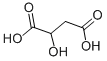
DL-Tartaric acid
Synonym(s):DL -2,3-Dihydroxybutanedioic acid;DL-Tartaric acid
- CAS NO.:133-37-9
- Empirical Formula: C4H6O6
- Molecular Weight: 150.09
- MDL number: MFCD00071626
- EINECS: 205-105-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:51
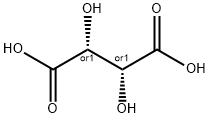
What is DL-Tartaric acid?
Chemical properties
DL-Tartaric acid is a water- and alcohol-soluble colorless crystalline solid with a characteristic acid taste and a melting temperature of 170°C(338°F). Naturally occurring tartaric acid is generally of the L-configuration (based on the absolute configuration of D-glyceric acid). The L-forms of tartrates are dextrorotatory in solution and thus are designated as L(+)-tartrates. It is also known as dihydroxy succinic acid. Tartaric acid is used as a chemical intermediate and a sequestrant,as well as in tanning, effervescent beverages, baking powder, ceramics, photography, textile processing,mirror silvering,and metal coloring.
Occurrence
d-Tartaric acid occurs in many fruits or other parts of the plant, free or combined with potassium, calcium or magnesium. It is also reported found in raw, lean fish, white wine, red wine and port wine.
The Uses of DL-Tartaric acid
DL-Tartaric acid is a synergist for antioxidants, emulsifier, sequestrant and flavoring agent. It is also added with citric acid to prepare effervescent salts, thereby enhancing the taste of oral medications. It is also utilized in pigments, processing aids, ink, toner and colorant products. It acts as a chelating agent in metal and farming industries. Further, it is used as a lubricant and grease. It is mixed with sodium bicarbonate and used as a leavening agent in food preparation. In the pharmaceutical industry, it is used in preparing tartar emetic, which is used in cough syrup as an expectorant. It can be used in the Debus–Radziszewski reaction as a weak acid for synthesising imidazolium ionic liquid. As an additive in electrochemical deposition technique for synthesising bismuth thin films to be used as X-ray absorbers. As a complexing agent for synthesising nano-crystalline indium tin oxide (ITO) powder. As a dopant for synthesising polyaniline nanofibers and nanotubes by oxidation polymerization.
Preparation
The tartrates used in commerce are obtained as a by-product of wine manufacture and have the L(+) configuration. Produced from argols or wine lees, which are formed in the manufacture of wine by extracting the potassium acid tartrate, transforming this into the calcium salt and then acidifying with dilute sulfuric acid; also by oxidation of d-glucose with nitric acid. The dl-tartaric acid is obtained by boiling the d-tartaric acid with an aqueous solution of NaOH or by oxidation of fumaric acid. The l- and the meso-tartaric acid are also known, but are less important.
Definition
DL-Tartaric acid is a tetraric acid that is butanedioic acid substituted by hydroxy groups at positions 2 and 3. It is a conjugate acid of a 3-carboxy-2,3-dihydroxypropanoate. It has a role as a human xenobiotic metabolite and a plant metabolite.
Properties of DL-Tartaric acid
| Melting point: | 210-212 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 191.59°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | [α]D20 -0.2~+0.2° (c=20, H2O) |
| Density | 1.788 |
| vapor pressure | <0.1 hPa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5860 (estimate) |
| FEMA | 3044 | TARTARIC ACID (D-, L-, DL-, MESO-) |
| Flash point: | 210 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 g/mL, clear |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 3.03, 4.37(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| PH | 3.19(1 mM solution);2.58(10 mM solution);2.03(100 mM solution); |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. very mild caramellic |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Merck | 14,9069 |
| JECFA Number | 621 |
| BRN | 1725148 |
| Dielectric constant | 35.9(-10℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with bases, oxidizing agents, reducing agents, silver. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 133-37-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Tartaric acid(133-37-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Butanedioic acid, 2,3-dihydroxy-, (2R,3R)-rel- (133-37-9) |
Safety information for DL-Tartaric acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for DL-Tartaric acid
| InChIKey | FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
DL-Tartaric acid manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Sip Chemical Industries
Meru Chem Private Limited
ASM Organics
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 DL – TARTARIC ACID 99%View Details
DL – TARTARIC ACID 99%View Details -
 DL-Tartaric acid CAS 133-37-9View Details
DL-Tartaric acid CAS 133-37-9View Details
133-37-9 -
 DL-Tartaric Acid extrapure CAS 133-37-9View Details
DL-Tartaric Acid extrapure CAS 133-37-9View Details
133-37-9 -
 DL-Tartaric acid 98% CAS 133-37-9View Details
DL-Tartaric acid 98% CAS 133-37-9View Details
133-37-9 -
 DL-Tartaric acid (synthetic) 99% CAS 133-37-9View Details
DL-Tartaric acid (synthetic) 99% CAS 133-37-9View Details
133-37-9 -
 DL-Tartaric Acid CAS 133-37-9View Details
DL-Tartaric Acid CAS 133-37-9View Details
133-37-9 -
 Powder Dl-Tartaric Acid, For IndustryView Details
Powder Dl-Tartaric Acid, For IndustryView Details
133-37-9 -
 Powder DL-Tartaric Acid CAS No.133-37-9, For IndustrialView Details
Powder DL-Tartaric Acid CAS No.133-37-9, For IndustrialView Details
133-37-9
