DAURICINE
- CAS NO.:524-17-4
- Empirical Formula: C38H44N2O6
- Molecular Weight: 624.77
- MDL number: MFCD26960929
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-25 12:42:02
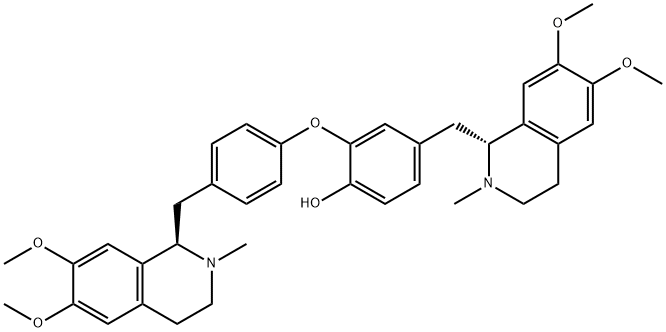
What is DAURICINE?
Description
Dauricine is a kind of phenolic aromatic compound which is isolated from
Menispermaceae plants such as Asian Menispermum dauricum or Canadian
Menispermum dauricum and can be classified as isoquinoline alkaloids.
Rhizoma Menispermi is the dry rhizome of Menispermaceae plant Menispermum
dauricum. Menispermum dauricum mainly distributes in the northern part of East
Asia and is mainly distributed in the north, east and northeast regions of China. The
usage of Rhizoma Menispermi as a kind of traditional Chinese medicine was firstly
recorded in Kaibao Herbs with its function of detoxifying many drugs, relieving
pains, reducing swelling and sore, curing fever and cough, and killing parasites.
According to the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, Rhizoma Menispermi in the north of
China is different from the herbs used in the south of China known as the same
name. Based on the traditional Chinese Medicine theory, Rhizoma Menispermi has
the feature of bitterness and coldness, with the meridian tropism in the lung, stomach,
and intestine. The main effects of Rhizoma Menispermi are heat-clearing,
detoxicating, wind-dispelling and pain-relieving according to its vital function lies
in the therapy of swollen sore throat, enteritis diarrhea and rheumatic arthralgia.
Alkaloid is the main chemical component of Rhizoma Menispermi, and besides
dauricine, there are also other kinds of alkaloids such as dauriciline,
O-methyldauricine, and daurisoline in it.
Physical properties
Appearance: yellowish-white powder or crystal. Solubility: soluble in ethanol, methanol, chloroform, acetone, benzene and slightly soluble in ether. Density: 1.185 g/cm3. Melting point: 115 °C. Boiling point: 712.3 °C at 760 mmHg atmospheric pressure. Specific optical rotation: MeOH-139.
History
Menispermum dauricum has been long used as a traditional Chinese medicine, but
the research of its effective components has been slow. Dauricine was firstly separated
and structure-confirmed by Fukuda Mayo using alumina column chromatography
separation assay in 1964. At the same year, dauricine was first synthesized
by two Japanese scientists, Tetsuji Tamayama and Rtani Rikazu, by means of Arndt-Eistert
reaction and Bischler-Napieralski reaction. Thereafter, lots of scientists
from various countries successively separated daurinoline, Menispermum Xinlin
alkali, Menispermum succinylcholine alkali, chelilanthifoline, stepholidine, and
many other monomeric components of Menispermum dauricum.
The study of dauricine in China started from the Cultural Revolution Period.
Under the guidance of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine, a large
number of effective components in traditional Chinese herbs were extracted, separated
and applied to clinic. Dauricine was firstly reported on the mainland as an
active ingredient in herbs which can clear away heat and toxic materials. Moreover,
dauricine was also used as an antineoplastic and muscle relaxant. There were many
medicines whose principal component was dauricine had been under clinical
research for its role of cardiovascular protection since the 1980s, most of these
medicines were stagnating in phase II clinical trials.
The Uses of DAURICINE
Dauricine is a bisbenzylisoquinoline allkaloid derivative that displays a noted number of pharmaceutical properties. It is known to induces severe lung toxicity in animals.
Definition
ChEBI: A bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid resulting from the formal oxidative dimerisation of 4-{[(1R)-6,7-dimethoxy-2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-1-yl]methyl}phenol by attachment of the phenolic oxygen of one molecule to the benzene ring f the second (ortho to the phenolic hydroxy group of the latter).
Indications
Drugs whose main component is dauricine are still in clinical trials. Several formulations of dauricine have currently been developed, including tablets, capsules, injections, and so on. The main indications of dauricine in clinical trials are antiplatelet,antihypertensive and anti-arrhythmic.
Pharmacology
The main pharmacological actions of dauricine are as follows;
Anti-arrhythmia: Dauricine can slow the heart rate and prolong conduction time in
sinus rhythm, therefore reducing the incidence of arrhythmia.
Anti-myocardial ischemia: Dauricine has protective effect on myocardial ischemia
and can improve hemodynamic disturbances during ischemia which is supposed
to produce effect via mechanism of improving myocardial metabolism and
anti-oxidation.
Anti-cerebral ischemia: Dauricine has an effective regulation on gene expression of
Bcl-2 and Bax in cortical neurons after the ischemic brain injury, protecting
against cerebral ischemia.
Anti-cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury: Dauricine can inhibit apoptosis induced
by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by upregulating Bcl-2 expression and
downregulating Bax expression. Also dauricine has the effect of anti-oxidation.
Antitumor activity: Dauricine can affect TGF-beta signaling pathway via upregulating
gene expression of DPC4, and then the gene expression of P53 and P16 in
tumor tissue, and finally reduce the gene expression of hFGF in tumor tissue.
Thereby, the growth of various tumor cells could be inhibited.
The investigations of metabolism in vivo of dauricine indicate that it is rapidly
and widely distributed in body and the drug concentration in organs is significantly
higher than that in plasma, and this is possibly related to its strong lipid solubility
and easy access to cells.
Clinical Use
No medicine in the market takes dauricine as the main component up till now. Many animal experiments and clinical studies suggest that dauricine can reverse the effect of MDR as verapamil. Since the clinical application of the classical drug verapamil is limited for the serious toxic side effects, the moderate pharmacological effect of dauricine has a vital clinical significance. The main side effect of dauricine by oral absorption is gastrointestinal reaction, such as diarrhea, nausea, abdominal distension, and so on. In addition, dauricine can accumulate in the body, leading to hepatorenal toxicity and central nervous system toxicity.
Properties of DAURICINE
| Melting point: | 115° |
| Boiling point: | 712.3±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D11 -139° in methanol |
| Density | 1.185±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 9.31±0.45(Predicted) |
| color | Pale Beige |
| Water Solubility | slightly soluble in water |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 524-17-4 |
Safety information for DAURICINE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P330:Rinse mouth. P362:Take off contaminated clothing and wash before reuse. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P403+P233:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for DAURICINE
| InChIKey | AQASRZOCERRGBL-ROJLCIKYSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(O)=CC=C(C[C@@H]2C3=C(C=C(OC)C(OC)=C3)CCN2C)C=C1OC1=CC=C(C[C@@H]2C3=C(C=C(OC)C(OC)=C3)CCN2C)C=C1 |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Dauricine CAS 524-17-4View Details
Dauricine CAS 524-17-4View Details
524-17-4 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
