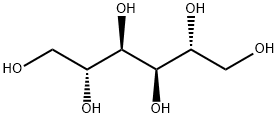
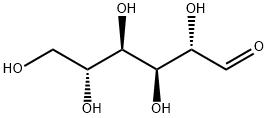
D-Mannitol
Synonym(s):D -Mannitol;Mannite;Mannitolum;Parteck Mannitol
- CAS NO.:69-65-8
- Empirical Formula: C6H14O6
- Molecular Weight: 182.17
- MDL number: MFCD00064287
- EINECS: 200-711-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
What is D-Mannitol ?
Absorption
Approximately 7% of ingested mannitol is absorbed during gastrointestinal perfusion in uremic patients.
Inhalation of 635 mg of mannitol powder yields a plasma Cmax of 13.71 μg/mL in 1.5 hours (Tmax) and a mean systemic AUC of 73.15 μg*h/mL.
Toxicity
Mannitol overdose may result in bronchoconstriction and should be counteracted using a short-acting bronchodilator and other symptomatic and supportive care, as necessary.
Description
A white, crystalline solid consisting of D-mannitol and a small quantity of sorbitol. It is odorless and has a sweet taste. It is soluble in water, very slightly soluble in alcohol, and practically insoluble in most other common organic solvents. It is prepared commercially by catalytic reduction of glucose. Mannitol occurs in small amounts in a variety of foods such as olives, beets, and celery, and in the exudate of certain trees.
Description
D-Mannitol [(2R,3R,4R,5R)-hexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol] is a reduced sugar found in plants ranging from flowering ash (the biblical “manna”, from which it gets its name) to seaweed. It can be prepared by the electrolytic reduction of glucose. It is an unusual sugar alcohol because it is slightly acidic in aqueous solution. It has several medicinal uses, including the controversial practice of reducing intracranial pressure following head trauma.
Chemical properties
Mannitol is D-mannitol. It is a hexahydric alcohol related to
mannose and is isomeric with sorbitol.
Mannitol occurs as a white, odorless, crystalline powder, or freeflowing
granules. It has a sweet taste, approximately as sweet as
glucose and half as sweet as sucrose, and imparts a cooling
sensation in the mouth. Microscopically, it appears as orthorhombic
needles when crystallized from alcohol. Mannitol shows
polymorphism.
Originator
Mannitol,MSD,US,1946
The Uses of D-Mannitol
Labelled D-Mannitol (M165000). D-Mannitol is widespread in plants and plant exudates; obtained from manna and seaweeds. D-Mannitol is used in the food industry as anticaking and free-flow agent, flavo ring agent, lubricant and release agent, stabilizer and thickener and nutritive sweetener.
The Uses of D-Mannitol
Used in titrimetric determination of boric acid. inhibitor of norepinephrine and seritonin uptake, treatment of fibromyalgia.
The Uses of D-Mannitol
Used with boric acid in the manufacture of dry electrolytic condensers for radio applications; in making artificial resins and plasticizers; in pharmacy as excipient and diluent for solids and liqs; in analytical chemistry for boron determinations; in the manufacture of mannitol hexanitrate. Used in the food industry as anticaking and free-flow agent, flavoring agent, lubricant and release agent, stabilizer and thickener and nutritive sweetener.
What are the applications of Application
D(?)Mannitol is a sugar alcohol that can be used as an inert osmotic control substance
Background
Mannitol is an osmotic diuretic that is metabolically inert in humans and occurs naturally, as a sugar or sugar alcohol, in fruits and vegetables. Mannitol elevates blood plasma osmolality, resulting in enhanced flow of water from tissues, including the brain and cerebrospinal fluid, into interstitial fluid and plasma. As a result, cerebral edema, elevated intracranial pressure, and cerebrospinal fluid volume and pressure may be reduced. Mannitol may also be used for the promotion of diuresis before irreversible renal failure becomes established; the promotion of urinary excretion of toxic substances; as an Antiglaucoma agent; and as a renal function diagnostic aid.
On October 30, 2020, mannitol was approved by the FDA as add-on maintenance therapy for the control of pulmonary symptoms associated with cystic fibrosis in adult patients and is currently marketed for this indication under the name BRONCHITOL? by Chiesi USA Inc.
Indications
Used for the promotion of diuresis before irreversible renal failure becomes established, the reduction of intracranial pressure, the treatment of cerebral edema, and the promotion of urinary excretion of toxic substances.
Mannitol is also indicated as add-on maintenance therapy for improving pulmonary function in cystic fibrosis patients aged 18 and over who have passed the BRONCHITOL tolerance test (BTT). It is recommended that patients take an orally inhaled short-acting bronchodilator 5-15 minutes prior to every inhaled mannitol dose.
Definition
ChEBI: D-mannitol is the D-enantiomer of mannitol. It has a role as an osmotic diuretic, a sweetening agent, an antiglaucoma drug, a metabolite, an allergen, a hapten, a food bulking agent, a food anticaking agent, a food humectant, a food stabiliser, a food thickening agent, an Escherichia coli metabolite and a member of compatible osmolytes.
Production Methods
Mannitol may be extracted from the dried sap of manna and other natural sources by means of hot alcohol or other selective solvents. It is commercially produced by the catalytic or electrolytic reduction of monosaccharides such as mannose and glucose.
Manufacturing Process
250 g of glucose is dissolved in distilled water to give a solution of 48% concentration. This solution is heated to 65°C and barium hydroxide added in quantity sufficient to make the concentration of the barium hydroxide 0.2 mol/liter. The solution is agitated and maintained at 65°C for 6 hours after the addition of the barium hydroxide. It is then cooled and neutralized to a pH of 6.8 with sulfuric acid. The precipitated barium sulfate is filtered out. A quantity of activated supported nickel catalyst containing 5 g of nickel is added.
The slurry is introduced into a 3-liter rocking autoclave, and hydrogen
admitted to a pressure of 1,500 psi. The autoclave is heated to a temperature
of 150°C in one hour and held at this temperature for 2.5 hours more.
Pressure rises to about 1,800 psi and then declines to about 1,600 during the
hydrogenation. The autoclave is then cooled, emptied, and the catalyst filtered
from the product. The filtrate is then concentrated under vacuum on a hot
water bath to remove a part of the water.
The concentrate is taken up in warm aqueous methanol so adjusted that the
composition of the solvent is 90% methanol/10% water, and the weight of the
solvent is 3 times the weight of the solids in the concentrate. This solution is
cooled to 20°C and held overnight. The mannitol which crystallizes is filtered
out. The filtrate is concentrated on a water bath under vacuum to remove
methanol and adjusted to a water percentage of 16%. The resulting syrup is
viscous, noncrystallizing and nongelling, and analysis shows a PN (Pyridine
Number) of 32 and essentially no reducing sugar, according to US Patent
2,749,371.
brand name
Osmitrol (Baxter Healthcare); Resectisol (B Braun).
Therapeutic Function
Diuretic, Diagnostic aid (kidney function)
General Description
Odorless white crystalline powder or free-flowing granules. Sweet taste.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
A sugar alcohol. More closely related to carbohydrates than to other polyhydric alcohols [Noller]. Flammable and/or toxic gases are generated by the combination with alkali metals, nitrides, strong reducing agents and strong oxidizing agents.
Hazard
Mildly toxic; mutagen.
Fire Hazard
D-Mannitol is probably combustible.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Mannitol is widely used in pharmaceutical formulations and food
products. In pharmaceutical preparations it is primarily used as a
diluent (10–90% w/w) in tablet formulations, where it is of
particular value since it is not hygroscopic and may thus be used
with moisture-sensitive active ingredients.
Mannitol may be used in direct-compression tablet applications,for which the granular and spray-dried forms are
available, or in wet granulations.Granulations containing
mannitol have the advantage of being dried easily. Specific tablet
applications include antacid preparations, glyceryl trinitrate tablets,
and vitamin preparations. Mannitol is commonly used as an
excipient in the manufacture of chewable tablet formulations
because of its negative heat of solution, sweetness, and ‘mouth
feel’.
In lyophilized preparations, mannitol (20–90% w/w) has been
included as a carrier to produce a stiff, homogeneous cake that
improves the appearance of the lyophilized plug in a vial.A
pyrogen-free form is available specifically for this use.
Mannitol has also been used to prevent thickening in aqueous
antacid suspensions of aluminum hydroxide (<7% w/v). It has been
suggested as a plasticizer in soft-gelatin capsules, as a component of
sustained-release tablet formulations,and as a carrier in dry
powder inhalers.It is also used as a diluent in rapidly
dispersing oral dosage forms.It is used in food applications as
a bulking agent.
Therapeutically, mannitol administered parenterally is used as
an osmotic diuretic, as a diagnostic agent for kidney function, as an
adjunct in the treatment of acute renal failure, and as an agent to
reduce intracranial pressure, treat cerebral edema, and reduce
intraocular pressure. Given orally, mannitol is not absorbed
significantly from the gastrointestinal tract, but in large doses it
can cause osmotic diarrhea;
Biochem/physiol Actions
A sugar alcohol sweet tastant. Used in sweetness inhibition studies.
Pharmacokinetics
Chemically, mannitol is an alcohol and a sugar, or a polyol; it is similar to xylitol or sorbitol. However, mannitol has a tendency to lose a hydrogen ion in aqueous solutions, which causes the solution to become acidic. For this reason, it is not uncommon to add a substance to adjust its pH, such as sodium bicarbonate. Mannitol is commonly used to increase urine production (diuretic). It is also used to treat or prevent medical conditions that are caused by an increase in body fluids/water (e.g., cerebral edema, glaucoma, kidney failure). Mannitol is frequently given along with other diuretics (e.g., furosemide, chlorothiazide) and/or IV fluid replacement.
Inhaled mannitol has the possibility to cause bronchospasm and hemoptysis; the occurrence of either should lead to discontinuation of inhaled mannitol.
Safety
Mannitol is a naturally occurring sugar alcohol found in animals
and plants; it is present in small quantities in almost all vegetables.
Laxative effects may occur if mannitol is consumed orally in large
quantities.If it is used in foods as a bodying agent and daily
ingestion of over 20g is foreseeable, the product label should bear
the statement ‘excessive consumption may have a laxative effect’.
After intravenous injection, mannitol is not metabolized to any
appreciable extent and is minimally reabsorbed by the renal tubule,
about 80% of a dose being excreted in the urine in 3 hours.
A number of adverse reactions to mannitol have been reported,
primarily following the therapeutic use of 20% w/v aqueous
intravenous infusions.The quantity of mannitol used as an
excipient is considerably less than that used therapeutically and is
consequently associated with a lower incidence of adverse reactions.
However, allergic, hypersensitive-type reactions may occur when
mannitol is used as an excipient.
An acceptable daily intake of mannitol has not been specified by
the WHO since the amount consumed as a sweetening agent was
not considered to represent a hazard to health.
LD50 (mouse, IP): 14 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, IV): 7.47 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, oral): 22 g/kg
LD50 (rat, IV): 9.69 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 13.5 g/kg
Metabolism
Mannitol is metabolized only slightly, if at all, to glycogen in the liver.
storage
Mannitol is stable in the dry state and in aqueous solutions.
Solutions may be sterilized by filtration or by autoclaving and if
necessary may be autoclaved repeatedly with no adverse physical or
chemical effects.In solution, mannitol is not attacked by cold,
dilute acids or alkalis, nor by atmospheric oxygen in the absence of
catalysts. Mannitol does not undergo Maillard reactions.
The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed container in a
cool, dry place.
Purification Methods
D-Mannitol is crystallised from EtOH, MeOH or H2O and dried at 100o. [Thomson Acta Chem Scand 6 270, 279, 280 1952, Beilstein 1 IV 2841.]
Incompatibilities
Mannitol solutions, 20% w/v or stronger, may be salted out by potassium chloride or sodium chloride.Precipitation has been reported to occur when a 25% w/v mannitol solution was allowed to contact plastic.Sodium cephapirin at 2 mg/mL and 30 mg/mL concentration is incompatible with 20% w/v aqueous mannitol solution. Mannitol is incompatible with xylitol infusion and may form complexes with some metals such as aluminum, copper, and iron. Reducing sugar impurities in mannitol have been implicated in the oxidative degradation of a peptide in a lyophilized formation.Mannitol was found to reduce the oral bioavailability of cimetidine compared to sucrose.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IP, IM, IV, and SC injections; infusions; buccal, oral and sublingual tablets, powders and capsules; ophthalmic preparations; topical solutions). Included in nonparenteral and parenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Mon-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of D-Mannitol
| Melting point: | 167-170 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 295°C |
| alpha | 141 º (c= USP-directives) |
| Density | 1.52 |
| refractive index | 1.3330 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 290-295°C/3.5mm |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| pka | 13.5(at 18℃) |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| color | White |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. odorless |
| PH | 5.0-6.5 (25℃, 1M in H2O) |
| optical activity | [α]25/D +23.3 to +24.3°(lit.) |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.04 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.04 |
| Merck | 14,5745 |
| BRN | 1721898 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 69-65-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | D-Mannitol(69-65-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | D-Mannitol (69-65-8) |
Safety information for D-Mannitol
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for D-Mannitol
| InChIKey | FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N |
D-Mannitol manufacturer
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 D-Mannitol, For ACS analysis CAS 69-65-8View Details
D-Mannitol, For ACS analysis CAS 69-65-8View Details
69-65-8 -
 D-Mannitol, For ACS analysis CAS 69-65-8View Details
D-Mannitol, For ACS analysis CAS 69-65-8View Details
69-65-8 -
 D-Mannitol ACS CAS 69-65-8View Details
D-Mannitol ACS CAS 69-65-8View Details
69-65-8 -
 D-Mannitol CAS 69-65-8View Details
D-Mannitol CAS 69-65-8View Details
69-65-8 -
 D-Mannitol, ≥99% (sum of enantiomers, HPLC) CAS 69-65-8View Details
D-Mannitol, ≥99% (sum of enantiomers, HPLC) CAS 69-65-8View Details
69-65-8 -
 D-Mannitol, for bacteriology CAS 69-65-8View Details
D-Mannitol, for bacteriology CAS 69-65-8View Details
69-65-8 -
 D-Mannitol AR CAS 69-65-8View Details
D-Mannitol AR CAS 69-65-8View Details
69-65-8 -
 D-Mannitol 98% CAS 69-65-8View Details
D-Mannitol 98% CAS 69-65-8View Details
69-65-8