Diquat dibromide
- CAS NO.:85-00-7
- Empirical Formula: C12H12Br2N2
- Molecular Weight: 344.05
- MDL number: MFCD01074187
- EINECS: 201-579-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02

What is Diquat dibromide?
Description
Diquat (DQ) is a bipyridyl herbicide that has been in use since the 1950s. It is employed as a general use herbicide that is fast acting and nonselective. Additionally, on average, 90% of DQ consumption is reported in North America, Europe, Australia, and Japan.
Chemical properties
Pale yellow crystals; forms monohydrate; mp320°C (608 °F) (decomposes); readily solublein water, insoluble in organic solvents; stablein acids or neutral solution.
The Uses of Diquat dibromide
Diquat Dibromide is a herbicidal desiccant.
The Uses of Diquat dibromide
Nonselective contact herbicide used to control broad-leaved weeds in fruit and vegetable crops.
The Uses of Diquat dibromide
DQ is used in a manner similar to paraquat. It is found predominantly as a mixture with paraquat, sold as Weedol and Pathclear. The most widely used formulation of DQ alone, Reglone, is an aqueous solution containing 200 g l-1 DQ dibromide. Besides the use as a general weed control agent on noncrop land, DQ is used as a preharvest desiccant on crops such as cotton, flax, and alfalfa. Additionally, almost one-third of all DQ sold is used to control emergent and subemergent aquatic weeds.
Health Hazard
The acute toxicity of diquat dibromide ismoderate to high in most species. In domes-tic animals, its toxicity is greater than thatin small laboratory animals. The oral LD50value in cows, dogs, rabbits, and mice is30, 187, 188, and 233 mg/kg, respectively.The symptoms of acute toxicity are somnolence, lethargy, pupillary dilation, and respiratory distress. Prolonged exposure to thiscompound produced cataracts in experimental animals. Intratracheal administration ofdiquat dibromide in rats showed toxic effectsin the lung and caused lung damage (Manabeand Ogata 1986). But when administered byoral or intravenous routes, there was no toxiceffect on the lung.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. A skin and eye irritant. Human mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx, and Br-. See also PARAQUAT
Environmental Fate
Biological. Under aerobic and anaerobic conditions, the rate of diquat mineralization in eutrophic water and sediments was very low. After 65 days, only 0.88 and 0.21% of the applied amount (5 μg/mL) evolved as carbon dioxide (Simsiman and Chesters, 1976). Diquat is readily mineralized to carbon dioxide in nutrient solutions containing microorganisms. The addition of montmorillonite clay in an amount equal to adsorb one-half of the diquat decreased the amount of carbon dioxide by 50%. Additions of kaolinite clay had no effect on the amount of diquat degraded by microorganisms (Weber and Coble, 1968).
Photolytic. Diquat has an absorption maximum of 310 nm (Slade and Smith, 1967). The sunlight irradiation of a diquat solution (0.4 mg/100 mL) yielded 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro1-oxopyrido[1,2-a]-5-pyrazinium chloride (TOPPS) as the principal metabolite.
Chemical/Physical. Decomposes at 320°C (Windholz et al., 1983) emitting toxic fumes of bromides and nitrogen oxides (Lewis, 1990). Diquat absorbs water forming wellde?ned, pale yellow crystalline hydrate (Calderbank and Slade, 1976).
In aqueous alkaline solutions, diquat decomposes forming complex colored products including small amounts of dipyridone (Calderbank and Slade, 1976).
Toxicity evaluation
DQ is a dipyridyl compound that is capable of redox cycling. DQ can become reduced to produce a free radical. It can then transfer this electron to molecular oxygen to yield superoxide anion. This redox cycling mechanism allows DQ to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) resulting in oxidative stress, damage to cellular macromolecules and even cell death. Due to its standard redox potential (E0), DQ is more likely to accept an electron compared to paraquat. Because of this property, DQ is expected to generate greater amounts of ROS compared to paraquat at equivalent concentrations. In vitro studies have shown that DQ is dependent on mitochondrial complex I and III in isolated mitochondria and primarily complex III in midbrain neuronal cultures for ROS production. DQ treatment can lead to NADPH depletion, lipid peroxidation, alteration in intracellular redox status, and liberation of ferritin-bound iron stores.
Properties of Diquat dibromide
| Melting point: | 337°C |
| Density | 1.25 |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 1.6800 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| form | Crystals |
| color | Pale yellow |
| Water Solubility | Soluble. 70 g/100 mL |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 0.5 mg/m3 (ACGIH and MSHA). |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 85-00-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Diquat dibromide (85-00-7) |
Safety information for Diquat dibromide
Computed Descriptors for Diquat dibromide
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
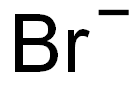

You may like
-
 Diquat dibromide 98% (HPLC) CAS 85-00-7View Details
Diquat dibromide 98% (HPLC) CAS 85-00-7View Details
85-00-7 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1