Ethylene glycol
Synonym(s):Ethylene Glycol;1,2-Ethanediol;Monoethylene glycol;Ethylene glycol in dimethyl sulfoxide;Ethylene glycol solution
- CAS NO.:107-21-1
- Empirical Formula: C2H6O2
- Molecular Weight: 62.07
- MDL number: MFCD00002885
- EINECS: 203-473-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:05
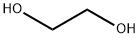
What is Ethylene glycol?
Description
Ethylene glycol is a clear, colorless syrupy liquid. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. It is widely used as an antifreeze in automobiles and in hydraulic fluids. It is used as a solvent for nitrocellulose and in the manufacture of acrylonitrile, dynamites, and resins.
Chemical properties
Ethylene glycol,CH20HCH20H, also known as glycol,ethylene alcohol, glycol alcohol, and dihydric alcohol, is a colorless liquid. It is soluble in water and in alcohol. Ethylene glycol is odorless and does not provide any warning of inhalation exposure to hazardous concentrations. The Odor Threshold in air is 25 ppm.
The Uses of Ethylene glycol
Ethylene glycol is a colorless, viscous, hydroscopic liquid with a sweetish taste. Often colored fluorescent yellow-green when used in automotive antifreeze. Ethyleneglycol is widely used as an antifreeze in automobiles and in hydraulic fluids. It is used as a solvent for nitrocellulose and in the manufacture of acrylonitrile, dynamites, and resins. Solvent in the paint and plastics industries. In the formulation of printers' inks, stamp pad inks, ball-point pen ink. Softening agent for cellophane. Stabilizer for soybean foam used to extinguish oil and gasoline fires.
Definition
ChEBI: Ethylene glycol is a 1,2-glycol compound produced via reaction of ethylene oxide with water. It has a role as a metabolite, a toxin, a solvent and a mouse metabolite. It is a glycol and an ethanediol.
Preparation
Ethylene glycol is prepared by the hydration of ethylene oxide:

This reaction is carried out in a manner comparable to that described for the preparation of propylene glycol from propylene oxide . Ethylene glycol is a colourless liquid, b.p. 197??C.
Reactivity Profile
Mixing Ethylene glycol in equal molar portions with any of the following substances in a closed container caused the temperature and pressure to increase: chlorosulfonic acid, oleum, sulfuric acid, [NFPA 1991].
Hazard
Questionable carcinogen. Toxic by ingestion and inhalation. Lethal dose reported to be 100 cc.
Toxicity
The acute inhalation toxicity of 1,2-ethanediolis low. This is due to its low vaporpressure, 0.06 torr at 20°C (68°F). Its saturationconcentration in air at 20°C (68°F)is 79 ppm and at 25°C (77°F) is 131 ppm(ACGIH 1986). Both concentrations exceedthe ACGIH ceiling limit in air, which is50 ppm. In humans, exposure to its mist orvapor may cause lacrimation, irritation ofthroat, and upper respiratory tract, headache,and a burning cough. These symptoms maybe manifested from chronic exposure toabout 100 ppm for 8 hours per day for severalweeks.
The acute oral toxicity of 1,2-ethanediol islow to moderate. The poisoning effect, however,is much more severe from ingestionthan from inhalation. Accidental ingestion of80–120 mL of this sweet-tasting liquid canbe fatal to humans. The toxic symptoms inhumans may be excitement or stimulation,followed by depression of the central nervoussystem, nausea, vomiting, and drowsiness,which may, in the case of severe poisoning,progress to coma, respiratory failure, anddeath. When rats were administered sublethaldoses over a long period, there was depositionof calcium oxalate in tubules, causinguremic poisoning.
LD50 value, oral (rats): 4700 mg/kg
Ingestion of 1,2-ethanediol produced reproductiveeffects in animals, causing fetotoxicity, postimplantation mortality, andspecific developmental abnormalities. Mutagenictests proved negative. It tested negativeto the histidine reversion–Ames test.
Fire Hazard
Ethylene glycol is combustible.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Ethylene glycol is a low toxicity molecule and is used for embryo cryopreservation in many domestic animals.Ethylene glycol 5M solution is an additive screening solution of Additive Screening Kit. Additive Screen kit is designed to allow rapid and convenient evaluation of additives and their ability to influence the crystallization of the sample. The Additive Kit provides a tool for refining crystallization conditions.
Potential Exposure
Ethylene glycol is used in antifreeze (especially as car radiator antifreeze) and in production of polyethylene terephthalate fibers and films; in hydraulic fluids; antifreeze and coolant mixtures for motor vehicles; electrolytic condensers; and heat exchangers. It is also used as a solvent and as a chemical intermediate for ethylene glycol dinitrate, glycol esters; resins, and for pharmaceuticals.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, getmedical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit
Environmental Fate
Ethylene glycol is considered an inert ingredient in pesticides. It
typically enters the environment through waste streams after
use of deicing products, where it is highly mobile in soil and
contaminates groundwater. Ethylene glycol is considered
‘readily biodegradable.’ It biodegrades relatively quickly; its
half-life (t1/2) is 2–12 days in soil.
Ethylene glycol is biodegraded in water under both aerobic
and anaerobic conditions within a day to a few weeks. In the
atmosphere, ethylene glycol photochemically degrades with
a t1/2 of approximately 2 days.
Solubility in organics
Miscible with water and alcohol, soluble in lower atifatic alcohols and ketones, Propylene glycol and Glycerin, poorly soluble in Hydrocarbons such as Terpenes as well as in Terpene alcohols, esters, etc.
Storage
Ethylene glycol must be stored to avoid contact with sulfuric acid since violent reactions occur. Store in tightly closedcontainers in a cool, well-ventilated area away from oxidizing agents (such as perchlorates, peroxides, permanganates,chlorates, and nitrates).
Toxicity evaluation
Ethylene glycol has low toxicity but it is metabolized to a variety of toxic metabolites. Ethylene glycol and glycolaldehyde have an intoxicating effect on the central nervous system that can lead to ataxia, sedation, coma, and respiratory arrest similar to ethanol intoxication. However, the profound metabolic acidosis reported in toxicity is secondary to accumulation of acid metabolites, especially glycolic acid. The oxalic acid metabolite complexes with calcium and precipitates as calcium oxalate crystals in the renal tubules, leading to acute renal injury. Further, oxalate’s ability to chelate calcium may cause clinically relevant serum hypocalcemia.
Incompatibilities
Reacts with sulfuric acid, oleum, chlorosulfonic acid; strong oxidizing agents; strong bases; chromium trioxide; potassium permanganate; sodium peroxide. Hygroscopic (i.e., absorbs moisture from the air)
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed. Alternatively, ethylene glycol can be recovered from polyester plant wastes
Properties of Ethylene glycol
| Melting point: | -13 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 195-198 °C |
| Density | 1.113 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.1 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.08 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 230 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | water: miscible |
| form | Viscous Liquid |
| appearance | Colorless liquid |
| pka | 14.22(at 25℃) |
| color | blue |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Relative polarity | 0.79 |
| PH | 6-7.5 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| explosive limit | 3.2%(V) |
| Water Solubility | miscible |
| FreezingPoint | -11.5℃ |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: ≤0.03 λ: 280 nm Amax: ≤0.01 |
| Merck | 14,3798 |
| BRN | 505945 |
| Exposure limits | Ceiling limit in air for vapor and mist
50 ppm (~125 mg/m3) (ACGIH); TWA 10
mg/m3 (particulates) (MSHA). |
| Dielectric constant | 37.0(20℃) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 107-21-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1,2-Ethanediol(107-21-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ethylene glycol (107-21-1) |
Safety information for Ethylene glycol
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Ethylene glycol
Ethylene glycol manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Shiv Shakti Trading Corporation
Veera Chemical
Dhairya International
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Ethylene glycol, 99+% CAS 107-21-1View Details
Ethylene glycol, 99+% CAS 107-21-1View Details
107-21-1 -
 Ethylene Glycol (ER) CAS 107-21-1View Details
Ethylene Glycol (ER) CAS 107-21-1View Details
107-21-1 -
 Ethylene Glycol (SQ) CAS 107-21-1View Details
Ethylene Glycol (SQ) CAS 107-21-1View Details
107-21-1 -
 Ethylene Glycol GC Reference Standard CAS 107-21-1View Details
Ethylene Glycol GC Reference Standard CAS 107-21-1View Details
107-21-1 -
 Monoethylene Glycol CASView Details
Monoethylene Glycol CASView Details -
 Liquid Ethylene Glycol, 99% Purity, 230 Kg Drum for Manufacturing Resin EstersView Details
Liquid Ethylene Glycol, 99% Purity, 230 Kg Drum for Manufacturing Resin EstersView Details
107-21-1 -
 Mono Ethylene GlycolView Details
Mono Ethylene GlycolView Details
107-21-1 -
 Industrial Grade Mono Ethylene Glycol, 200 L Drum, 10472-24-9View Details
Industrial Grade Mono Ethylene Glycol, 200 L Drum, 10472-24-9View Details
10472-24-9
