Encorafenib (LGX818)
- CAS NO.:1269440-17-6
- Empirical Formula: C22H27ClFN7O4S
- Molecular Weight: 540.01
- MDL number: MFCD25976758
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 16:58:18
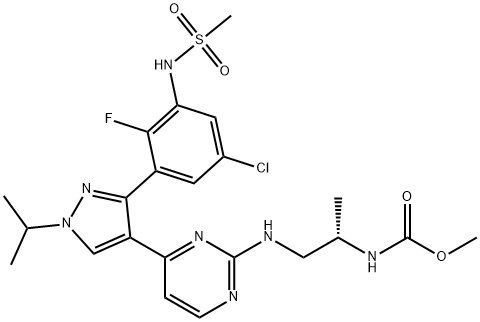
What is Encorafenib (LGX818)?
Absorption
The pharmacokinetics of encorafenib were studied in healthy subjects and patients with solid tumors, including advanced and unresectable or metastatic cutaneous melanoma harboring a BRAF V600E or V600K mutation, BRAF V600E mutation-positive metastatic CRC. After a single dose, systemic exposure of encorafenib was dose-proportional over the dose range of 50 mg to 700 mg (0.1 to 1.6 times the maximum recommended dose of 450 mg). After once-daily dosing, systemic exposure of encorafenib was less than dose-proportional over the dose range of 50 mg to 800 mg (0.1 to 1.8 times the maximum recommended dose of 450 mg). Steady-state was
reached within 15 days, with exposure being 50% lower compared to Day 1; intersubject variability (CV%) of AUC ranged from 12% to 69%.
After oral administration, the median Tmax of encorafenib is 2 hours. At least 86% of the dose is absorbed.
Following administration of a single dose of encorafenib 100 mg (0.2 times the maximum recommended dose of 450 mg) with a high-fat, high-calorie meal (consisting of approximately 150 calories from protein, 350 calories from carbohydrates, and 500 calories from fat) the mean maximum encorafenib concentration (Cmax) decreased by 36% and there was no effect on AUC.
Toxicity
New primary malignancies, cutaneous and non-cutaneous, have been observed in patients treated with BRAF inhibitors and can occur with encorafenib.
In COLUMBUS, a phase 3 safety and efficacy trial, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cuSCC), including keratoacanthoma (KA), occurred in 2.6%, and basal cell carcinoma occurred in 1.6% of patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib. The median time to first occurrence of cuSCC/KA was 5.8 months (range 1 to 9 months).
Tumor promotion in BRAF Wild-Type Tumors has been observed with encofarenib use.
Hemorrhage, uveitis, QT interval prolongation are also other adverse events observed while taking this medication.
Encorafenib, when used as a single agent, is associated with an increased risk of certain adverse reactions compared to when BRAFTOVI is used in combination with binimetinib. Grades 3 or 4 dermatologic reactions occurred in 21% of patients treated with BRAFTOVI therapy alone compared to 2% of patients treated with BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib.
Advise females with reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective non-hormonal contraception during treatment with BRAFTOVI and for 2 weeks after the final dose.
Carcinogenicity studies with encorafenib have not been conducted. Encorafenib was not genotoxic in studies evaluating reverse mutations in bacteria, chromosomal aberrations in mammalian cells, or micronuclei in the bone marrow of rats.
No dedicated fertility studies were performed with encorafenib in animals. In a general toxicology study in rats, decreased testes and epididymis weights, tubular degeneration in testes, and oligospermia in epididymides were observed at doses approximately 13 times the human exposure at the 450 mg clinical dose based on AUC. No effects on reproductive organs were observed in either sex in any of the non-human primate toxicity studies.
Since encorafenib is 86% bound to plasma proteins, hemodialysis is likely to be ineffective in the treatment of overdose with encorafenib.
Description
Encorafenib (LGX818) is a new-generation BRAF inhibitor that is under evaluation in clinical trials. However, the underlying mechanism remains to be elucidated. Here we show that LGX818 potently decreased ERK phosphorylation and inhibited proliferation in BRAFV600E melanoma cell lines. Moreover, LGX818 downregulated CyclinD1 in a glycogen synthase kinase 3β-independent manner and induced cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase.
The Uses of Encorafenib (LGX818)
LGX 818 is potent and selective BRAFV600E kinase inhibitor and can be used for the treatment of proliferative diseases such as solid tumor diseases.
Background
Encorafenib, also known as BRAFTOVI, is a kinase inhibitor. Encorafenib inhibits BRAF gene, which encodes for B-raf protein, which is a proto-oncogene involved in various genetic mutations. This protein plays a role in regulating the MAP kinase/ERK signaling pathway, which impacts cell division, differentiation, and secretion. Mutations in this gene, most frequently the V600E mutation, are the most commonly identified cancer-causing mutations in melanoma, and have been isolated in various other cancers as well, including non-Hodgkin lymphoma, colorectal cancer, thyroid carcinoma, non-small cell lung carcinoma, hairy cell leukemia and adenocarcinoma of the lung.
On June 27, 2018, the Food and Drug Administration approved encorafenib and binimetinib (BRAFTOVI and MEKTOVI, Array BioPharma Inc.) in combination for patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with a BRAF V600E or V600K mutation, as detected by an FDA-approved test.
Indications
Encorafenib is indicated in combination with binimetinib for the treatment of adult patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with a BRAF V600E or V600K mutation and metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with a BRAF V600E mutation. It is also indicated in combination with cetuximab for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic colorectal cancer with a BRAF V600E mutation.
brand name
Braftovi
General Description
Class: dual threonine/tyrosine kinase; Treatment: melanoma with BRAFV600E/K; Oral bioavailability = 85%; Elimination half-life = 6 h; Protein binding = 86%
Biological Activity
Encorafenib (LGX818) is a highly potent RAF inhibitor with selective anti-proliferative and apoptotic activity in cells expressing B-RAF(V600E) with EC50 of 4 nM. Phase 3.
Pharmacokinetics
Encorafenib has a pharmacologic profile that is distinct from that of other clinically active BRAFisand has shown improved efficacy in the treatment of metastatic melanoma.
Once-daily dosing of single-agent encorafenib has a distinct tolerability profile and shows varying antitumor activity across BRAFi-pretreated and BRAFi-na?ve patients with advanced/metastatic stage melanoma .
Encorafenib inhibited in vitro growth of tumor cell lines expressing BRAF V600 E, D, and K mutations. In mice implanted with tumor cells expressing BRAF V600E, encorafenib induced tumor regressions associated with RAF/MEK/ERK pathway suppression.
Encorafenib and binimetinib target two different kinases in the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway. Compared with either drug alone, the co-administration of encorafenib and binimetinib resulted in greater anti-proliferative activity in vitro in BRAF mutation-positive cell lines and greater anti-tumor activity with respect to tumor growth inhibition in BRAF V600E mutant human melanoma xenograft studies in mice. Additionally, the combination of encorafenib and binimetinib delayed the emergence of resistance in BRAF V600E mutant human melanoma xenografts in mice compared to either drug alone. In a BRAF V600E mutant NSCLC patient-derived xenograft
model in mice, coadministration of encorafenib and binimetinib resulted in greater anti-tumor activity compared to binimetinib alone, with respect to tumor growth inhibition. Increased tumor growth delay after dosing cessation was also observed with the co-administration compared to either drug alone.
In the setting of BRAF-mutant CRC, induction of EGFR-mediated MAPK pathway activation has been identified as a mechanism of resistance to BRAF inhibitors. Combinations of a BRAF inhibitor and agents targeting EGFR have been shown to overcome this resistance mechanism in nonclinical models. The co-administration of encorafenib and cetuximab had an anti-tumor effect greater than either drug alone, in a mouse model of colorectal cancer with mutated BRAF V600E.
Pharmacokinetics
Encorafenib shows an oral bioavailability of 85%
and a half-life of 6 h. It is administered orally once a
day (450 mg), whereas the other two dabrafenib and
vemurafenib are taken twice a day (Table 2, Section
10.1). The primary metabolic pathway is N-dealkylation, with CYP3A4 as the main contributor
(Fig. 1).
Clinical Use
Encorafenib (LGX818) is a new-generation BRAF inhibitor. It is currently under investigation in clinical trials for the treatment of BRAF mutant metastatic melanoma patients . LGX818 induces sustained mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway inhibition and has selective anti-proliferative and apoptotic activity in cells expressing BRAFV600E. However, the mechanism by which LGX818 suppresses BRAF mutant melanoma cell proliferation has not been thoroughly investigated.
Metabolism
Encorafenib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 (83%) and to a lesser extent by CYP2C19 (16%) and CYP2D6 (1%).
References
[1] stuart d d, li n, poon d j, et al. preclinical profile of lgx818: a potent and selective raf kinase inhibitor. cancer research, 2012, 72(8 supplement): 3790.
[2] huang t, karsy m, zhuge j, et al. b-raf and the inhibitors: from bench to bedside. j hematol oncol, 2013, 6(1): 30.
Properties of Encorafenib (LGX818)
| Melting point: | 184-185°C |
| Density | 1.45±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 5.94±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
Safety information for Encorafenib (LGX818)
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Encorafenib (LGX818)
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 LGX-818 99.00% CAS 1269440-17-6View Details
LGX-818 99.00% CAS 1269440-17-6View Details
1269440-17-6 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8