Chromyl chloride
Synonym(s):Chromium(VI) dichloride dioxide;Chromium(VI) oxychloride;Dichlorochromium(VI) oxide
- CAS NO.:14977-61-8
- Empirical Formula: Cl2CrO2
- Molecular Weight: 154.9
- MDL number: MFCD00010951
- EINECS: 239-056-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
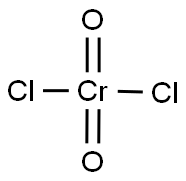
What is Chromyl chloride?
Description
Chromyl chloride is a dark red fuming liquidwith a musty, burning odor. Molecular weight = 154.90;Specific gravity (H2O:1) =1.91 at 25℃; Boilingpoint =117℃; Freezing/Melting point =-96.5℃; Vaporpressure =20 mmHg at 25℃. Soluble in water(decomposes).
Chemical properties
DEEP RED LIQUID
Chemical properties
Chromyl chloride is a dark red fuming liquid with a musty, burning odor.
Physical properties
Dark red, fuming liquid; reddish yellow vapors; musty buring odor; density 1.91 g/mL; freezes at -96.5°C; boils at 117°C; reacts with water; soluble in chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, benzene, carbon disulfide and nitrobenzene.
The Uses of Chromyl chloride
Highly spin-polarized chromium dioxide (CrO2) thin films were deposited on 100 TiO2 substrates by chemical vapor deposition using chromyl chloride as a precursor. Chromyl chloride (Cr02C12) reacts with cyclohexane solvent at 75 OC to give a dark precipitate along with chlorocyclohexane and a small amount of cyclohexene (in 10.0 and ca. 0.3% yields based on chromium). Chromyl chloride, CrO2C12, oxidizes cyclooctane, isobutane, and toluene under mild conditions (25-60" C). The reactions give chlorinated products (chlorocyclooctane, tert- butyl chloride, and benzyl chloride) and a dark chromium-containing precipitate. Used for Organic oxidations and chlorination, chromium coordination complexes, catalyst for polymerization of olefins. Chromyl chloride in carbon tetrachloride solution reacts in the cold with cyclohexene, cyclopentene, and 1-hexene to give the various isomeric chlorohydrins as the major products.
The Uses of Chromyl chloride
Catalyst for polymerization of olefins; oxidation of hydrocarbons; in the Etard reaction for production of aldehydes and ketones; in the preparation of various coordination complexes of Cr.
The Uses of Chromyl chloride
In organic oxidations and chlorinations; as a solvent for chromium oxide; in making chromium complexes and dyes
Definition
A dark red covalent liquid prepared either by distilling a dry mixture of potassium dichromate and sodium chloride with concentrated sulfuric acid or by the action of concentrated sulfuric acid on chromium(VI) oxide dissolved in concentrated hydrochloric acid. Chromyl chloride is hydrolyzed by water, and with solutions of alkalis it undergoes immediate hydrolysis to produce chromate ions. It is used as an oxidizing agent in organic chemistry. Chromyl chloride oxidizes methyl groups at the ends of aromatic side chains to aldehyde groupings (étard’s reaction).
Preparation
Chromyl chloride is prepared by reacting chromium(III) chloride with hydrochloric acid:
CrO3 + 2HCl → CrO2Cl2 + H2O
Also, it may be prepared by warming potassium dichromate with potassium chloride in concentrated sulfuric acid:
K2Cr2O7 + 4KCl + 3H2SO4 → 2Cr2O2Cl2 + 3K2SO4 + 3H2O.
General Description
A dark red fuming liquid with a pungent odor. Corrosive to tissue.
Reactivity Profile
Chromyl chloride is a powerful and often violent oxidizing agent. Reacts readily with many inorganic and organic materials in the absence of a dilutent. Contact with hydrogen sulfide or phosphine can cause ignition. Contact with phosphorus tribromide, acetone, ethanol, ether, and turpentine causes ignition. Contact with moist phosphorus or with phosphorus trichloride leads to explosive reaction. Contact with ammonia causes incandescence. Reacts with sodium azide to form chromyl azide, which is explosive in the absence of a dilutent. Causes ignition of flowers of sulfur and of urea on contact. [Bretherick, 1979, p. 822-823].
Hazard
Corrosive to tissue. Strong oxidizing agent. Skin and upper respiratory tract irritant. Probable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Inhalation causes severe irritation of upper respiratory system. Contact with eyes or skin causes irritation and burning. Ingestion causes burning of mouth and stomach.
Fire Hazard
Behavior in Fire: Vapors are very irritating to eyes and mucous membranes. May increase severity of fire.
Safety Profile
Suspected carcinogen. Probably a poison by various routes. Mutation data reported. Corrosive. A strong irritant. Hydrolyzes to form chromic and hydrochloric acids. A strong oxidner and chlorinating agent. Violent reaction with water. Reacts violently with alcohol, ether, acetone, turpentine. Ignites or explodes on contact with nonmetal halides (e.g., disulfur dichloride, phosphorus trichloride, and phosphorus tribromide), nonmetal hydrides (e.g., hydrogen sulfide and hydrogen phosphide), flowers of sulfur, moist phosphorus, sodium azide, and urea. During preparation can violently explode. Incompatible with ammonia, disulfur dichloride, organic solvents, phosphorus, phosphorus trichloride, sodium azide, and sulfur. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-. See also CHROMIUM COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
Chromium oxychloride is used in making chromium complexes and dyes; and used in various organic oxidation and chlorination reactions
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least30 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. If victim is conscious, administer water ormilk. Do not induce vomiting.
storage
Color Code—White: Corrosive or ContactHazard; Store separately in a corrosion-resistant location.Prior to working with Chromium chloride you should betrained on its proper handling and storage. A regulated,marked area should be established where this chemical ishandled, used, or stored in compliance with OSHAStandard 1910.1045. Chromium chloride must be stored toavoid contact with water since violent reactions occur,releasing poisonous materials including chromic acid,hydrogen chloride, chromic chloride, and chlorine. Store intightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated areaaway from flammable and combustible materials, ammonia, alcohol and turpentine, and other incompatible materials listed above.
Shipping
UN1758 Chromium oxychloride, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
Purification Methods
Purify it by distillation under reduced pressure. It hydrolyses violently with H2O and is a powerful oxidant which explodes with P, and ignites in contact with S, NH3, EtOH and many organic compounds. TOXIC.
Incompatibilities
Contact with water is violent and forms hydrochloric and chromic acids, and chlorine gas. A powerful oxidizer. Reacts violently with acetone, alcohol, ammonia, ether, fuels, organic solvents, moist phosphorus, phosphorus trichloride; sodium azide; sulfur, reducing agents; turpentine. Contact with nonmetal halides, such as disulfur dichloride, phosphorus trichloride; and phosphorus tribromide; nonmetal hydrides, such as hydrogen sulfide; hydrogen phosphide, and urea, causes a danger fire and explosion hazard
Properties of Chromyl chloride
| Melting point: | -96.5 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 117 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.911 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| Flash point: | 117°C |
| solubility | reacts with H2O; soluble in ctc, chloroform,benzene |
| form | liquid |
| Specific Gravity | 1.911 |
| color | red |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in carbon tetrachloride, carbon disulfide, benzene, nitrobenzene, chloroform, and POCL3. Insoluble in water(Reacts). |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,2248 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.0001 ppm; STEL 0.00025 ppm (Skin) NIOSH: TWA 0.0002 mg/m3 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.6(20℃) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 14977-61-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Chromium(VI) dioxychloride (14977-61-8) |
Safety information for Chromyl chloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Over Circle Oxidizers GHS03  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H271:Oxidising liquids;Oxidising solids H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H340:Germ cell mutagenicity H350:Carcinogenicity H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Chromyl chloride
New Products
(R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
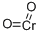

You may like
-
 Chromyl chloride CAS 14977-61-8View Details
Chromyl chloride CAS 14977-61-8View Details
14977-61-8 -
 Chromyl chloride CAS 14977-61-8View Details
Chromyl chloride CAS 14977-61-8View Details
14977-61-8 -
 Chromyl chloride CAS 14977-61-8View Details
Chromyl chloride CAS 14977-61-8View Details
14977-61-8 -
 Ethyl-2-Chloroacetoacetate 609-15-4View Details
Ethyl-2-Chloroacetoacetate 609-15-4View Details
609-15-4 -
 CIS- BROMO BENZOATEView Details
CIS- BROMO BENZOATEView Details
61397-56-6 -
 609-15-4View Details
609-15-4View Details
609-15-4 -
![1-(6-Methylpyridin-3-Yl)-2-[4-(Methylsulfonyl)Phenyl]Ethanone [Ketosulfone] 99%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) 1-(6-Methylpyridin-3-Yl)-2-[4-(Methylsulfonyl)Phenyl]Ethanone [Ketosulfone] 99%View Details
1-(6-Methylpyridin-3-Yl)-2-[4-(Methylsulfonyl)Phenyl]Ethanone [Ketosulfone] 99%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 27143-07-3View Details
27143-07-3View Details
27143-07-3
