D-Serine
Synonym(s):β-Hydroxyalanine;(R)-2-Amino-3-hydroxypropionic acid;Ser
- CAS NO.:312-84-5
- Empirical Formula: C3H7NO3
- Molecular Weight: 105.09
- MDL number: MFCD00004269
- EINECS: 206-229-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
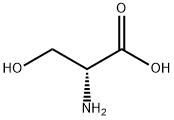
What is D-Serine?
Description
Serine is one of the 20 naturally-occurring amino acids used by all organisms in the biosynthesis of proteins. Having a single chiral center, serine can exist as one of two stereoisomers (L-Serine and D-Serine).
D-serine is categorized as a nootropic. It is an amino acid found in the brain and is produced primarily in astrocytes; the conversion of L-serine to D-serine is catalyzed by the serine racemase enzyme. D-serine acts as a co-agonist of glutamate NMDA receptors and binds at the glycine site. NMDA receptors mediate synaptic plasticity, synaptogenesis, excitotoxicity, memory acquisition, and learning. Schizophrenia is characterized by reduced NMDA receptor signaling and therefore, D-serine supplementation has been tested extensively in patients with schizophrenia. It is thought to improve cognitive symptoms in this population. It is worth noting that in Alzheimer’s disease, there is excess glutamate receptor activation. Memantine, one of the drugs used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, is an NMDA receptor antagonist.
Chemical properties
D-serine is a off-white crystalline powder with a faint musty odor.It is an amino acid found in the brain. Derived from Glycine, d-serine is a neuromodulator, meaning it regulates the activities of neurons.
D-Serine supplementation can reduce symptoms of cognitive decline. It is also able to reduce symptoms of diseases characterized by reduced N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) signaling, which includes cocaine dependence and schizophrenia.
The Uses of D-Serine
D-Serine is involved in the biosynthesis of purines, pyrimidines, and other amino acids. D-Serine also is an agonist of glycine site of the NMDA-type glutamate receptor. It also acts as Lacosamide intermediate.
The Uses of D-Serine
A proteinogenic amino acids involved in the biosynthesis of purines and pyrimidines. Inhibitor of serine palmitoyltransferase. A neuromodulator.
The Uses of D-Serine
D-serine has been used as a substrate in D-amino acid oxidase (DAO) activity in human 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. It has also been used in intracerebroventricular administration in rat for the induction of antinociceptive effect.
Background
A non-essential amino acid occurring in natural form as the L-isomer. It is synthesized from GLYCINE or THREONINE. It is involved in the biosynthesis of PURINES; PYRIMIDINES; and other amino acids. [PubChem]
What are the applications of Application
D-Serine is a non-essential amino acid involved in the biosynthesis of amino acids
Definition
D-serine is the R-enantiomer of serine. It has a role as a NMDA receptor agonist, a human metabolite and an Escherichia coli metabolite. It is a D-alpha-amino acid and a serine. It is a conjugate base of a D-serinium. It is a conjugate acid of a D-serinate. It is an enantiomer of a L-serine. It is a tautomer of a D-serine zwitterion.
What are the applications of Application
D-serine has been used as a substrate in D-amino acid oxidase (DAO) activity in human 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. It has also been used in intracerebroventricular administration in rat for the induction of antinociceptive effect.
D-serine has been used to prevent glycine-dependent desensitization of N-methyl D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) and to study its effects on NMDARs to correct behavioral abnormalities in rats after partial sciatic nerve ligation (PSNL).
General Description
D-serine is an unusual amino acid expressed in the mammalian brain.
Biological Activity
D-serine is an agonist and glycine mimic which is active at the strychnine-insensitive glycine binding site associated with the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor as well as the inhibitory post-synaptic glycine receptor. Along with glutamate, it has a role in various physiological processes including synaptic plasticity and receptor transmission. Dysregulation of D-serine signaling has been linked with neurodegenerative diseases and disorders.
D-serine is essential for the normal development of dendrites, neuroblast migration and may have therapeutic potential for treating schizophrenia and depression states. The levels of D-serine is elevated in traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Biochem/physiol Actions
D-serine is an agonist and glycine mimic which is active at the strychnine-insensitive glycine binding site associated with the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor as well as the inhibitory post-synaptic glycine receptor. Along with glutamate, it has a role in various physiological processes including synaptic plasticity and receptor transmission. Dysregulation of D-serine signaling has been linked with neurodegenerative diseases and disorders.
Metabolism
Not Available
storage
Room temperature
Properties of D-Serine
| Melting point: | 220 °C |
| Boiling point: | 197.09°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | -14.75 º (c=10 2 N HCl) |
| Density | 1.3895 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4368 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 g/mL, clear, colorless |
| pka | 2.16±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | 346 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,8460 |
| BRN | 1721403 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 312-84-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | D-Serine (312-84-5) |
Safety information for D-Serine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for D-Serine
| InChIKey | MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-UWTATZPHSA-N |
D-Serine manufacturer
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 312-84-5 99%View Details
312-84-5 99%View Details
312-84-5 -
 D-Serine extrapure CAS 312-84-5View Details
D-Serine extrapure CAS 312-84-5View Details
312-84-5 -
 D-Serine CAS 312-84-5View Details
D-Serine CAS 312-84-5View Details
312-84-5 -
 D-Serine CAS 312-84-5View Details
D-Serine CAS 312-84-5View Details
312-84-5 -
 D-Serine CAS 312-84-5View Details
D-Serine CAS 312-84-5View Details
312-84-5 -
 D-Serine CAS 312-84-5View Details
D-Serine CAS 312-84-5View Details
312-84-5 -
 D-Serine 95% CAS 312-84-5View Details
D-Serine 95% CAS 312-84-5View Details
312-84-5 -
 D-Serine CAS 312-84-5View Details
D-Serine CAS 312-84-5View Details
312-84-5
