, whilst stirring. Simultaneously 20-30 g of water are added,
dropwise. At once the vigorous reaction begins. It is moderated by periodical
cooling. Activated aluminum is aluminum, which has been amalgamated with
mercury. When it contacts with water, it liberates hydrogen and an insoluble
aluminum hydroxide is formed. Activated aluminum thus serves as the source
of hydrogen for the reaction. When the reaction is complete the ethereal
solution is filtered and the optically active base, which formed is extracted
from the filtrate by means of dilute acid. There is obtained the hydrochloride
of L-1-phenyl-2-methylamino-propanol-1 having a melting point of 214°C, and
having the optical rotation given in the literature. The yield amounts to 25-45
g of the hydrochloride depending upon the nature of the parent material.
360 g of ether extract phenylpropanolone used above as parent material are
distilled under reduced pressure. 300 grams of the fraction, which distils at
100-150°C/14 mm Hg are subjected to catalytic hydrogenation in presence of
colloidal platinum (70 ml of a 1% solution) and 85 grams of a 33% solution of
methylamine. It is advantageous to add some ether to the reaction mixture.
When absorption of hydrogen is complete, the ethereal solution is shaken with
hydrochloric acid and the L-phenyl-2-methylamino-propanol-1 is isolated from
the hydrochloric acid extract. The yield of the hydrochloride amounts to 110
grams. MP: 214°C.
100 g of L-1-phenylpropanol-1-one-2 isolated by the method of Neuberg
(Biochemische Zeitschrift Vol. 128, 1922, page 611) are dissolved in 200 ml of
ether, 75 g of a solution of methylamine (33%) are added and the whole is
shaken for about half an hour; condensation occurs with evolution of heat.
The reaction mixture is then treated with hydrogen in presence of 70 ml of a
1% colloidal solution of platinum. The reduction product was isolated as
hydrochloride. The hydrochloride of L-phenyl-2-methyl-amino-propanol-1
crystallizes from alcohol in the form of coarse prisms. MP: 214°-216°C. The
free base melts at 40°C.
brand name
Isofedrol (Boehringer Mannheim GmbH, Germany).
Therapeutic Function
Sympathomimetic; Bronchodilator
Biological Functions
Ephedrine is a naturally occurring alkaloid that can cross the blood-brain barrier and thus exert a strong CNS-stimulating effect in addition to its peripheral actions.The latter effects are primarily due to its indirect actions and depend largely on the release of norepinephrine. However, ephedrine may cause some direct receptor stimulation, particularly in its bronchodilating effects. Because it resists metabolism by both COMT and MAO, its duration of action is longer than that of norepinephrine. As is the case with all indirectly acting adrenomimetic amines, ephedrine is much less potent than norepinephrine; in addition, tachyphylaxis develops to its peripheral actions. Unlike epinephrine or norepinephrine, however, ephedrine is effective when administered orally.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion.
Mechanism of action
Ephedrine is a naturally occurring sympathomimetic amine that possesses both direct (agonist at α- and β-receptors) and indirect activity via its potentiation of noradrenaline release from sympathetic nerve terminals. It causes an increase in HR, contractility, CO and arterial pressure (systolic > diastolic). Bronchodilation occurs via a β2-mediated mechanism, and it is occasionally used for this purpose. Its duration of action is longer than endogenous catecholamines as it is not metabolised by COMT or MAO. Tachyphylaxis can occur as a result of depletion of noradrenaline from nerve terminals and persistent occupation of adrenergic receptors. Ephedrine crosses the placenta and can increase fetal metabolic rate with a subsequent metabolic acidosis. It is usually administered by i.v. bolus at a dose of 3– 9 mg.
Pharmacokinetics
Ephedrine increases blood pressure by stimulating heart rate and cardiac output and variably increasing peripheral resistance. It causes bronchodilation due to the activation of beta-adrenergic receptors in the lungs. By stimulating alpha-adrenergic receptors in bladder smooth muscle cells, ephedrine also increases the resistance to the outflow of urine. The therapeutic window of ephedrine is wide, as patients can be given doses of 5mg up to 50mg. Patients should be counselled regarding the pressor effects of sympathomimetic amines and the risk of tachyphylaxis. Also, the use of ephedrine for hypotension prophylaxis is associated with a higher risk of hypertension, compared to when ephedrine is used to treat hypotension.
Pharmacology
Ephedrine increases systolic and diastolic blood pressure; heart rate is generally not increased. Contractile force of the heart and cardiac output are both increased. Ephedrine produces bronchial smooth muscle relaxation of prolonged duration when administered orally. Aside from pupillary dilation, ephedrine has little effect on the eye.
Clinical Use
Ephedrine is useful in relieving bronchoconstriction and mucosal congestion associated with bronchial asthma, asthmatic bronchitis, chronic bronchitis, and bronchial spasms. It is often used prophylactically to prevent asthmatic attacks and is used as a nasal decongestant, as a mydriatic, and in certain allergic disorders. Although its bronchodilator action is weaker than that of isoproterenol, its oral effectiveness and prolonged duration of action make it valuable in the treatment of these conditions. Because of their oral effectiveness and greater bronchiolar selectivity, terbutaline and albuterol are replacing ephedrine for bronchodilation.
Side Effects
Symptoms of overdose are related primarily to cardiac and CNS effects. Tachycardia, premature systoles, insomnia, nervousness, nausea, vomiting, and emotional disturbances may develop. Ephedrine should not be used in patients with cardiac disease, hypertension, or hyperthyroidism.
Safety Profile
A human poison by an unspecified route. An experimental poison by intravenous, subcutaneous, intramuscular, and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion and parented routes. Causes rapid pulse, rise in blood pressure, and other actions similar to epinephrine. An experimental teratogen. Used in production of drugs of abuse. Has been known to cause allergic sensitization. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Metabolism
Ephedrine is largely unmetabolized in the body. Ephedrine can be N-demethylated to norephedrine, or demethylated and deaminized to benzoic acid conjugates and 1,2-hydroxypropylbenzene.
Purification Methods
Purify (-)-ephedrine by vacuum distillation (dehydrates) and forms waxy crystals or granules, and may pick up 0.5 H2O. The presence of H2O raises its melting point to 40o. [Moore & Taber J Amer Pharm Soc 24 211 1935.] The anhydrous base crystallises from dry ether [Fleming & Saunders J Chem Soc 4150 1955]. It gradually decomposes on exposure to light and is best stored in an inert atmosphere in the dark (preferably at -20o). Its solubility in H2O is 5%, in EtOH it is 1% and it is soluble in CHCl3, Et2O and mineral oils. It has pKa values in H2O of 10.25 (0o) and 8.69 (60o) [Everett & Hyne J Chem Soc 1136 1958, Prelog & H.flinger Helv Chim Acta 33 2021 1950] and pK a 8.84 in 80% aqueous methoxyethanol [Simon Helv Chim Acta 41 1835 1958]. The hydrochloride has m 220o (from EtOH/Et2O) and [] D20 -38.8o (c 2, EtOH). [IR: Chatten & Levi Anal Chem 31 1581 1959.] The anhydrous base crystallises from Et2O [Fleming & Saunders J Chem Soc 4150 1955]. [Beilstein 13 H 373, 13, III 1720, 13 IV 1879.]
Properties of Ephedrine
| Melting point: | 37-39 °C(lit.) |
| alpha | -41 º (c=5, 1M HCl) |
| Boiling point: | 255 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.124 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index | 1.4820 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 186 °F |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator (+4°C) |
| pka | pKa 8.02 (Uncertain);9.5 (Uncertain) |
| optical activity | [α]21/D 41°, c = 5 in 1 M HCl |
| Water Solubility | 47.62g/L(25 ºC) |
| Merck | 13,3639 |
| BRN | 2208730 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, strong oxidizing agents. May discolour in light. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 299-42-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ephedrine(299-42-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ephedrine (299-42-3) |
Safety information for Ephedrine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Ephedrine
Ephedrine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
