Diphenylamine
Synonym(s):Diphenylamine;DPA;N-Phenylaniline
- CAS NO.:122-39-4
- Empirical Formula: C12H11N
- Molecular Weight: 169.22
- MDL number: MFCD00003014
- EINECS: 204-539-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
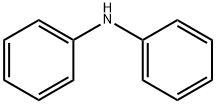
What is Diphenylamine?
Description
Solutions of diphenylamine are used to treat apples a few days before harvest. Residue on apples’ surfaces of 10 ppm is permitted by regulation in Australia, Canada, and the United States.
Chemical properties
Diphenylamine is a colorless monoclinic leafl et substance. It is used in the manufacture of a variety of substances, i.e., dyestuffs and their intermediates, pesticides, antihelmintic drugs, and as reagents in analytical chemistry laboratories.
Chemical properties
white crystals or powder
The Uses of Diphenylamine
Diphenylamine is an aromatic amine that was shown to exhibit antioxidant activities and is now used as an anti-scald agent. It is also used in the manufacture of a variety of substances, for instance, dye stuffs and their intermediates, pesticides, anthelmintic drugs, and as reagents in analytical chemistry laboratories.
The Uses of Diphenylamine
Diphenylamine is used in the manufactureof dyes, as a stabilizer for nitrocelluloseexplosives, and as an analytical reagent forcolorimetric tests for nitrate and chlorate.
Other applications of this compoundinclude preventing postharvest deteriorationof apple and peer crops; as an antioxidant inrubber and elastomer industry and in the per fumery. As a stabilizer for propellants andexplosives, it binds their degradation prod ucts thus prolonging the storage time of suchpropellants.
The Uses of Diphenylamine
Diphenylamine is used post-harvest to prevent superficial scald in apples in cold store.
Definition
diphenylamine: A colourless crystallinearomatic compound,(C6H5)2NH; m.p. 54°C. It is made byheating phenylamine (aniline) withphenylamine hydrochloride. It is asecondary amine and is both slightlyacidic (forming an N-potassium salt)and slightly basic (forming salts withmineral acids). Its derivatives are employedas stabilizers for syntheticrubber and rocket fuels.
What are the applications of Application
Diphenylamine is a redox indicator exhibits red fluorescence
Definition
ChEBI: An aromatic amine containing two phenyl substituents. It has been used as a fungicide for the treatment of superficial scald in apples and pears, but is no longer approved for this purpose within the European Union.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 58, p. 6900, 1993 DOI: 10.1021/jo00076a063
General Description
Light tan to brown solid with a pleasant odor. Sinks in water.
Air & Water Reactions
Dust may be explosive if mixed with air in critical proportions and in the presence of a source of ignition [USCG, 1999]. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Diphenylamine discolors in light. Diphenylamine can react violently with hexachloromelamine and trichloromelamine. Diphenylamine is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and strong acids. Diphenylamine is also incompatible with iron and silver salts. Diphenylamine reacts with nitrogen oxides.
Health Hazard
Inhalation may irritate mucous membranes. Overexposure, including ingestion of solid or skin contact, may cause fast pulse, hypertension, and bladder trouble. Contact with dust irritates eyes.
Health Hazard
Diphenylamine is highly toxic and is rapidly absorbed by the skin and through inhalation. It has caused anorexia, hypertension, eczema, and bladder symptoms. Experimental animals exposed to diphenylamine demonstrated cystic lesions but failed to demonstrate cancerous growth. Inhalation of diphenylamine dust may cause systemic poisoning. The symptoms of toxicity include, but are not limited to, anoxia, headache, fatigue, anorexia, cyanosis, vomiting, diarrhea, emaciation, hypothermia, bladder irritation, kidney, heart, and liver damage.
Health Hazard
Diphenylamine is much less toxic than aniline. The acute oral toxicity is low. A doseof 3000 mg/kg was lethal to rats. At a concentration of >500 ppm, a diet fed to ratsfor over 7 months resulted in renal cysts inanimals. Its absorption through the skin andthe respiratory system is lower than that ofaniline. Exposure to its dusts caused changesin liver, spleen, and kidney in test animals.Industrial exposure to diphenylamine hascaused tachycardia, hypertension, eczema,and bladder symptoms in workers (Fairhall1957). Carcinogenicity of this compound isunknown. It showed an adverse reproduc tive effect in animals, causing developmentalabnormalities in urogenital system in pregnant rats.
LD50 value, oral guinea pig: 300 mg/kg.
Fire Hazard
Noncombustible solid; autoignition temperature 634°C (1173°F); low reactivity.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide, Fungicide, Herbicide, Plant growth regulator: Topically in anti-screwworm mixtures, foliar application in a modified growth chamber to decrease ozone injury to leaves of apple, bean, muskmelon, petunia, and tobacco plants. To control weather fleck in tobacco and inhibit algae formation. To prolong the fresh appearance of snapdragons. Protect rice from the toxic effects of thiolcarbamate herbicides [83] . Not currently approved for use in EU countries (resubmitted) . Registered for use in the U.S. and other countries.
Trade name
NOSCALD DPA 31; NOSCALD DPA 283; SCALDIP; Z-876
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion. Experimental teratogenic effects. Action similar to anhne but less severe. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. Can react violently with hexachloromelamine or trichloromelamine. Can react with oxilzing materials. To fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of NOx,. See also ANILINE, AMINES, and AROMATIC AMINES.
Potential Exposure
AgriculturalChemical; Mutagen; Reproductive Effector. DPA is used asa stabilizer for plastics including solid rocket propellants;antioxidant for polymers, greases, and industrial oils; in themanufacture of pharmaceuticals; pesticides, explosives, anddyes.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Medical observation is recommended.
Environmental Fate
Diphenylamine is present in waste water from industrial
processes. Diphenylamine has been detected in milk of
animals (cow, sheep, goat, water buffalo) raised in Italy and
France.
Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata (Algae) growth was inhibited
with a dose of 0.30 mg l-1. Aquatic invertebrates Daphnia
magna showed an acute 48 h EC50 dose of 1.2 mg l-1.
Metabolic pathway
The major metabolite of diphenylamine (DPA) identified in stored apples is a glucose conjugate of 4-hydroxydiphenylamine, and additional metabolites, characterized as glycosyl conjugates of 2-hydroxy- DPA, 3-hydroxy-DPA, 4-hydroxy-DPA, or dihydroxy- DPA, are also detected along with their intact (i.e. non-conjugated) forms in apple pulp.
Storage
Diphenylamine should be protected from physical damage. Storage of diphenylamine outside or a detached area is preferred. Inside storage should be in a standard flammable liquids storage room or cabinet. Diphenylamine should be kept separately from oxidizing materials and incompatible chemical substances. Storage and work areas should be no smoking areas. Diphenylamine should be kept protected from light.
Shipping
Toxic solids, flammable, organic, n.o.s. requiresa shipping label of “POISONOUS/TOXIC MATERIALS.”It falls into Hazard Class 6.1.
Purification Methods
Crystallise diphenylamine from pet ether, MeOH, or EtOH/water. Dry it under vacuum. [Beilstein 12 H 174, 12 IV 271.]
Degradation
Diphenylamine is an anti-oxidant and therefore reacts with oxygen under conditions of use. It darkens on exposure to sunlight. Aqueous photolysis is pH and oxygen dependant (Lopez et al., 1980). It is converted into carbazole (2) and hydrogen peroxide in the presence of dissolved oxygen. In degassed solution it is converted into carbazole (2) and tetrahydrocarbazole (3) (see Scheme 1).
Incompatibilities
Dust may form an explosive mixturewith air. Incompatible with strong acids, strong oxidizers,aldehydes, organic anhydrides, isocyanates, hexachloromelamine, trichloromelamine. Reacts with nitrogen oxidesforming n-nitrosodiphenylamine and heat-, friction-, andshock-sensitive nitro products
Precautions
Students and occupational workers should be careful during use and handling of diphenylamine. Workers should wear impervious protective clothing, including boots, gloves, a laboratory coat, apron or coveralls, as appropriate, to prevent skin contact. Finely dispersed particles of diphenylamine form explosive mixtures in air. Diphenylamine is very harmful on exposures by swallowing, inhalation, and/or skin absorption. Diphenylamine causes irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract, and causes blood vascular changes leading to methemoglobinemia.
Properties of Diphenylamine
| Melting point: | 52 °C |
| Boiling point: | 302 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.16 |
| vapor density | 5.82 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 108 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5785 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 307 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | alcohol: passes test |
| pka | 0.79(at 25℃) |
| form | crystalline |
| color | tan |
| Odor | Floral odor |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble. 0.03 g/100 mL |
| Sensitive | Air & Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,3317 |
| BRN | 508755 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 10 mg/m3 (ACGIH and MSHA). |
| Dielectric constant | 3.3(11℃) |
| Stability: | Stable; may discolour on exposure to light. Incompatible with strong acids, strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 122-39-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Diphenylamine(122-39-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Diphenylamine (122-39-4) |
Safety information for Diphenylamine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Diphenylamine
Diphenylamine manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Manav Biochem Impex Private Limited
Triveni Interchem Private Limited (Group Of Triveni Chemicals)
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
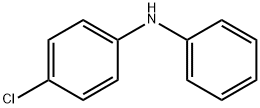
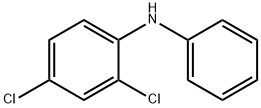
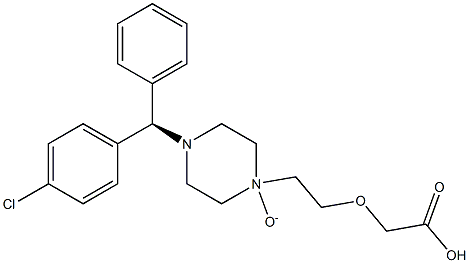
![(RS)-2-[2-[4-[(2-Chloro-phenyl)phenylMethyl]piperazin-1-yl]ethoxy]aceticAcidDihydrochloride](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20130318/GIF/CB02617026.gif)

You may like
-
 Diphenylamine 98%View Details
Diphenylamine 98%View Details -
 Diphenylamine, For analysis ACS CAS 122-39-4View Details
Diphenylamine, For analysis ACS CAS 122-39-4View Details
122-39-4 -
 Diphenylamine, For analysis ACS CAS 122-39-4View Details
Diphenylamine, For analysis ACS CAS 122-39-4View Details
122-39-4 -
 Diphenylamine extrapure AR CAS 122-39-4View Details
Diphenylamine extrapure AR CAS 122-39-4View Details
122-39-4 -
 Diphenylamine 98% CAS 122-39-4View Details
Diphenylamine 98% CAS 122-39-4View Details
122-39-4 -
 DI PHENYL AMINEView Details
DI PHENYL AMINEView Details
122-39-4 -
 Diphenyl amine ChemicalsView Details
Diphenyl amine ChemicalsView Details
122-39-4 -
 Diphenylamine, Grade: Industrial GradeView Details
Diphenylamine, Grade: Industrial GradeView Details
122-39-4
