Chromium nicotinate
- CAS NO.:64452-96-6
- Empirical Formula: C6H5CrNO2
- Molecular Weight: 175.11
- MDL number: MFCD00186328
- EINECS: 456-568-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-31 18:15:48
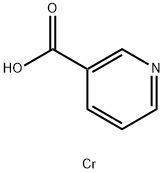
What is Chromium nicotinate?
Absorption
Chromium compounds are both absorbed by the lung and the gastrointestinal tract. Oral absorption of chromium compounds in humans can range between 0.5% and 10%, with the hexavalent (VI) chromium more easily absorbed than the trivalent (III) form . Absorption of chromium from the intestinal tract is low, ranging from less than 0.4% to 2.5% of the amount consumed . Vitamin C and the vitamin B niacin is reported to enhance chromium absorption .
Most hexavalent Cr (VI) undergoes partial intragastric reduction to Cr (III) upon absorption, which is an action mainly mediated by sulfhydryl groups of amino acids . Cr (VI) readily penetrates cell membranes and chromium can be found in both erythrocytes and plasma after gastrointestinal absorption of Cr (IV). In comparison, the presence of chromium is limited to the plasma as Cr (III) displays poor cell membrane penetration . Once transported through the cell membrane, Cr (VI) is rapidly reduced to Cr (III), which subsequently binds to macromolecules or conjugate with proteins. Cr (III) may be bound to transferrin or other plasma proteins, or as complexes, such as glucose tolerance factor (GTF).
Toxicity
Oral LD50 for Cr (VI) is 135 - 175 mg/kg in mouse and 46 - 113 mg/kg in rat . Oral LD50 for Cr (III) in rat is >2000 mg/kg . LD50 of chromium (III) oxide in rats is reported to be > 5g/kg . Other LD50 values reported for rats include: 3.5 g/kg (CI 3.19-3.79 g/kg) for chromium sulphate; 11.3 g/kg for chromium (III) acetate; 3.3 g/kg for chromium nitrate; and 1.5 g/kg for chromium nitrate nonahydrate .
Acute overdose of chromium is rare and seriously detrimental effects of hexavalent chromium are primarily the result of chronic low-level exposure . In case of overdose with minimal toxicity following acute ingestion, treatment should be symptomatic and supportive . There is no known antidote for chromium toxicity.
Hexavalent chromium is a Class A carcinogen by the inhalation route of exposure and Class D by the oral route . The oral lethal dose in humans has been estimated to be 1-3 g of Cr (VI); oral toxicity most likely involves gastrointestinal bleeding rather than systemic toxicity . Chronic exposure may cause damage to the following organs: kidneys, lungs, liver, upper respiratory tract . Soluble chromium VI compounds are human carcinogens. Hexavalent chromium compounds were mutagenic in bacteria assays and caused chromosome aberrations in mammalian cells. There have been associations of increased frequencies of chromosome aberrations in lymphocytes from chromate production workers . In human cells in vitro, Cr (VI) caused chromosomal aberrations, sister chromatid exchanges and oxidative DNA damage .
Chemical properties
gray, fine crystalline powder, stable, slightly soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol.
The Uses of Chromium nicotinate
Chromium nicotinate was widely used in food health care and feed additives.
The Uses of Chromium nicotinate
Chromium nicotinate is an organic chromium chelate formed by nicotinic acid and trivalent chromium ions. It can be used as medicine, health food and feed additive. Also Chromium nicotinate can be used as a functional factor of medicine and health care products: hypoglycemic and lipid-lowering, weight loss supplement, muscle strengthening, and immunity enhancement.
Indications
Indicated for use as a supplement to intravenous solutions given for total parenteral nutrition (TPN), to maintain chromium serum levels and to prevent depletion of endogenous stores and subsequent deficiency symptoms .
Pharmacokinetics
Trivalent chromium is part of glucose tolerance factor, an essential activator of insulin-mediated reactions. Chromium helps to maintain normal glucose metabolism and peripheral nerve function. Chromium increases insulin binding to cells, increases insulin receptor density and activates insulin receptor kinase leading to enhanced insulin sensitivity . In chromium deficiency, intravenous administration of chromium resulted in normalization of the glucose tolerance curve from the diabetic-like curve typical of chromium deficiency .
Metabolism
The metabolism of Cr (VI) involves reduction by small molecules and enzyme systems to generate Cr (III) and reactive intermediates. During this process, free radicals can be generated, which is thought to induce damage of cellular components and cause toxicity of chromium . The metabolites bind to cellular constituents .
Properties of Chromium nicotinate
| CAS DataBase Reference | 64452-96-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Chromium nicotinate
Computed Descriptors for Chromium nicotinate
Chromium nicotinate manufacturer
SLN Pharmachem
Pure Ingredients
Oceanic Laboratories Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 64452-96-6 Chromium Polynicotinate 99%View Details
64452-96-6 Chromium Polynicotinate 99%View Details
64452-96-6 -
 64452-96-6 99%View Details
64452-96-6 99%View Details
64452-96-6 -
 Chromium polynicotinate 98%View Details
Chromium polynicotinate 98%View Details
64452-96-6 -
 Chromium polynicotinate 64452-96-6 98%View Details
Chromium polynicotinate 64452-96-6 98%View Details
64452-96-6 -
 64452-96-6 Chromium polynicotinate 98%View Details
64452-96-6 Chromium polynicotinate 98%View Details
64452-96-6 -
 64452-96-6 98%View Details
64452-96-6 98%View Details
64452-96-6 -
 Chromium nicotinate 95% CAS 64452-96-6View Details
Chromium nicotinate 95% CAS 64452-96-6View Details
64452-96-6 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1