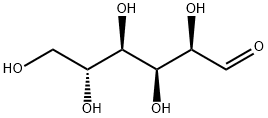
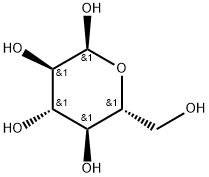
D-Galactose
Synonym(s):D -(+)-Galactose;Galactose
- CAS NO.:59-23-4
- Empirical Formula: C6H12O6
- Molecular Weight: 180.16
- MDL number: MFCD00871336
- EINECS: 200-416-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-25 11:31:46
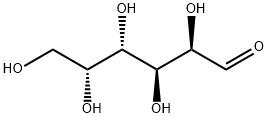
What is D-Galactose ?
Absorption
The absorption of galactose from the human jejunum was calculated to be 1.0 g per minute per 30 cm of the gut .
Toxicity
It is typically uncommon to experience an overdosage situation with dietary galactose or from galactose as an ingredient in a therapeutic agent. At the same time, the experiencing a situation characterized by excessive amounts of galactose in the body defines the challenge with galactosemia, which is itself a rare genetic metabolic disorder. In individuals with galactosemia, the enzymes needed for further metabolism of galactose (ie. such as galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase) are severely diminished or missing entirely, leading to toxic levels of galactose 1-phosphate in various tissues . This toxic excess typically results in hepatomegaly, cirrhosis, renal failure, cataracts, vomiting, hypoglycemia, lethargy, brain damage, and ovarian failure . Without treatment, mortality in infants with galactosemia is about 75% .
Description
D-Galactose is a naturally occurring aldohexose, which is a monosaccharide. It is also a C-4 epimer of glucose, which serves as a source of energy and as a glycosylated component. D-galactose is converted enzymatically into D-glucose for metabolism or polysaccharides for storage. Chronic, systemic exposure to D-galactose accelerates senescence in invertebrates and mammals and has been used as a model for aging. In bacteria, D-galactose is imported by a methyl-galactoside transport system to drive chemotaxis.
Chemical properties
White powder
The Uses of D-Galactose
D-Galactose is a monosaccharide found in milk and sugar beets, and can also be synthesised by the body. It is also the C-4 dimer of glucose (G595000), which provides the body with a source of energy and is an important component of glycolipids and glycoproteins. It is used in cell culture systems that require sugar additives. It is also used in the oral treatment of nephrotic syndrome focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis. Because it is a component of antigens, it plays a vital role in the determination of blood groups in the ABO blood grouping system.
Background
Galactose has been used in trials studying the treatment and diagnosis of Hepatitis C, Hepatic Cancer, Wilsons Disease, Diabetic Macular Oedema, and Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis, among others. There are even proposals for its use in accelerating senescence in mice, rats, and Drosophila, for its association with ovarian cancer, or even for the potential treatment of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nevertheless, none of these ongoing studies have yet provided formal elucidation for their proposals.
As a naturally occurring sugar, it may be found in a number dairy products. Even then, however, it is not generally used as a sweetener considering it is only about 30% as sweet as sucrose. Regardless, although it is predominantly used as a pathway to generate glucose fuel for the human body, galactose is involved as an ingredient in some commonly used vaccines and non-prescription products.
Indications
D-Galactose is used in pharmaceutical applications including (1) the use of galactose to facilitate the construction of structurally and immunologically effective attenuated vaccines; (2) for the treatment of constipation and/or hepatic encephalopathy (HE); and (3) hepatic coma.
Definition
A monosaccharide commonly occurring in milk sugar or lactose.
What are the applications of Application
Galactose has been used:
as a component of galactosyltransferase labeling buffer.
as a supplement in MRS broth for the growth of thermophilic lactobacilli.
to induce the expression of uncoupling protein (UCP) in yeast transformants.
General Description
Galactose is a constituent of lactose. It is one of the main nutrients for newborn infants and young children. It is produced in the body for the formation of lactose and is also a component of glycolipids (cerebrosides) and glycoproteins.
Biological Activity
Galactose is a simple monosaccharide that serves as an energy source and as an essential component of glycolipids and glycoproteins. Galactose contributes to energy metabolism via its conversion to glucose by the enzymes that constitute the Leloir pathway. Defects in the genes encoding these proteins lead to the metabolic disorder galactosemia.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Galactose is a simple monosaccharide that serves as an energy source and as an essential component of glycolipids and glycoproteins. Galactose contributes to energy metabolism via its conversion to glucose by the enzymes that constitute the Leloir pathway. Defects in the genes encoding these proteins lead to the metabolic disorder galactosemia.
Pharmacokinetics
Galactose is a naturally occurring monosaccharide that forms the disaccharide lactose when combined with glucose (another monosaccharide) . Subsequently, when lactose or small amounts of free galactose found in various common dairy products (and other foods) are consumed, the hydrolysis of lactose to glucose and galactose occurs and galactose is itself further metabolized to generate glucose . Such glucose is, of course, ultimately relied upon and used as the primary metabolic fuel for humans in a variety of biological reactions.
Conversely, however, the ways in which galactose is commonly used in therapeutic agents generally do not rely upon such pharmacodynamics, even though they ultimately remain the most important ways in which galactose exerts or elicits useful biological actions for the human body.
Metabolism
The primary pathway for galactose metabolism is called the Leloir pathway, so named after Luis Federico Leloir. The initial stage of this pathway is the conversion of beta-D-galactose to alpha-D-galactose by the enzyme galactose mutarotase (GALM) . The pathway then performs the conversion of alpha-D-galactose to UDP-glucose by way of three principal enzymes and their reactions: galactokinase (GALK) phosphorylates alpha-D-galactose to galactose-1-phosphate (Gal-1-P); galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (GALT) transfers a UMP group from UDP-glucose to Gal-1-P to form UDP-galactose; and finally, UDP galactose-4-epimerase (GALE) interconverts UDP-galactose and UDP-glucose, which completes the pathway .
Purification Methods
D-Galactose is crystallised twice from aqueous 80% EtOH at -10o, then dried in a vacuum oven at 90o over P2O5 for 10hours. [Link Biochemical Preparations 3 75 1953, Hansen et al. Biochemical Preparations 4 2 1955.] Also purify it by recrystallising the dried solid (150g) in hot H2O (150mL), then adding hot MeOH (250mL) and hot EtOH (500mL), stirring to mix, filtering through a bed of charcoal, and the clear filtrate is stirred to initiate crystallisation. After standing overnight at 10o, the crystals of the -anomer are filtered off by suction, washed with MeOH, then EtOH, and dried (yield 130g), and more can be obtained by evaporation of the filtrate and washing as before. [Wolfrom & Thompson Methods in Carbohydrate Chemistry I 120 1962, Academic Press, Beilstein 1 IV 4336.]
Properties of D-Galactose
| Melting point: | 168-170 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 232.96°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | +79.0~+81.0°(D/20℃) (c=10, dil. NH4OH) |
| Density | 1,5 g/cm3 |
| refractive index | 80 ° (C=10, H2O) |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | H2O: 100 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | pK1:12.35 (25°C) |
| color | White |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | 4.5-6.0 (H2O)Aqueous solution |
| PH Range | 5 - 7 at 180 g/l at 25 °C |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +80±1°, 24 hr, c = 5% in H2O |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Merck | 14,4335 |
| BRN | 1724619 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 59-23-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | D-Galactose(59-23-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | D-Galactose (59-23-4) |
Safety information for D-Galactose
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H312:Acute toxicity,dermal H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P330:Rinse mouth. P363:Wash contaminated clothing before reuse. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for D-Galactose
| InChIKey | GZCGUPFRVQAUEE-DPYQTVNSSA-N |
D-Galactose manufacturer
Merck Life Science Private Limited
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 D-Galactose extrapure CAS 59-23-4View Details
D-Galactose extrapure CAS 59-23-4View Details
59-23-4 -
 D-Galactose CAS 59-23-4View Details
D-Galactose CAS 59-23-4View Details
59-23-4 -
 D-(+)-Galactose Anhydrous CAS 59-23-4View Details
D-(+)-Galactose Anhydrous CAS 59-23-4View Details
59-23-4 -
 D-(+)-Galactose CAS 59-23-4View Details
D-(+)-Galactose CAS 59-23-4View Details
59-23-4 -
 D-Galactose 98% CAS 59-23-4View Details
D-Galactose 98% CAS 59-23-4View Details
59-23-4 -
 D-Galactose (CAS Number: 59-23-4)View Details
D-Galactose (CAS Number: 59-23-4)View Details
59-23-4 -
 D-(+)-Galactose (C6H12O6), CAS Number: 59-23-4, Packaging Size: 1 kgView Details
D-(+)-Galactose (C6H12O6), CAS Number: 59-23-4, Packaging Size: 1 kgView Details
59-23-4 -
 D - galactose 99%View Details
D - galactose 99%View Details
59-23-4
