Diosmin
Synonym(s):3′,5,7-Trihydroxy-4′-methoxyflavone 7-rutinoside;Barosmin;Buchu resin;Diosmetin 7-O-rhamnosylglucoside;Diosmetin 7-rutinoside
- CAS NO.:520-27-4
- Empirical Formula: C28H32O15
- Molecular Weight: 608.54
- MDL number: MFCD00009772
- EINECS: 208-289-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 08:49:36
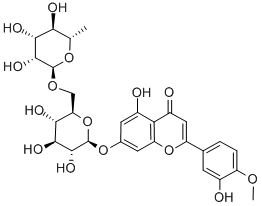
What is Diosmin?
Absorption
Diosmin is rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. After a 900 mg single oral dose in a study using liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method, Cmax was 4.2±3.8 ng·mL-1, Tmax was 18.7±9.9 hours, and AUC0~96 was 185.4±166.2 ng·mL-1 in healthy volunteers. Another pharmacokinetic study of 5 adults revealed a Cmax of 417±94.1 ng/dL.
Toxicity
The LD50 of diosmin is >3g/kg in animal studies, with an LD50 of great than 3000 mg/kg in rats. No cases of overdose have been reported, however, an overdose is likely to result in gastrointestinal effects such as nausea, dyspepsia, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Description
Diosmin was separated from the root of Scrophularia nodosa L. in 1925. The root of Scrophularia nodosa L. has the function of nourishing, reducing fever, relieving internal heat, and detoxicating. It was firstly recorded in the Shen Nong’s Classic of Materia Medica, as a class of middle-grade drug and is currently recorded in the Ch.P 2015, Volume I. The natural resource was abundant in China, mainly provided from Zhejiang, Sichuan, Hubei, Anhui, and Jiangsu provinces. In the clinical practice, Scrophularia nodosa L. was employed to eliminate pathogenic heat from the blood. In the clinical indication, diosmin was mainly applied to treat fever, polydipsia, maculitis, gingivitis, amygdalitis, laryngopharyngitis, acute lymphadenitis, etc. It also has the biological function of antiplatelet aggregation and antitumor. The chemical components include iridoids, phenylpropanoid glycoside, flavonoids, and fatty acids.
Chemical properties
Diosmin is a natural flavonoid mainly present in the peel of some citrus fruits, such as oranges and lemons. Flavonoids are anti-inflammatory plant compounds that protect your body from free radicals and other unstable molecules. The most prevalent uses for Diosmin include hemorrhoids and leg sores caused by poor blood flow. Diosmin was first found in 1925 in the wort plant and has since been used as a natural treatment for hemorrhoids, varicose veins, venous insufficiency, leg ulcers, and other circulatory issues.
Physical properties
Appearance: Grayish yellow or light yellow hygroscopic powder. Solubility: Practically insoluble in water, soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide, practically insoluble in alcohol. It dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides. Melting point: 277–278°C.
Originator
Diosmil,Bellon,France,1971
History
Diosmin was firstly introduced as a medicine in 1969. It was launched in France in
1987 with the product name “Alvenor.” As the protecting agent for blood vessel and
therapeutic agent for chronic venous disease, diosmin has been used for over
30?years in Europe
Diosmin is a typical flavonoid. It could be prepared from natural resources or
semisynthesized from the natural product hesperidin by dehydrogenation reaction.
The Uses of Diosmin
Diosmin is an agonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and exhibits anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory. It is used in the treatment of venous disease, i.e., chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) and hemorrhoidal disease (HD). Diosmin also reduces capillary hyperpermeability and expression of endothelial adhesion molecules (ICAM1, VCAM1). It effectively inhibits the P-glycoprotein (Pgp)-mediated efflux in cells.
What are the applications of Application
Diosmin is a naturally occurring flavonic glycoside isolated from various plants. Diosmin is a capillary protectant and It is used for the improvement of capillary fragility or venous insufficiency, including chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) and hemorrhoids. Diosmin is widely available over-the-counter and demonstrates a favourable a favorable safety profile.
Background
Chronic venous insufficiency is a common condition the western population. Compression and pharmacotherapy are frequently used to manage chronic venous insufficiency, improving circulation and symptoms of venous disease.
Diosmin is a bioflavonoid isolated from various plants or synthesized from hesperidin. It is used for the improvement of capillary fragility or venous insufficiency, including chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) and hemorrhoids. Diosmin is widely available over-the-counter and demonstrates a favourable a favorable safety profile.
Indications
Diosmin is used over-the-counter alone or with ingredients such as hesperidin and diosmetin to support vein and capillary function.
What are the applications of Application
Diosmin is a flavonoid glycoside that reduces venous hyperpressure
Definition
ChEBI: Diosmin is a disaccharide derivative that consists of diosmetin substituted by a 6-O-(alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl moiety at position 7 via a glycosidic linkage. It has a role as an antioxidant and an anti-inflammatory agent. It is a glycosyloxyflavone, a rutinoside, a disaccharide derivative, a monomethoxyflavone and a dihydroxyflavanone. It derives from a diosmetin.
Indications
The clinical indications of diosmin are those symptoms related to venous-lymphatic dysfunction such as leg heaviness, pains, soreness, and swelling in the morning. Besides, the symptoms related to acute hemorrhoids could also be treated with diosmin.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 72 g hesperidin, 288 ml acetic anhydride and 300 ml glacial
acetic acid were boiled in reflux with 15 ml pyridine as the catalyst for 144
hours until during the control of the reaction the band disappeared at a wave
length between 264 to 280 nm, and a new maximum appeared at 330 nm.
Thereafter in a rotation evaporator the reaction mixture was concentrated by
evaporation under vacuum conditions.
The residue was absorbed in 1,200 ml ethyl acetate, admixed with 20 ml ethanol and boiled for one hour under reflux action. The solution was filtered
and compressed to dryness. The residue was dried in a vacuum drying
cabinet. The yield amounted to 107.5 g.
35.8 g thereof were then dissolved in 280 ml glacial acetic acid and
ominated with a solution of 6.05 g
omine in 30 ml glacial acetic acid.
Thereafter the mixture compressed to dryness by means of the rotation
evaporator, there being obtained a residue of 41.8 g. Such was dissolved in
150 ml methanol, admixed with a solution of 36 g sodium hydroxide in 180 ml
water and stirred for one hour at 50°C.
The diosmin was precipitated out by adding 120 ml glacial acetic acid and
stirring at 70°C for 30 minutes. The precipitate was filtrated in a suction filter
or strainer, washed with methanol, water and again methanol and dried at
60°C in the drying cabinet. Raw yield: 17.0 g corresponding to 71% yield.
omine content 0.51%.
10 g of the thus-obtained diosmin was dissolved in a solution of 24 g sodium
hydroxide in 120 ml water, admixed with 100 ml methanol and 100 ml
pyridine and stirred for one hour at 50°C. The diosmin was precipitated by the
addition of 100 ml glacial acetic acid and stirred for 30 minutes at 70°C,
filtered and washed with methanol and water and again methanol.
After drying at 60°C there was obtained a pure yield of 9.2 g diosmin (65%
based upon the employed hesperidin) having a
omine content of 0.07%.
Therapeutic Function
Bioflavonoid
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Pharmacokinetics
Diosmin is a venoactive drug supporting circulatory health through various actions on blood vessels; it supports lymphatic drainage and improves microcirculation while increasing venous tone and elasticity. For these reasons, diosmin is frequently taken by individuals with chronic venous disease to support vascular health and has been demonstrated to improve quality of life. In addition to the above effects, diosmin exerts antioxidant activity and scavenges oxygen free radicals, reducing levels of oxidative stress normally detected through biomarkers such as prostaglandins isoprostane precursors.
In one clinical study, mean content of TNF alpha, VEGF-C, VEGF-A IL-6, in addition to FGF2 were decreased by after the therapy with diosmin; findings were statistically significant. Additionally, a decrease in edema and mean leg circumference of patients taking diosmin for three months was observed in a clinical study. Diosmin has been demonstrated to enhance the metabolism of glucose in diabetic disorders.
Pharmacology
Diosmin is a micronized, purified, flavonoid-structure drug. It is helpful for lymphatic return and stimulating microcirculation, treating hemorrhoids and venous
dysfunction by increasing the venous tension.
1. Increasing the venous tension. Diosmin could strengthen the tensile force of the
venous wall even under high temperature. Diosmin’s action in venous constriction is stronger than other drugs like rutin. Even under the acidic toxicity in the
body, it could still raise the venous tension. Diosmin has special affinity to the
venous other than the arterial system.
2. Improving the microcirculation. Diosmin could effectively reduce adhesion and
migration of leukocyte and vascular endothelial cells. It could also release
inflammatory substances such as histamine, bradykinin, alexin, leukotriene,
prostaglandin, and surplus free radicals. Hence, the penetration of capillary
blood vessel was reduced, and the tension was enhanced. Besides, diosmin could
decrease blood viscosity, accelerate erythrocyte flow rate, and finally reduce the
chances of microcirculatory stasis
3. Stimulating the lymphatic return. Diosmin could effectively increase the speed
of lymphatic drainage and the lymphatic contraction, accelerating the circumfluence of interstitial fluid, improving lymphatic return, and relieving edema.
Clinical Use
Diosmin was mainly used to treat diseases like chronic venous dysfunction, haemorrhoids, lymphedema, phlebeurysm, etc.
Side Effects
Diosmin can cause some side effects such as nausea, stomach pain, diarrhea, insomnia, dizziness, headache, drowsiness, skin redness and hives, muscle pain, blood problems, and altered heart rate.
There may be a few of minor gastrointestinal reactions and adverse reactions such as plant nerve function disorder, but generally mild and don't have to stop the drug.
Pregnant women and nursing mothers with hemorrhoids are safe to use this product.
Metabolism
Degradation products of diosmin such as alkyl-phenolic acids confirm a metabolic pattern similar to that of other flavonoids.
Mode of action
1. Enhance the vein tension, even not exceptional under high temperature condition. It has a stronger effect causing the constriction of vein than other drugs such as rutin, still can enhance the tension of the vein when the body was acidosis. Diosmin has specific affinity for vein without affecting the arterial system.
2. Improve microcirculation. Diosmin can obviously reduce the white blood cells and vascular endothelial cell adhesion, migration, disintegrating the release of inflammatory substances, such as histamine, slow excitation peptide, complement, leukotriene, prostaglandins, and too many free radicals, reducing the permeability of capillaries and enhance its tension. Diosmin can lower blood viscosity, enhance the function of red blood cell velocity, thus reduce the microcirculation clogged.
3. Promote lymphatic circumfluence. Diosmin can increase the speed of lymphatic drainage.
Properties of Diosmin
| Melting point: | 277-278°C |
| Boiling point: | 926.8±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.68±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 20℃ |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide, practically insoluble in alcohol. It dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides. |
| form | neat |
| pka | 6.10±0.40(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Pale Beige to Brown |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (50 mg/ml), water (122 mg/ml at 25°C), and ethanol (<1 mg/ml at 25°C). |
| λmax | 345nm(EtOH)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,3297 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 520-27-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Diosmin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Diosmin
| InChIKey | GZSOSUNBTXMUFQ-YFAPSIMESA-N |
Diosmin manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 520-27-4 Diosmin 98%View Details
520-27-4 Diosmin 98%View Details
520-27-4 -
 520-27-4 Diosmin 98%View Details
520-27-4 Diosmin 98%View Details
520-27-4 -
 Diosmin 99%View Details
Diosmin 99%View Details -
 Diosmin, 90% CAS 520-27-4View Details
Diosmin, 90% CAS 520-27-4View Details
520-27-4 -
 Diosmin CAS 520-27-4View Details
Diosmin CAS 520-27-4View Details
520-27-4 -
 Diosmin 98% (HPLC) CAS 520-27-4View Details
Diosmin 98% (HPLC) CAS 520-27-4View Details
520-27-4 -
 Diosmin 95.00% CAS 520-27-4View Details
Diosmin 95.00% CAS 520-27-4View Details
520-27-4 -
 Diosmin >98% (HPLC) CAS 520-27-4View Details
Diosmin >98% (HPLC) CAS 520-27-4View Details
520-27-4
