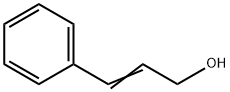
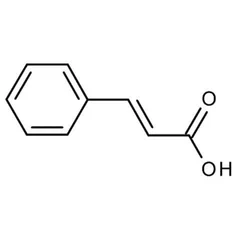
Cinnamic acid
Synonym(s):(2E)-3-Phenyl-2-propenoic acid;trans-3-Phenylacrylic acid;trans-Cinnamic acid;Cinnamic acid
- CAS NO.:621-82-9
- Empirical Formula: C9H8O2
- Molecular Weight: 148.16
- MDL number: MFCD00004369
- EINECS: 210-708-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-19 17:28:17
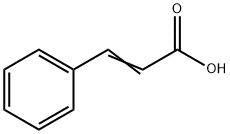
What is Cinnamic acid ?
Description
Cinnamic acid is a white crystalline organic acid, which is slightly soluble in water.
It is obtained from oil of cinnamon, or from balsams such as storax. It is also found in shea butter and is the best indication of its environmental history and post-extraction conditions. It can also be made synthetically.
Cinnamic acid is used in flavors, synthetic indigo, and certain pharmaceuticals, though its primary use is in the manufacturing of the methyl, ethyl, and benzyl esters for the perfume industry. Cinnamic acid has a honey- like odor; it and its more volatile ethyl ester (ethyl cinnamate) are flavor components in the essential oil of cinnamon, in which related cinnamaldehyde is the major constituent. Cinnamic acid is also part of the biosynthetic shikimate and phenyl propanoid pathways. Its biosynthesis is performed by action of the enzyme phenylalanine ammonia - lyase (PAL) on phenylalanine.
Cinnamic acid is freely soluble in benzene, diethyl ether, acetone, and it is insoluble in hexane.
Cinnamic acid is also a kind of self-inhibitor produced by fungal spore to prevent germination.
Chemical properties
Cinnamic acid is almost odorless with a burning taste, and then turning sweet and reminiscent of apricot.
Occurrence
The trans- form has been found among the constituents of the essential oils of basil, Chinese cinnamon, Melaleuca bracteata, Alpinia galanga. It is reported found in Peru balsam, Asian and American storax and cocoa leaves. Also reported found in strawberry fruit, beer, cognac, starfruit (Averrhoa carambola L) and loquat. The cis- form is present in the oil of Alpinia malacensis.
The Uses of Cinnamic acid
cinnamic acid has sunscreen capabilities. Some manufacturers use it to replace PABA because of its lower allergic and phototoxic reaction incidence. Cinnamic acid is found in cinnamon leaves and cocoa leaves, and is an essential oil of certain mushrooms. It may cause allergic skin rashes.
The Uses of Cinnamic acid
fragrance & flavoring agent, antidiabetic
The Uses of Cinnamic acid
Cinnamic Acid is a flavoring agent that consists of crystalline scales, white in color, with an odor resembling honey and flowers. it is slightly soluble in water, soluble in alcohol, chloroform, acetic acid, acetone, benzene, and most oils, and alkali salts soluble in water. it is obtained by chemical synthesis. it is also termed 3-phenylpro- penoic acid.
Definition
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid that consists of acrylic acid bearing a phenyl substituent at the 3-position. It is found in Cinnamomum cassia.
Preparation
Two isomers, trans- and cis- exist; the trans-isomer is of interest for use in flavoring; in addition to the extraction from natural sources (storax), it can be prepared as follows: (1) from benzaldehyde, anhydrous sodium acetate and acetic anhydride in the presence of pyridine (Perkin reaction); (2) from benzaldehyde and ethyl acetate (Claisen condensation); (3) from benzaldehyde and acetylene chloride; (4) by oxidation of benzylidene acetone with sodium hypochlorite.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 75, p. 1068, 1953 DOI: 10.1021/ja01101a016
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 59, p. 710, 1994 DOI: 10.1021/jo00083a006
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion. A skin irritant. Combustible liquid. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes.
Synthesis
Rainer Ludwig Claisen (1851–1930), German chemist, described for the first time in 1890 the synthesis of cinnamates by reacting aromatic aldehydes with esters. The reaction is known as the Claisen condensation.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the acid from *benzene, CCl4, hot water, water/EtOH (3:1), or 20% aqueous EtOH. Dry it at 60o in vacuo. It is steam volatile. [Beilstein 9 IV 2002.]
Properties of Cinnamic acid
| Melting point: | 133 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 300 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.2475 |
| refractive index | 1.5049 (estimate) |
| FEMA | 2288 | CINNAMIC ACID |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pK (25°) 4.46 |
| color | White to Off-White |
| PH | 3.76(1 mM solution);3.23(10 mM solution);2.72(100 mM solution) |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. balsam sweet storax |
| Water Solubility | 511.2mg/L(25 ºC) |
| JECFA Number | 657 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 621-82-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2-Propenoic acid, 3-phenyl-(621-82-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cinnamic acid (621-82-9) |
Safety information for Cinnamic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Cinnamic acid
Cinnamic acid manufacturer
NRS Chemicals LLP
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![(aR)-alpha-[(1S)-1-[2,6-Dimethoxy-4-(2-propen-1-yl)phenoxy]ethyl]-4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzenemethanol](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/171485-39-5.gif)
You may like
-
 CINNAMIC ACID 99%View Details
CINNAMIC ACID 99%View Details -
 621-82-9 Cinnamic acid 98%View Details
621-82-9 Cinnamic acid 98%View Details
621-82-9 -
 Cinnamic Acid (SQ) CAS 621-82-9View Details
Cinnamic Acid (SQ) CAS 621-82-9View Details
621-82-9 -
 Cinnamic Acid CASView Details
Cinnamic Acid CASView Details -
 Cinnamic Acid (140-10-3), 96-98%View Details
Cinnamic Acid (140-10-3), 96-98%View Details
140-10-3 -
 Cinnamic Acid (140-10-3)View Details
Cinnamic Acid (140-10-3)View Details
140-10-3 -
 Powder Cinnamic Acid, For Industrial, Grade Standard: Bio-Tech GradeView Details
Powder Cinnamic Acid, For Industrial, Grade Standard: Bio-Tech GradeView Details
621-82-9 -
 Liquid Cinnamic Acid, 99%View Details
Liquid Cinnamic Acid, 99%View Details
140-10-3
