Copper(I) chloride
Synonym(s):Copper monochloride;Copper(I) chloride;Cuprous chloride
- CAS NO.:7758-89-6
- Empirical Formula: ClCu
- Molecular Weight: 99
- MDL number: MFCD00010971
- EINECS: 231-842-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
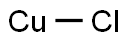
What is Copper(I) chloride?
Chemical properties
white or pale grey powder
Chemical properties
Copper chloride is a brownish-yellow powder.
Physical properties
White cubic crystal which turns blue when heated at 178°C; density 4.14 g/cm3; the mineral nantokite (CuCl) has density 4.14 g/cm3, hardness 2.5 (Mohs), refractive index 1.930; melts at 430°C becoming a deep, green liquid; vaporizes around 1,400°C; vapor pressure 5 torr at 645°C and 400 torr at 1250°C; low solubility in water (decomposes partially); Ksp 1.72x10-7; insoluble in ethanol and acetone; soluble in concentrated HCl and ammonium hydroxide.The space lattice of CuCl belongs to the cubic system, and its zinc-blende structure has a lattice
constant of a=0.541 nm and Cu–Cl=0.235 nm below 407°C, and it belongs to the hexagonal
system and has a wurtzite structure at 407°C–422°C.
The reflection peaks at room temperature are positioned at λ: 58 and 65.4 mm. The transmission
peak is located at λ: 18.5 mm. The absorption spectrum near the absorption edge λ: 370.0 nm at liquid He temperature shows
many structures because of exciton absorption.
The Uses of Copper(I) chloride
Copper(I) chloride (CuCl) or cuprous chloride is a white powder used as an absorbing agent for carbon dioxide gas in enclosed breathing areas such as space vehicles.
The Uses of Copper(I) chloride
Shows unique character as an initiator of radical reactions such as the hydrostannation of α,β-unsaturated ketones.1
The Uses of Copper(I) chloride
It is used for absorption of carbon monoxide in gas analysis. Cuprous chloride is used as a light modulator for λ: 0.43–2.5 mm.
The Uses of Copper(I) chloride
As catalyst for organic reactions; catalyst, decolorizer and desulfuring agent in petroleum industry; in denitration of cellulose; as condensing agent for soaps, fats and oils; in gas analysis to absorb carbon monoxide.
The Uses of Copper(I) chloride
Copper chloride is also known as cupric chloride, this substance was made by treating copper carbonate with hydrochloric acid. The greenish blue crystals are soluble in water, alcohol, and ether. This halide was added to printing-out and silver bromide emulsions for increased contrast.
What are the applications of Application
Copper(I) chloride is an initiator of radical reactions
Definition
ChEBI: An inorganic chloride of copper in which the metal is in the +1 oxidation state.
Preparation
Copper(I) chloride is prepared by reduction of copper(II) chloride in solution: 2CuCl2 + H2 2CuCl + 2HCl Alternatively, it can be prepared by boiling an acidic solution of copper(II) chloride with copper metal, which on dilution yields white CuCl: Cu + CuCl2 2CuCl Copper(I) chloride dissolved in concentrated HCl absorbs carbon monoxide under pressure forming an adduct, CuCl(CO). The complex decomposes on heating releasing CO. Copper(I) chloride is slightly soluble in water. However, in the presence of Cl- ion, it forms soluble complexes of discrete halogeno anions such as, CuCl2-, CuCl3 2-, and CuCl4 3-. Formation of complexes and organocopper derivatives as outlined below are not confined only to copper(I) chloride, but typify Cu+ in general. Reaction with ethylenediamine (en) in aqueous potassium chloride solution forms Cu(II)-ethylenediamine complex, while Cu+ ion is reduced to its metallic state: 2CuCl + 2en → [Cuen2]2+ + 2Cl- + Cu° It dissolves in acetonitrile, CH3CN forming tetrahedral complex ion [Cu(CH3CN)4]+ which can be precipitated with large anions such as ClO4 - or PF6- . Reactions with alkoxides of alkali metals produce yellow copper(I) alkoxides. For example, reaction with sodium ethoxide yield copper(I) ethoxide, a yellow compound that can be sublimed from the product mixture: CuCl + NaOC2H5 → CuOC2H5 + NaCl Copper(I) chloride forms complexes with ethylene and other alkenes in solutions that may have compositions such as [Cu(C2H4)(H2O)2]+ or [Cu(C2H4)(bipy)]+. (bipy = bipyridyl) Reactions with lithium or Grignard reagent yield alkyl or aryl copper(I) derivatives, respectively. Such organocopper compounds containing Cu-Cu bonds are formed only by Cu+ and not Cu2+ ions.
Production Methods
Cuprous chloride crystal is grown by direct deposition on the substrate from vapor (vapor phase
growth). Small, zinc-blende crystals without deformation can be obtained from solution.
Large single crystals are grown by the Czochralski method. The first grown crystal takes a
wurtzite structure, which changes to a zinc-blende structure below 407℃. It is inevitable to keep a
constant strain.
Cuprous chloride is soluble in water and ethyl alcohol is used for cutting and polishing.
Preparation
To a suspension of CuCl2 (450 mg, 3.4 mmol) in ACN (8 mL) was added t-BuONO (0.52 mL, 3.9 mmol). The mixture was stirred for 5 min then a solution of the SM (830 mg, 2.8 mmol) in ACN (8 mL) was added dropwise. The reaction mixture was stirred at 60 C for 1 h. After allowing to cool to RT, the mixture was concentrated onto silica gel and purified by silica gel chromatography (0-40% EtOAc/hexane) to provide the product as a light brown powder. [450 mg, 51%]
General Description
The structure of copper(I) chloride is similar to zinc-blende crystal at room temperature; the structure is wurtzite at 407 °C and at higher temperatures it forms copper(I) chloride vapor as per mass spectroscopy.
Hazard
Copper(I) chloride is moderately toxic by ingestion and possibly other routes of entry into the body. The oral LD50 in mouse is reported to be 347 mg/kg; and subcutaneous LD50 in guinea pigs is 100 mg/kg.
Shipping
UN2802 Copper chloride, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
Purification Methods
Wash the solid with ethanol and diethyl ether, then dry it and store it in a vacuum desiccator [.sterl.f Acta Chem Scand 4 375 1950]. Alternatively, to an aqueous solution of CuCl2.2H2O is added, with stirring, an aqueous solution of anhydrous sodium sulfite. The colourless product is dried at 80o for 30minutes and stored under N2. Cu2Cl2 can be purified by zone-refining [Hall et al. J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans 1 79 343 1983]. [Glemser & Sauer in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol II p 1005 1965.]
Incompatibilities
Contact with strong acids forms monovalent copper salts and toxic hydrogen chloride gas. Forms shock-sensitive and explosive compounds with potassium, sodium, sodium hypobromite, nitromethane, acetylene. Keep away from moisture and alkali metals. Attacks metals in the presence of moisture. Reacts with moist air to form cupric chloride dihydrate. May attack some metals, paints, and coatings. May be able to ignite combustible materials.
Properties of Copper(I) chloride
| Melting point: | 430 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 1490 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.15 g/mL at 20 °C |
| vapor pressure | 1.3 mm Hg ( 546 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.93 |
| Flash point: | 1490°C |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | 0.06 g/L (25°C) |
| form | beads |
| appearance | light-green to white solid |
| color | Slightly greenish-gray |
| Specific Gravity | 4.14 |
| PH | 5 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃)(slurry) |
| Water Solubility | 0.06 g/L (25 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Air & Moisture Sensitive |
| Crystal Structure | Hexagonal, Wurtzite (Zincite) Structure - Space Group P 63mc |
| Merck | 14,2660 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 6.76 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 1 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 100 mg/m3; TWA 1 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, potassium, water. Air, light and moisture sensitive. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7758-89-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Cuprous monochloride(7758-89-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cuprous chloride (7758-89-6) |
Safety information for Copper(I) chloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Copper(I) chloride
Copper(I) chloride manufacturer
Aashi Chem
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Cuprous Chloride 98%View Details
Cuprous Chloride 98%View Details -
 Copper(I)chloride 98%View Details
Copper(I)chloride 98%View Details -
 Copper(I)chloride 98%View Details
Copper(I)chloride 98%View Details -
 Copper(I) chloride CAS 7758-89-6View Details
Copper(I) chloride CAS 7758-89-6View Details
7758-89-6 -
 Copper(I) chloride CAS 7758-89-6View Details
Copper(I) chloride CAS 7758-89-6View Details
7758-89-6 -
 Copper(I) chloride CAS 7758-89-6View Details
Copper(I) chloride CAS 7758-89-6View Details
7758-89-6 -
 Copper(I) chloride CAS 7758-89-6View Details
Copper(I) chloride CAS 7758-89-6View Details
7758-89-6 -
 Copper(I) chloride CAS 7758-89-6View Details
Copper(I) chloride CAS 7758-89-6View Details
7758-89-6
