Citral
Synonym(s):3,7-Dimethyl-2,6-octadienal;Citral;Geranial and neral mixture;Lemonal
- CAS NO.:5392-40-5
- Empirical Formula: C10H16O
- Molecular Weight: 152.23
- MDL number: MFCD00006997
- EINECS: 226-394-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 08:49:36
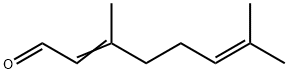
What is Citral?
Chemical properties
mobile light yellow liquid with a lemon-like smell
Chemical properties
Citral occurs as (2Z)- and (2E)-isomers (citral a and b, respectively)
analogous to the corresponding alcohols, geraniol and nerol: geranial
(citral a), bp2.7 kPa 118–119 °C, d20 0.8888, n20
D 1.4898; neral (citral b),
bp2.7 kPa 120 °C, d20 0.8869, n20
D 1.4869.
Natural citral is nearly always a mixture of the two isomers. It occurs in lemongrass
oil (up to 85%), in Litsea cubeba oil (up to 75%), and in small amounts inmany
other essential oils. The citrals are colorless to slightly yellowish liquids, with an
odor reminiscent of lemon.
Since citral is an α,β-unsaturated aldehyde with an additional double bond, it
is highly reactive and may undergo reactions such as cyclization and polymerization.
Geraniol, citronellol, and 3,7-dimethyloctan-l-ol can be obtained from citral
by stepwise hydrogenation. Citral can be converted into a number of addition
compounds; the (Z)- and (E)-isomers can be separated via the hydrogen sulfite
addition compounds.The condensation of citral with active methylene groups is
used on an industrial scale in the synthesis of pseudoionones, which are starting
materials for ionones and vitamins.
Chemical properties
Citral has a strong, lemon-like odor and a characteristic bittersweet taste. Commercially, the product is a mixture of two geometric isomers—α-citral and β-citral, each exhibiting cis- and trans-isomers because of the position of the double bond.
Occurrence
Reported found in apricot, clary sage, ginger, grape, grapefruit, lemon, lime, mandarin, orange, raspberry, tamarind, tangerine, tea and tomato.
The Uses of Citral
Citral is an anti-microbial agent found in plants with antibacterial activity against some food pathogens. It is also a fragrance compound with a distinct lemon scent.
The Uses of Citral
citral is a naturally occurring aroma compound used to provide a lemon-type fragrance. Citral is a constituent of lemon oil, lemongrass oil, lime oil, ginger oil, verbena oil, and other plant-derived C essential oils.
The Uses of Citral
Citral is a liquid flavoring agent, light yellow in color with a citrus odor. it occurs in lemon and lemongrass oils. it is usually obtained from citral-containing oils by chemical means but may also be pre- pared synthetically. it is soluble in fixed oils, mineral oil, and pro- pylene glycol. it is moderately stable and should be stored in glass, tin, or resin-lined containers. it is used in flavors for lemon with applications in candy, baked goods, and ice cream at 20–40 ppm. it is also termed 2,6-dimethyl-octadian-2-6-al-8.
What are the applications of Application
Citral is a reagent used in the synthesis of vitamin A, ionone, and methylionone
Definition
Commercial material is a mixture of α and β isomers.
Preparation
Since citral is used in bulk as a starting material for the synthesis of
vitamin A, it is produced industrially on a large scale. Smaller quantities are also
isolated from essential oils.
1) Isolation from essential oils: Citral is isolated by distillation from lemongrass
oil and from L. cubeba oil. It is the main component of these oils.
2) Synthesis from geraniol: Currently, the most important synthetic procedures
are vapor-phase dehydrogenation and oxidation of geraniol or geraniol–nerol
mixtures. Catalytic dehydrogenation under reduced pressure using copper
catalysts is preferred.
3) Synthesis from dehydrolinalool: Dehydrolinalool is produced on a large scale
from 6-methyl-5-hepten-2-one and acetylene and can be isomerized to citral
in high yield by a number of catalysts. Preferred catalysts include organic
orthovanadates, organic trisilyl oxyvanadates, and vanadium catalysts
with silanols added to the reaction system.
4) Synthesis from isobutene and formaldehyde: 3-Methyl-3-buten-l-ol, obtained
from isobutene and formaldehyde, isomerizes to form 3-methyl-
2-buten-lol. However, it is also converted into 3-methyl-2-butenal
by dehydrogenation and subsequent isomerization. Under
azeotropic conditions in the presence of nitric acid, 3-methyl-2-buten-l-ol
and 3-methyl-2-butenal form an acetal (shown as follows), which
eliminates one molecule of 3-methyl-2-buten-l-ol at higher temperatures.
The intermediate enol ether undergoes Claisen rearrangement followed by
Cope rearrangement to give citral in excellent yield:
Today, this route is performed on a very large industrial scale in a continuous
reactive distillation process.
Aroma threshold values
Detection at 1.0%: characterizing lemon-like, distilled lime peel, intense aldehydic citruslike.
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 5 ppm in 5% sugar and 0.1% CA: characteristic lemon, peely, citrus, green floral juicy with woody and candy notes.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 101, p. 7131, 1979 DOI: 10.1021/ja00517a088
Tetrahedron Letters, 35, p. 4007, 1994 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)76726-8
General Description
A clear yellow colored liquid with a lemon-like odor. Less dense than water and insoluble in water. Toxic by ingestion. Used to make other chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Citral is an aldehyde. Aldehydes are frequently involved in self-condensation or polymerization reactions. These reactions are exothermic; they are often catalyzed by acid. Aldehydes are readily oxidized to give carboxylic acids. Flammable and/or toxic gases are generated by the combination of aldehydes with azo, diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, nitrides, and strong reducing agents. Aldehydes can react with air to give first peroxo acids, and ultimately carboxylic acids. These autoxidation reactions are activated by light, catalyzed by salts of transition metals, and are autocatalytic (catalyzed by the products of the reaction). The addition of stabilizers (antioxidants) to shipments of aldehydes retards autoxidation. Citral can react with alkalis and strong acids. Citral can readily isomerize.
Hazard
Questionable carcinogen.
Fire Hazard
Citral is combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Contact allergens
Citral is an aldehyde fragrance and flavoring ingredient, a blend of isomers cis (Neral) and trans (geranial). As a fragrance allergen, citral has to be mentioned by name in cosmetics within the EU.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route. Mildly toxic by ingestion. Experimental reproductive effects. A severe human and experimental skin irritant. Mutation data reported. Combustible liquid. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Synthesis
Citral is usually isolated from the citral-containing oil by chemical means or by chemical synthesis (from β-pinene, isoprene, etc.).
Properties of Citral
| Melting point: | <-10°C |
| Boiling point: | 229 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.888 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 5 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.2 mm Hg ( 200 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 2303 | CITRAL |
| Flash point: | 215 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 0.42g/l |
| form | Liquid |
| color | colorless to light yellow |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. sweet lemon citral |
| explosive limit | 4.3-9.9%(V) |
| Water Solubility | PRACTICALLY INSOLUBLE |
| Merck | 14,2322 |
| JECFA Number | 1225 |
| BRN | 1721871 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 5 ppm (Skin) |
| Stability: | Stable. but readily isomerizes. Incompatible with alkalies, strong oxidizing agents, strong acids. Combustible. Air and light sensitive. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 5392-40-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Citral(5392-40-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Citral (5392-40-5) |
Safety information for Citral
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P272:Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Citral
Citral manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Citral 99%View Details
Citral 99%View Details -
 Citral 98%View Details
Citral 98%View Details
5392-40-5 -
 Citral (cis- and trans- mixture) CAS 5392-40-5View Details
Citral (cis- and trans- mixture) CAS 5392-40-5View Details
5392-40-5 -
 Citral CAS 5392-40-5View Details
Citral CAS 5392-40-5View Details
5392-40-5 -
 Citral CAS 5392-40-5View Details
Citral CAS 5392-40-5View Details
5392-40-5 -
 Citral CAS 5392-40-5View Details
Citral CAS 5392-40-5View Details
5392-40-5 -
 Citral CAS 5392-40-5View Details
Citral CAS 5392-40-5View Details
5392-40-5 -
 Citral CAS 5392-40-5View Details
Citral CAS 5392-40-5View Details
5392-40-5
