DEUTERIUM OXIDE
Synonym(s):Deuterated water;Deuterium oxide;Heavy water;Water-d2
- CAS NO.:7789-20-0
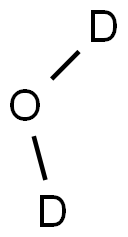
- Empirical Formula: D2O
- Molecular Weight: 20.03
- MDL number: MFCD00044636
- EINECS: 232-148-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-03 09:04:23
What is DEUTERIUM OXIDE?
Description
Deuterium oxide (D2O), aka “heavy water”, is the form of water that contains two atoms of the 2H, or D, isotope. The term heavy water is also used for water in which 2H atoms replace only some of the 1H atoms. In this case, rapid exchange between the two isotopes forms twice as many “semiheavy” HDO molecules as D2O.
Harold Urey, the 1934 Nobel Prize laureate in chemistry, pioneered deuterium chemistry. In 1931, he and his colleagues at Columbia University (New York City) carefully distilled 5 L of liquid nitrogen to produce 1 mL of molecular deuterium. Shortly afterward, they produced D2O from ordinary water by using prolonged electrolysis.
For decades, D2O has been extremely useful in many chemical applications. The difference between a reaction rate in D2O solvent versus that in H2O often provides clues as to the reaction’s mechanism. This is especially important if water is one of the reactants.
In some nuclear reactors, D2O is used to slow down neutrons so that they react with fissionable 235U rather than nonfissioning 238U, thus eliminating the need for uranium enrichment. D2O is superior to H2O for this use because of its ≈6 times greater thermal neutron capture cross section.
The Uses of DEUTERIUM OXIDE
Deuterium oxide is used in nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR). It is also useful in the identification of labile hydrogens. As a source of deuterium, it is utilized for preparing specifically labeled isotopologs of organic compounds. It is often used as a substitute for water in the analysis of proteins in solution by using fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). It finds application in certain types of nuclear reactors and in tritium production.
General Description
Deuterium oxide (D2O) is a 100% isotopically enriched NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) solvent. It is widely employed in high resolution NMR studies. Various thermodynamic properties (such as intermolecular vibrational frequencies, energy of the hydrogen bond, free energy, enthalpy and entropy) of liquid deuterium oxide have been evaluated. Ionization constant for D2O (in the range of 5-50°C), pK values (at 25°C) and enthalpy, entropy, heat capacity change (for the dissociation of D2O) have been reported.
Production
As obtained from most natural sources, ordinary water contains about one deuterium atom for every 6,760 ordinary hydrogen atoms. Continued electrolysis of hundreds of liters of water until only a few milliliters remain yields practically pure deuterium oxide. This operation, until 1943 the only large-scale method used, has been superseded by less expensive processes, such as the Girdler sulfide process (deuterium is exchanged between hydrogen sulfide [H2S] and water) and fractional distillation (D2O becomes concentrated in the liquid residue because it is less volatile than H2O).
Applications
The deuterium oxide (heavy water) can be used as a moderator of neutrons in nuclear power plants. In the laboratory heavy water is employed as an isotopic tracer in studies of chemical and biochemical processes.
Properties of DEUTERIUM OXIDE
| Melting point: | 3.8 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 101.4 °C |
| Density | 1.107 g/mL at 25 °C |
| vapor pressure | 27.464hPa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 101.4°C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | miscible |
| appearance | colorless liquid |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | pK (25°) 14.955 (molarity scale); 16.653 (mole fraction scale): A. K. Covington et al., J. Phys. Chem. 70, 3820 (1966) |
| color | Colorless |
| Relative polarity | 0.991 |
| PH | 7 (H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | Miscible with water. |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,2940 |
| Dielectric constant | 78.3(25℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Hygroscopic. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7789-20-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Water-d2 (7789-20-0) |
Safety information for DEUTERIUM OXIDE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for DEUTERIUM OXIDE
| InChIKey | XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-ZSJDYOACSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Deuterium Oxide 99.8atom%D CAS 7789-20-0View Details
Deuterium Oxide 99.8atom%D CAS 7789-20-0View Details
7789-20-0 -
 Deuterium oxide, 99.8% CAS 7789-20-0View Details
Deuterium oxide, 99.8% CAS 7789-20-0View Details
7789-20-0 -
 Deuterium oxide-D 99.9% CAS 7789-20-0View Details
Deuterium oxide-D 99.9% CAS 7789-20-0View Details
7789-20-0 -
 Deuterium oxide CAS 7789-20-0View Details
Deuterium oxide CAS 7789-20-0View Details
7789-20-0 -
 Deuterium oxide CAS 7789-20-0View Details
Deuterium oxide CAS 7789-20-0View Details
7789-20-0 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
