Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
Synonym(s):DCC;N,N′-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide;DCC impregnated tablets;ChemDose, N,N′-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide impregnated tablets;N,N′-Methanetetraylbis[cyclohexanamine]
- CAS NO.:538-75-0
- Empirical Formula: C13H22N2
- Molecular Weight: 206.33
- MDL number: MFCD00011659
- EINECS: 208-704-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-01 18:09:03
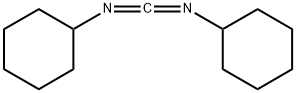
What is Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide?
Description
Dicydohexyl carbodiimide is used in peptide chemistry as a coupling reagent. It is both an irritant and a sensitizer, and caused contact dermatitis in pharmacists and chemists.
Chemical properties
Colorless solid
Chemical properties
N,N0 -Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) is a white crystalline solid. Odor is sweet and heavy.
The Uses of Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is a carbodiimide used to couple amino acids during peptide synthesis. N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is used as a dehydrating agent for the preparation of amides, ketones , nitriles as well as in the inversion and esterification of secondary alcohols.
The Uses of Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
This product is mainly used in amikacin, glutathione dehydrants, as well as in synthesis of acid anhydride, aldehyde, ketone, isocyanate; when it is used as dehydrating condensing agent, it reacts to dicyclohexylurea through short-time reaction under normal temperature. This product can also be used in synthesis of peptide and nucleic acid. It is easy to use this product to react with compound of free carboxy and amino-group into peptide. This product is widely used in medical, health, make-up and biological products, and other synthetic fields.
The Uses of Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is used as a dehydrating agent at room temperature after a short reaction time, after the reaction product is dicyclohexylurea. the product is very small solubility in an organic solvent, so that easy separation of the reaction product.
The Uses of Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
In the synthesis of peptides.
What are the applications of Application
DCC is a carboxyl activating reagent commonly employed in peptide synthesis
Definition
ChEBI: A carbodiimide compound having a cyclohexyl substituent on both nitrogen atoms.
Preparation
A stirred mixture of N,N′-dicyclohexylurea (19.7 g), phosphorus pentoxide (100 g), sand (175 g), and pyridine (700 mL) was refluxed for 2.25 h. Stirring was no longer possible after about 30 min. The mixture was filtered and the residue was extracted with pyridine (100 mL). Pyridine was removed from the combined solutions on a flash evaporator, and the residual oil was extracted with boiling petroleum ether (bp 60–80 C°) (2 × 100 mL), and then with diethyl ether (100 mL). The combined extracts were washed with iced water (3×80 mL), dried over calcium chloride, and filtered. The solvents were removed from the filtrate under reduced pressure to give 17.4 g of an oil, which on distillation yielded 13.7 g (76%) of a clear liquid; bp 143 C° (3.5 mmHg), which solidified in the receiver; mp 34–35 C°.
Another method for producing DCC from dicyclohexylurea is a two-step process using phosphoryl chloride in dichloromethane at 40 C° for 4 h under non-basic conditions followed by removal of acidic components with aq. sodium hydroxide. This method, which gives an 89% yield of DCC, has been presented in a patent application.
Preparation
Palladium acetate (22 mg, 0.1 mmol), iodine (50 mg, 0.2 mmol), and anhydrous sodium carbonate (320 mg, 3.0 mmol) were placed in a pressure vessel. Cyclohexylamine (0.11 mL, 1.0 mmol) and cyclohexyl isocyanide (0.1 mL, 0.8 mmol) were dissolved in acetonitrile (10 mL) and this solution was added to the reaction vessel, which was then pressurized with oxygen (40 psi) and heated to 100 C° for 3 h. The initially deep-red reaction mixture turned yellow-orange; no Pd black precipitation was observed. There was no obvious reaction rate dependence on oxygen pressure. The mixture was cooled to ambient temperature, depressurized, filtered, and analyzed by GC. DCC was isolated by evaporating the solvent and residual amine, followed by vacuum distillation.
Palladium(II) complexes with a carbodiimide ligand, in which a nitrogen of the linear NbCbN moiety is bonded to the metal center, and bis(carbodiimido)palladium(II) complexes, both derived from isocyanides, have been described.
General Description
White crystalline solid with a heavy sweet odor.
Air & Water Reactions
Sensitive to moisture.
Reactivity Profile
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is an imide. Amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx). Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is incompatible with acids and oxidizing agents. Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide reacts with water.
Hazard
A poison by skin contact. Moderately toxic by ingestion and inhalation.
Fire Hazard
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is probably combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Contact allergens
Used in peptide chemistry as a coupling reagent. It is both an irritant and a sensitizer and has caused contact dermatitis in pharmacists and chemists.
Potential Exposure
Laboratory reagent
First aid
Eyes: Check the victim for contact lenses andremove. Flush victim’s eyes with water or normal salinesolution for 20-30 min, lifting lower and upper eyelidsoccasionally. Remove contaminated clothing and shoes. Getmedical attention immediately. Do not put any ointments,oils, or medication in the victim’s eyes without specificinstructions from a physician. Immediately transport thevictim after flushing eyes to a hospital even if no symptoms(such as redness or irritation) develop. Skin: Immediatelyflood affected skin with water and wash for at least 15 min.Remove and isolate all contaminated clothing. Gently wash all affected skin areas thoroughly with soap and water. Ifsymptoms such as redness or irritation develop, immediately call a physician. Transport the victim to a hospital fortreatment. Inhalation: Remove victim to fresh air. If notbreathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult,give oxygen. Get medical attention immediately. Ingestion:Do not induce vomiting. If the victim is conscious and notconvulsing, give large amount of water to dilute the chemical. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. If symptoms (such as wheezing, coughing, shortness ofbreath, or burning in the mouth, throat, or chest) develop,call a physician. In all cases get medical attention immediately. If the victim is convulsing or unconscious, do notgive anything by mouth, ensure that the victim’s airway isopen and lay the victim on his/her side with the head lowerthan the body.
Chemical properties
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is a white crystalline solid with a heavy, sweet odor. The C-N=C=N?C core of carbodiimides (N=C=N) is linear and related to the allene structure. The molecule has idealized C2 symmetry.
Mode of action
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) is one of the most frequently used coupling agents, especially in organic synthesis applications. Sheehan and Hess introduced dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) as a coupling reagent for preparing amide bonds 1955. Since then, DCC has been used for peptide synthesis. The mechanism involves forming and propagating an amide or peptide bond via an O-acylisourea active intermediate. The intermediate is violently reactive and difficult to isolate. It reacts vigorously with nucleophiles like amines to form an amide bond accompanied by the formation of a byproduct called dicyclohexylurea.
storage
Color Code—White: Corrosive or Contact Hazard;Store separately in a corrosion-resistant location. KeepDCC in a tightly closed container in a cool, dry, ventilatedarea away from sources of incompatible materials, heat,direct sunlight, moisture, or ignition; best stored under aninert atmosphere at refrigerated temperatures. Containers ofDCC may be hazardous when empty since they retain product residues (dust, solids); observe all warnings and precautions listed for the product. Shelf life when stored underideal conditions: .4 years.
Shipping
UN2928 Toxic solids, corrosive, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, 8- Corrosive material, Technical Name Required. UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1- Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required
Purification Methods
It is sampled as a liquid after melting in warm H2O. It is sensitive to air, and it is a potent skin irritant. It can be distilled in a vacuum and is best stored in a tightly stoppered flask in a freezer. It is very soluble in CH2Cl2 and pyridine where the reaction product with H2O, after condensation, is dicyclohexyl urea which is insoluble and can be filtered off. Alternatively dissolve it in CH2Cl2, add powdered anhydrous MgSO4, shake for 4hours, filter, evaporate and distil at 0.6mm pressure and oil bath temperature of 145o. [Bodansky et al. Biochemical Preparations 10, 122 1963, Schmidt & Seefelder Justus Liebigs Ann Chem 571 83 1951, Schmidt et al. Justus Liebigs Ann Chem 612 11 1958, Beilstein 12 IV 72.]
Incompatibilities
Dust may for explosive mixture with air. Reacts with steam and water. N,N0 - Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is an amine/imide: contact with strong oxidizers may cause fire and explosions. Incompatible with acids, strong bases, strong reducing agents (may form flammable gasses); azo and diazo compounds (may form toxic gases); chlorinated hydrocarbons; nitro compounds. Contact with mixture of acetic acid 1 dinitrogen trioxide may cause explosion. The combustion of amide compounds generate nitrogen oxides (NOx). In the presence of moisture, may attack metals and plastics.
Waste Disposal
Whatever cannot be saved for recovery or recycling should be managed in an appropriate and approved waste facility. Although not a listed RCRA hazardous waste, this material may exhibit one or more characteristics of a hazardous waste and require appropriate analysis to determine specific disposal requirements. Processing, use or contamination of this product may change the waste management options. State and local disposal regulations may differ from federal disposal regulations. Dispose of container and unused contents in accordance with federal, state and local requirements
Properties of Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
| Melting point: | 34-35 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 122-124 °C6 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 1.247 g/mL at 25 °C |
| vapor pressure | 1.044-1.15Pa at 20-25℃ |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 190 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | methylene chloride: 0.1 g/mL, clear, colorless |
| appearance | White solid |
| form | Waxy Solid or Crystalline Mass |
| color | White to pale yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 1.247 |
| Water Solubility | Reaction |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,3096 |
| BRN | 610662 |
| Stability: | Stable, but moisture sensitive. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Avoid exposure to air or moisture. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 538-75-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Methanediimine, n,n'-dicyclohexyl-(538-75-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (538-75-0) |
Safety information for Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H312:Acute toxicity,dermal H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects H351:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
| InChIKey | QOSSAOTZNIDXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide manufacturer
Virchow Groups
Clean Science and Technology Limited
Paushak Limited
United Phosphorus Limited
Greenwave Pharmaceuticals
Tosco Pharmachem Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 DCC (1, 3-Di cyclo hexyl carbodiimide) 538-75-0 98%View Details
DCC (1, 3-Di cyclo hexyl carbodiimide) 538-75-0 98%View Details
538-75-0 -
 N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, 99% 98%View Details
N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, 99% 98%View Details
538-75-0 -
 N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide CAS 538-75-0View Details
N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide CAS 538-75-0View Details
538-75-0 -
 N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, 99% CAS 538-75-0View Details
N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, 99% CAS 538-75-0View Details
538-75-0 -
 N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide CASView Details
N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide CASView Details -
 N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide 98%View Details
N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide 98%View Details -
 Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide CAS 538-75-0View Details
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide CAS 538-75-0View Details
538-75-0 -
 N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide 98% CAS 538-75-0View Details
N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide 98% CAS 538-75-0View Details
538-75-0