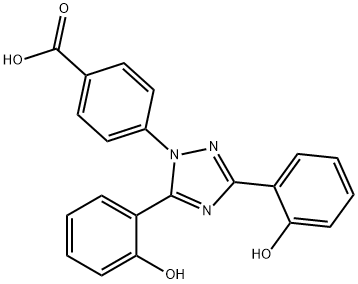
Deferasirox
- CAS NO.:201530-41-8
- Empirical Formula: C21H15N3O4
- Molecular Weight: 373.36
- MDL number: MFCD09951804
- EINECS: 685-491-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 13:58:55
What is Deferasirox?
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability (AUC) of deferasirox tablets for oral suspension is 70% compared to an intravenous dose.
Description
Linagliptin was originally discovered at Boehringer Ingelheim as an orally active dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-4) inhibitor. Eli Lilly and Boehringer Ingelheim co-developed and launched linagliptin for type II diabetes as an adjunct to diet and exercise for the improvement of adult glycemic control. Linagliptin has a superior DPP-4 IC50 value of 1 nM, compared with 19 nM for sitagliptin, 24 nM for alogliptin, 50 nM for saxagliptin and 62 nM for vildagliptin. In addition, linagliptin exhibited prolonged pharmacodynamic activity with long-lasting DPP-4 inhibition in several preclinical species. Linagliptin showed good efficacy in phase II clinical trials with doses as low as 5 mg and no signs of hypoglycemia with doses as high as 600 mg. The prolonged pharmacological effect of DPP-4 activity and the good safety/tolerability profile provided the basis for linagliptin’s approval.
Chemical properties
White to Off-White Solid
Originator
Novartis (Switzerland)
The Uses of Deferasirox
Deferasirox is an orally active tridentate iron chelator with a very high binding affinity for iron. It is primarily used to reduce chronic iron overload in patients undergoing long-term blood transfusions. It can also be used as an internal standard for the quantification of Deferasirox by gas chromatography or liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.
What are the applications of Application
Deferasirox is a tridentate chelator that binds iron with high affinity, while having low affinity for zinc and copper.
Background
Deferasirox is an iron chelator and the first oral medication FDA approved for chronic iron overload in patients receiving long term blood transfusions.
Indications
For the treatment of chronic iron overload due to blood transfusions (transfusional hemosiderosis) in patients 2 years of age and older.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of triazoles, deferasirox is 1,2,4-triazole substituted by a 4-carboxyphenyl group at position 1 and by 2-hydroxyphenyl groups at positions 3 and 5. An orally active iron chelator, it is used to manage chronic iron overload in patient receiving long-term blood transfusions.
brand name
Exjade (Novartis).
Pharmacokinetics
Deferasirox is an orally active chelator that is selective for iron (as Fe3+). It is a tridentate ligand that binds iron with high affinity in a 2:1 ratio. Although deferasirox has very low affinity for zinc and copper there are variable decreases in the serum concentration of these trace metals after the administration of deferasirox. The clinical significance of these decreases is uncertain.
Clinical Use
Treatment of iron overload
Synthesis
Synthesis of deferasirox started with cyclization of salicylamide (26) with salicyloyl chloride (27) by heating at 170 C without any solvents to give 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-benz[e]oxazin-4-one (28) in 55% yield. Compound 28 was reacted with 4-hydrazinobenzoic acid (29) in refluxing ethanol for 2 hours to give deferasirox V as colorless crystals.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Aluminium-containing antacids: avoid concomitant
use.
Aminophylline and theophylline: concentration of
aminophylline and theophylline increased, consider
reducing aminophylline and theophylline dose.
Other nephrotoxic agents: avoid concomitant
therapy
Metabolism
Metabolism of deferasirox is mainly glucuronidation by uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes. Cytochrome P450 isoenzyme-mediated metabolism appears to be minor. Deconjugation of the glucuronidates in the intestine and subsequent enterohepatic recycling are likely to occur. It is excreted mainly in the faeces via bile, as metabolites and as unchanged drug. About 8% of a dose is excreted in the urine.
Metabolism
Hepatic. CYP450-catalyzed (oxidative) metabolism of deferasirox appears to be minor in humans (about 8%). Glucuronidation is the main metabolic pathway for deferasirox, with subsequent biliary excretion.
Side Effects
Common side effects of Deferasirox include: diarrhoea, dizziness, earache or ear pain, nausea, stomach pain, voice changes and vomiting. A very small percentage of patients experience blindness, vision or hearing changes, and eye pain or discomfort. Other possible side effects include: black tarry stools, bleeding gums, blood in the urine or faeces, dark urine, decreased urine output, feeling tired or weak all over the body, hives, abrasions, rashes, swelling of the face/eyelids/lips/tongue/throat/hands/legs/feet or genitals, pain in the lower back or flanks, pale skin, reddening of the skin, soreness, itching, ulcers, blisters, stomach pain that persists abnormally Bleeding or bruising, unusual drowsiness, sluggishness, tiredness, vomiting blood or material that looks like coffee grounds, yellowing of the eyes or skin.
References
Heinz et al. (1999), 4-[3,5-Bis(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]-benzoic acid: A Novel Efficient and Selective Iron(III) Complexing Agent; Ang. Chem. Int. Ed., 38 2568 Palumbo et al. (2021), From Biology to Clinical Practice: Iron Chelation Therapy With Deferasirox; Front. Oncol., 11 752192 Roatsch et al. (2019), The Clinically Used Iron Chelator Deferasirox Is an Inhibitor of Epigenetic JumonjiC Domain-Containing Histone Demethylases; ACS Chem. Biol., 14 1737 Lui et al. (2015), Targeting cancer by binding iron: Dissecting cellular signaling pathways; Oncotarget, 6 18748 Ibrahim and O’Sullivan (2020), Iron chelators in cancer therapy; Biometals, 33 201 Szymonik et al. (2021), The Impact of Iron Chelators on the Biology of Cancer Stem Cells; Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23 89
Properties of Deferasirox
| Melting point: | 260-2620C |
| Boiling point: | 672.1±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.40±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (10 mg/ml) |
| form | solid |
| pka | pKa1 4.57, pKa2 8.71, pKa3 10.56 (Nick); Also reported in H2O/DMSO (CDMSO = 0.20) as pKa1 4.61, pKa2 10.12, pKa3 12.08 (Steinhauser) |
| color | Off-white to white |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20°C for up to 1 month. |
Safety information for Deferasirox
Computed Descriptors for Deferasirox
Deferasirox manufacturer
KP INNOVATIVE
SRINI PHARMACEUTICALS PVT LTD
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Deferasirox 99%View Details
Deferasirox 99%View Details -
 Deferasirox 99%View Details
Deferasirox 99%View Details -
 Deferasirox 98%View Details
Deferasirox 98%View Details -
 Deferasirox 99%View Details
Deferasirox 99%View Details -
 Deferasirox 98%View Details
Deferasirox 98%View Details -
 Deferasirox USP API MANUFACTURER INDIAView Details
Deferasirox USP API MANUFACTURER INDIAView Details
201530-41-8 -
 Deferasirox Powder, 25 kgView Details
Deferasirox Powder, 25 kgView Details
201530-41-8 -
 Deferasirox APIView Details
Deferasirox APIView Details
201530-41-8
