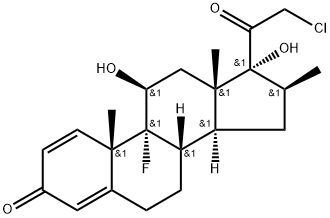
Dexamethasone
Synonym(s):(11β,16α)-9-Fluoro-11,17,21-trihydroxy-16-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione;9α-Fluoro-16α-methyl-11β,17α,21-trihydroxy-1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione;9α-Fluoro-16α-methylprednisolone;Dexamethasone - CAS 50-02-2 - Calbiochem;Dexamethasonum
- CAS NO.:50-02-2
- Empirical Formula: C22H29FO5
- Molecular Weight: 392.47
- MDL number: MFCD00064136
- EINECS: 200-003-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-09 10:27:52

What is Dexamethasone?
Absorption
Absorption via the intramuscular route is slower than via the intravenous route. A 3mg intramuscular dose reaches a Cmax of 34.6±6.0ng/mL with a Tmax of 2.0±1.2h and an AUC of 113±38ng*h/mL. A 1.5mg oral dose reaches a Cmax of 13.9±6.8ng/mL with a Tmax of 2.0±0.5h and an AUC of 331±50ng*h/mL. Oral dexamethasone is approximately 70-78% bioavailable in healthy subjects.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 in female mice was 6.5g/kg and 794mg/kg via the intravenous route.
Overdoses are not expected with otic formulations. Chronic high doses of glucocorticoids can lead to the development of cataract, glaucoma, hypertension, water retention, hyperlipidemia, peptic ulcer, pancreatitis, myopathy, osteoporosis, mood changes, psychosis, dermal atrophy, allergy, acne, hypertrichosis, immune suppression, decreased resistance to infection, moon face, hyperglycemia, hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, metabolic acidosis, growth suppression, and secondary adrenal insufficiency. Overdose may be treated by adjusting the dose or stopping the corticosteroid as well as initiating symptomatic and supportive treatment.
Description
The activity of dexamethasone, as measured by glycogen deposition, is 20 times greater than that of hydrocortisone. It has five times the anti-inflammatory activity of prednisolone. Clinical data indicate that this compound has seven times the antirheumatic potency of prednisolone. It is roughly 30 times more potent than hydrocortisone. Its pharmacokinetics are presented in Table 33.3. Routes of metabolism for dexamethasone are similar to those for prednisolone, with its primary 6β-hydroxy metabolite being recovered in urine. Dexamethasone sodium phosphate is the water-soluble sodium salt of the 21-phosphate ester, with an IV half-life of less than 10 minutes because of rapid hydrolysis by plasma phosphatases. Peak plasma levels for dexamethasone usually are attained in approximately 10 to 20 minutes following its IV administered dose. A similar reaction occurs when the phosphate ester is applied topically or by inhalation.
Description
Dexamethasone is a venerable corticosteroid medication that has been used against a wide range of diseases and conditions. Wikipedia credits the first preparation of the drug in 1957 to physician Philip S. Hench and co-workers at the Mayo Clinic (Rochester, MN); but no peer-reviewed references are cited. (Hench was a co-winner of the 1950 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine for the discovery of cortisone.)
The following year, Glen E. Arth and colleagues at Merck (Rahway, NJ) reported the synthesis of dexamethasone as part of their search for new steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines. One month later, Eugene P. Oliveto and coauthors at Schering (Bloomfield, NJ) and Massachusetts General Hospital (Boston) published a different synthesis. Patents describing dexamethasone syntheses were awarded to two other drug companies in 1961.
Dexamethasone has been used to treat allergies, brain swelling, tuberculosis, autoimmune conditions, and several lung diseases. Its versatility prompted the World Health Organization to include it in its Model List of Essential Medicines. But dexamethasone has many adverse side effects that range from acne to vertigo.
Perhaps it is not surprising that the variety of dexamethasone’s medical uses has led researchers to administer it to COVID-19 patients. In a British study called RECOVERY (for Randomised Evaluation of COVID-19 Therapy), more than 11,000 patients with serious cases of the disease were given one of several treatments, including oral or injected dexamethasone. Of the approximately 2100 subjects given dexamethasone, the patients on ventilators had one-third fewer deaths compared with control subjects. Those who required oxygen without a ventilator had about 20% fewer deaths.
It should be noted that as of June 22, 2020, the study’s results had not been peer-reviewed.
Chemical properties
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Originator
Dexacen,Central,US,1977
The Uses of Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone is used for the same indications as all corticosteroids; however, it exhibits a significantly more powerful anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic action. It is used for circulatory collapse—shock during or after surgical operations, trauma, blood loss, myocardial infarction, and burns. It is also used in severe infections—toxemia, vascular collapse in meningococcosis, septicemia, diphtheria, typhoid fever, and peritonitis. It is used in severe allergic conditions—asthmatic status, laryngeal edema, severe anaphylactic reactions to medicinal drugs, and pyrogenic reactions.
The Uses of Dexamethasone
Anti-inflammatory glucocorticoidDexamethasone is used to treat inflammatory and autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and bronchospasm. It is useful to study apoptosis, cell signaling pathways and gene expression. It is associated with marbofloxacin and clotrimazole and finds application in veterinary medicine to treat difficult ear infections in dogs. It is also used to treat horses with swelling of of distal limbs and general bruising in combination with trichlormethiazide. It is also an anti-inflammatory glucocorticoid.
Indications
Dexamethasone and ciprofloxacin otic suspension is indicated for bacterial infections with inflammation in acute otitis media and acute otitis externa. Intramuscular and intravenous injections are indicated for a number of endocrine, rheumatic, collagen, dermatologic, allergic, ophthalmic, gastrointestinal, respiratory, hematologic, neoplastic, edematous, and other conditions. Oral tablets are indicated for the treatment of multiple myeloma. An intravitreal implant is indicated for some forms of macular edema and non-infectious posterior uveitis affecting the posterior of the eye. Various ophthalmic formulations are indicated for inflammatory conditions of the eye.
Background
Dexamethasone, or MK-125, is a corticosteroid fluorinated at position 9 used to treat endocrine, rheumatic, collagen, dermatologic, allergic, ophthalmic, gastrointestinal, respiratory, hematologic, neoplastic, edematous, and other conditions. Developed in 1957, it is structurally similar to other corticosteroids like hydrocortisone and prednisolone.
Dexamethasone was granted FDA approval on 30 October 1958. In a press release for the Randomized Evaluation of COVID-19 Therapy (RECOVERY) trial on 16 June 2020, dexamethasone was recommended for use in COVID-19 patients with severe respiratory symptoms. Dexamethasone reduced deaths by approximately one third in patients requiring ventilation and by one fifth in those requiring oxygen.
What are the applications of Application
Dexamethasone is a glucocorticoid which induces the production of phospholipase A2 inhibitory protein
Indications
Cushing’s disease is defined as hypercortisolism due to chronic overproduction of corticotrophin by a corticotroph adenoma. Cortisol’s lack of suppressibility during the administration of low doses of dexamethasone but suppressibility during high-dose dexamethasone is the key diagnostic finding in 99% of the patients with Cushing’s disease. This contrasts with the lack of glucocorticoid suppressibility typically found in patients with corticotrophin-independent hypercortisolism (Cushing’s syndrome). A judicious selection of the available tests may be necessary to obtain an accurate diagnosis in patients with Cushing’s syndrome.
Definition
ChEBI: Dexamethasone is a fluorinated steroid that is 9-fluoropregna-1,4-diene substituted by hydroxy groups at positions 11, 17 and 21, a methyl group at position 16 and oxo groups at positions 3 and 20. It is a synthetic member of the class of glucocorticoids. It has a role as an adrenergic agent, an antiemetic, an antineoplastic agent, an environmental contaminant, a xenobiotic, an immunosuppressive agent and an anti-inflammatory drug. It is a fluorinated steroid, a 3-oxo-Delta(1),Delta(4)-steroid, a glucocorticoid, a 20-oxo steroid, an 11beta-hydroxy steroid, a 17alpha-hydroxy steroid and a 21-hydroxy steroid. It derives from a hydride of a pregnane.
Manufacturing Process
The preparation of dexamethasone acetate is described in US Patent
3,007,923 as follows. 1.5 cc of dimethylformamide and 1.5 cc of anhydrous
hydrofluoric acid are admixed and treated with 480 mg of 9β,11β-epoxy-17αhydroxy-21-acetoxy-16α-methyl-?1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione (prepared
according to E.P. Oliveto et al, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 80, 44331, 1958). The
steroid dissolves in about 15 minutes. The reaction mixture is shaken for two
hours at a temperature between 0 and +5°C, and then poured into 75 cc of
water containing in suspension, 7.5 grams of sodium bicarbonate. The mixture
is vacuum filtered, the filter cake washed and then dried at 100°C, yielding
460 mg of crude hexadecadrol contaminated with a small amount of the
starting material. A single recrystallization from methylene chloride yields 370
mg of the pure product having a melting point of 170°C and 229°C. The
mother liquor yields 62 mg of the starting material, and a remainder
constituting a mixture of starting and final materials with little other
contamination.
brand name
Aeroseb-Dex (Allergan); Decadron (Merck); Dexone (Solvay Pharmaceuticals); Hexadrol (Organon); Maxidex (Alcon); Mymethasone (Morton Grove).
Therapeutic Function
9-Fluoro-11β,17-dihydroxy-21-acetoxy-16α-methylpregna1,4-diene-3,20-dione
General Description
Odorless white to off-white crystalline powder with a slightly bitter taste.
General Description
Dexamethasone, 9-fluoro-11β,17,21-trihydroxy-16α-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione,is the 16 -isomer of betamethasone.
Dexamethasone acetate, USP (21-acetate)
Dexamethasone sodium phosphate, USP (21-sodiumphosphate).
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Dexamethasone may be sensitive to prolonged exposure to light. Dexamethasone is incompatible with strong oxidizers, strong acids, acid chlorides and acid anhydrides. Oxidation may occur with bases.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Dexamethasone are not available; however, Dexamethasone is probably combustible.
Biological Activity
Glucocorticoid; anti-inflammatory. Reduces levels of activated NF- κ B in immature dendritic cells (DCs) and inhibits differentiation into mature DCs.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Target IC50: 5 nM Inhibiting the expression of inducible but not constitutive nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial cells
Pharmacokinetics
Corticosteroids bind to the glucocorticoid receptor, inhibiting pro-inflammatory signals, and promoting anti-inflammatory signals. Dexamethasone's duration of action varies depending on the route. Corticosteroids have a wide therapeutic window as patients may require doses that are multiples of what the body naturally produces. Patients taking corticosteroids should be counselled regarding the risk of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression and increased susceptibility to infections.
Pharmacokinetics
The activity of dexamethasone, as measured by glycogen deposition, is 20 times greater than that of hydrocortisone. It has five times the anti-inflammatory activity of prednisolone. Clinical data indicate that this compound has seven times the antirheumatic potency of prednisolone. It is roughly 30 times more potent than hydrocortisone. Its pharmacokinetics are presented in Table 33.3. Routes of metabolism for dexamethasone are similar to those for prednisolone, with its primary 6β-hydroxy metabolite being recovered in urine. Dexamethasone sodium phosphate is the water-soluble sodium salt of the 21-phosphate ester, with an IV half-life of less than 10 minutes because of rapid hydrolysis by plasma phosphatases. Peak plasma levels for dexamethasone usually are attained in approximately 10 to 20 minutes following its IV administered dose. A similar reaction occurs when the phosphate ester is applied topically or by inhalation.
Pharmacology
Dexamethasone is a corticosteroid with high glucocorticoid activity and virtually no mineralocorticoid activity. I ts mechanism of action as an antiemetic is unknown, but it is possible that either direct genomic or indirect non-genomic effects on 5-HT3 and GABAA receptors contribute to its antiemetic activity. Many of the original studies were carried out using 8– 10mg of dexamethasone phosphate, but smaller doses (2.5–4mg) provide equal antiemetic efficacy with minimal risk of adverse effects. Concerns relating to adrenal suppression and other steroid-induced adverse effects (including increased risk of bleeding) after a single dose of dexamethasone remain largely unfounded. O ne of the most unpleasant adverse effects of dexamethasone involves intense perineal stimulation after rapid i.v. injection.
Clinical Use
Corticosteroid:
Cerebral oedema
Bacterial meningitis (unlicensed indication)
Suppression of inflammatory and allergic disorders
Rheumatic disease
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Anti-emetic (unlicensed indication)
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal and subcutaneous routes. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of F-.
Synthesis
Dexamethasone, 9|á-fluoro-16|á-methyl-11|?,17,21-trihydroxypregna-
1,4-dien-3,20-dione (27.1.51), or simply 9|á-fluoro-16|á-methylprednisolone. The distinctive
characteristic of dexamethasone is the presence of a fluorine atom at C9 of the steroid
ring.
Dexamethasone is synthesized in a multistage process from 3|á-acetoxy-16-pregnen-
11,20-dione, which is reacted with methylmagnesium bromide in the presence of lithium
bromide to give 3|á-hydroxy-16|á-methylpregnan-11,20-dione (27.1.39), after which a 17|á-
hydroxyl group is added. This is done by a reaction with acetic anhydride in the presence of
p-toluenesulfonic acid, forming the 3-acetoxy-17-enolacetate 27.1.40, which is epoxidized
by perbenzoic acid 27.1.41, and the product is hydrolyzed by an alkali to give an oxyketone
27.1.42. Addition of another hydroxyl group at C21 is accomplished by subsequent bromination
of a methyl group with molecular bromine, replacing the bromine atom with iodine, and
reacting iodide with potassium acetate, which forms the corresponding acetoxyketone
27.1.43. The hydroxyl group at C3 is oxidized to a carbonyl by chromium(VI) oxide in pyridine,
giving the 3,11,20-triketone 27.1.44, which again undergoes bromination by molecular
bromine, but at position C4. Dehydrogenation of this compound is accomplished using semicarbazide,
which results in the formation of an unsaturated triketone 27.1.45. In order to
avoid formation of semicarbazones at the keto-groups at C3 and C20, the final product is
treated with pyruvic acid. Semicarbazones are then specially formed at the keto-groups of C3
and C20, and the keto-group at C11 that does not take part in semicarbazone formation is
reduced to hydroxyl group using sodium borohydride. After removing the protective semicarbzone
groups, 21-O-acetoxy-16|?-methylhydrocortisone (27.1.46) is formed. This is
reacted with potassium acetate and transformed to the epoxide 27.1.49. Reacting this with
hydrofluoric acid results in an opening of the epoxide ring, during which the fluorohydrin
27.1.50 is formed. Finally, microbiological dehydrogenation of this compound at C1¨CC2 and
simultaneous deacetylation gives dexamethasone (27.1.51).

Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Glucocorticoids have been used in an attempt to treat practically
every malady that afflicts man or animal, but there are three broad
uses and dosage ranges for use of these agents. 1) Replacement of
glucocorticoid activity in patients with adrenal insufficiency, 2) as an
antiinflammatory agent, and 3) as an immunosuppressive. Among
some of the uses for glucocorticoids include treatment of: endocrine
conditions (e.g., adrenal insufficiency), rheumatic diseases (e.g.,
rheumatoid arthritis), collagen diseases (e.g., systemic lupus), allergic
states, respiratory diseases (e.g., asthma), dermatologic diseases
(e.g., pemphigus, allergic dermatoses), hematologic disorders (e.g.,
thrombocytopenias, autoimmune hemolytic anemias), neoplasias,
nervous system disorders (increased CSF pressure), GI diseases (e.g.,
ulcerative colitis exacerbations), and renal diseases (e.g., nephrotic
syndrome). Some glucocorticoids are used topically in the eye and
skin for various conditions or are injected intra-articularly or intralesionally.
The above listing is certainly not complete. For specific
dosages and indications refer to the Doses section.
High dose dexamethasone use for shock or CNS trauma is controversial;
recent studies have not demonstrated significant benefit
and it actually may cause increased deleterious effects.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Aldesleukin: avoid concomitant use.
Antibacterials: metabolism accelerated by rifamycins;
metabolism possibly inhibited by erythromycin;
concentration of isoniazid possibly reduced.
Anticoagulants: efficacy of coumarins and
phenindione may be altered.
Antiepileptics: metabolism accelerated by
carbamazepine, fosphenytoin, phenobarbital,
phenytoin and primidone
Antifungals: increased risk of hypokalaemia with
amphotericin - avoid; metabolism possibly inhibited
by itraconazole and ketoconazole; caspofungin
concentration possibly reduced (may need to increase
dose).
Antivirals: concentration of indinavir, lopinavir,
saquinavir and telaprevir possibly reduced; avoid
with rilpivirine; concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir.Ciclosporin: rare reports of convulsions in patients
on ciclosporin and high-dose corticosteroids.
Cobicistat: concentration possibly increased by
cobicistat.
Cytotoxics: possibly decreases axitinib concentration,
increase dose of axitinib.
Diuretics: enhanced hypokalaemic effects of
acetazolamide, loop diuretics and thiazide diuretics.
Netupitant: concentration of dexamethasone
increased - halve dexamethasone dose.
Vaccines: high dose corticosteroids can impair
immune response to vaccines; avoid concomitant use
with live vaccines.
Metabolism
Dexamethasone is 6-hydroxylated by CYP3A4 to 6α- and 6β-hydroxydexamethasone. Dexamethasone is reversibly metabolized to 11-dehydrodexamethasone by corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 2 and can also be converted back to dexamethasone by Corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 1.
Metabolism
Corticosteroids are metabolised mainly in the liver but also in other tissues, and are excreted in the urine. The slower metabolism of the synthetic corticosteroids with their lower protein-binding affinity may account for their increased potency compared with the natural corticosteroids. Up to 65% of a dose of dexamethasone is excreted in urine within 24 hours.
Storage
-20°C (protect from light)
Purification Methods
Dexamethasone has been recrystallised from Et2O or small volumes of EtOAc. Its solubility in H2O is 10 mg/100mL at 25o; and is freely soluble in Me2CO, EtOH and CHCl3. [Arth et al. J Am Chem Soc 80 3161 1958; for the -methyl isomer see Taub et al. J Am Chem Soc 82 4025 1960, see Beilstein 8 IV 3501.]
References
1) Merck Index 14 2943
Properties of Dexamethasone
| Melting point: | 262-264 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 568.2±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | 75 º (c=1, dioxane) |
| Density | 1.1283 (estimate) |
| refractive index | 76 ° (C=1, Dioxane) |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | ethanol: 1 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| appearance | white to off-white crystalline powder |
| pka | 12.13±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | off-white |
| Water Solubility | 10 mg/100 mL (25 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,2943 |
| BRN | 2066651 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases, acid anhydrides, acid chlorides. May be light sensitive. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 50-02-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Prednisolone, 9alpha-fluoro-16alpha-methyl-(50-02-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dexamethasone (50-02-2) |
Safety information for Dexamethasone
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Dexamethasone
| InChIKey | UREBDLICKHMUKA-CXSFZGCWSA-N |
Dexamethasone manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Dexamethasone 99%View Details
Dexamethasone 99%View Details -
 Dexamethasone 99%View Details
Dexamethasone 99%View Details -
 Dexamethasone 99%View Details
Dexamethasone 99%View Details -
 Dexamethasone 98%View Details
Dexamethasone 98%View Details
50-02-2 -
 50-02-2 98%View Details
50-02-2 98%View Details
50-02-2 -
 Dexamethasone 99%View Details
Dexamethasone 99%View Details -
 Dexamethasone 98% HPLC CAS 50-02-2View Details
Dexamethasone 98% HPLC CAS 50-02-2View Details
50-02-2 -
 Dexamethasone-D4View Details
Dexamethasone-D4View Details
50-02-2
