cryolite
Synonym(s):Kryolith;Sodium hexafluoroaluminate
- CAS NO.:15096-52-3
- Empirical Formula: AlF6Na3
- Molecular Weight: 209.94
- MDL number: MFCD00003507
- EINECS: 239-148-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-06 13:21:43
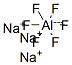
What is cryolite?
Description
Cryolite is an uncommon mineral salt of sodium, fluoride and aluminum that was first discovered on the west coast of Greenland. The supply was depleted by 1987, and synthetic cryolite is now produced from the common mineral fluorite. Cryolite is used at very high application rates of 5-30 kg/ha to control Lepidoptera and Coleoptera on certain fruits, vegetables and citrus. 92% of total cryolite applied in the U.S. is used on grapes in California.
Chemical properties
Sodium aluminum fluoride is a snow-white crystalline solid, powder or vitreous mass. The crystalline solid (natural product (cryolite) may be colored reddish or brown or even black but loses this discoloration on heating); synthetic product is an amorphous powder. Odorless
Physical properties
Habit: massive, granular, pseudocubic euhedral crystals.
Color: snow white, gray,
reddish white, or brownish white.
Diaphaneity: transparent to translucent.
Luster: vitreous, greasy.
Streak: white.
Cleavage: [001], [110], [101].
Fracture: uneven.
Occurrence: large bed in a granitic vein in gray gneiss.
Melting point: 1009°C.
The Uses of cryolite
Cryolite is commonly used as an electrolyte for aluminum electrolysis. Alumina is dissolved in molten cryolite is used to dissolve alumina during aluminium processing.
The Uses of cryolite
Electrolyte in the reduction of alumina to aluminum; ceramics; insecticide; binder for abrasives; electric insulation; explosives; polishes.
What are the applications of Application
Cryolite is an insecticide and a pesticide
Definition
A natural fluoride of sodium and aluminum or made synthetically from fluorspar, sulfuric acid, hydrated alumina, and sodium carbonate.
General Description
An odorless white solid or powder. Mp: 1291°C. Density: 2.95 g cm-3. Dust irritates the eyes and skin; inhaled dust irriates the nose, mouth and lungs. Insoluble in water. Synthesized by fusion of sodium fluoride and aluminum fluoride as a electrolyte in the reduction of alumina to aluminum metal. Occurs in nature as the mineral cryolite. Aqueous suspensions of powdered sodium aluminum fluoride are used as insecticides.
Reactivity Profile
SODIUM ALUMINUM FLUORIDE is non-combustible. Emits toxic fumes when heated to decomposition. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and strong acids. Decomposed by bases, which can generate soluble fluorides. Soluble in concentrated sulfuric acid.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide: Sodium aluminum fluoride is used as an insecticide on food crops and ornamentals, and also in aluminum refining and making ceramics, glass and polishes. Cryolite is used to control a variety of pests on cucurbits (melons, cantaloupe, water melon, pumpkins, all types of squash), fruiting vegetables (eggplant, pepper, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower, collards, head and leaf lettuce, kohlrabi), kiwi (in California only), pears, radish, cranberry and peaches, grapefruit, lemon, lime, orange, tangelo, tangerines, tomatoes, apples, potatoes, beans and grapes. Also on ornamental plants, woody shrubs and vines. Not listed for use in EU countries. Registered for use in the U.S
Trade name
KRYOCIDE®; CHIOLITE®; CRYOLITE 93®; ICE-SPAR®; ICETONE®; KOYOSIDE®; KRIOLIT®; PROKIL® Sodium aluminum fluoride; VILLIAUMITE®
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion. Used as a pesticide. Mutation data reported.When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Fand NazO. See also FLUORIDES.
Potential Exposure
Sodium aluminum fluoride is used in making pesticides, ceramics, glass, and polishes; in refining reduction of aluminum, flux, glass, and enamel.
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with strong acids such as sulfuric, strong oxidizers, hydrogen fluoride.
Waste Disposal
In accordance with 40CFR 165 recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of cryolite
| Melting point: | 1012 |
| Boiling point: | decomp |
| Density | 2.9 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index | 1.338 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| Merck | 13,2634 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 15096-52-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cryolite (15096-52-3) |
Safety information for cryolite
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. |
Computed Descriptors for cryolite
cryolite manufacturer
Jayfluoride PVT LTD
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 7-Bromo-1H-indazole N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid Electrolytic Iron Powder Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 1-(4-Methylphenylsulfonyl)-1H-1,2,3-benzotriazole 1-(2-Chlorobenzyl)-4-nitro-1H-pyrazole 1-(2-Nitrophenyl)-4-phenylpiperazineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 15096-52-3 / 13775-53-6 Cryolite 99%View Details
15096-52-3 / 13775-53-6 Cryolite 99%View Details
15096-52-3 / 13775-53-6 -
 15096-52-3 / 13775-53-6 98%View Details
15096-52-3 / 13775-53-6 98%View Details
15096-52-3 / 13775-53-6 -
 Cryolite 98%View Details
Cryolite 98%View Details
15096-52-3 / 13775-53-6 -
 Cryolite CAS 15096-52-3View Details
Cryolite CAS 15096-52-3View Details
15096-52-3 -
 Sodium aluminium fluoride CAS 15096-52-3View Details
Sodium aluminium fluoride CAS 15096-52-3View Details
15096-52-3 -
 CRYOLITE Extra Pure CAS 15096-52-3View Details
CRYOLITE Extra Pure CAS 15096-52-3View Details
15096-52-3 -
 Cryolite CAS 15096-52-3View Details
Cryolite CAS 15096-52-3View Details
15096-52-3 -
 1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6