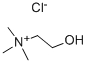
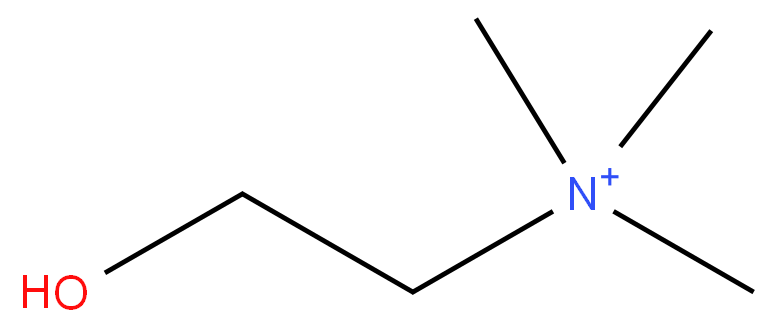
CHOLINE
- CAS NO.:62-49-7
- Empirical Formula: C5H14NO+
- Molecular Weight: 104.17
- MDL number: MFCD00272239
- EINECS: 204-625-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02

What is CHOLINE?
Toxicity
Oral rat LD50: 3400 mg/kg
Description
Choline is a water-soluble B vitamin. Unlike most vitamins, it is cationic, which accounts for its solubility.
In 1862, German chemist Adolph Strecker* isolated choline from the bile of pigs and oxen. (Its name is derived from the Greek word for bile.) A few years later, German pharmacologist Oscar Liebreich synthesized choline in the lab.
Choline is an essential nutrient for animals, but humans do not need to ingest it in food or as a dietary supplement unless their diet is low in methionine and folate. If choline supplementation is needed, eggs and meat are excellent sources.
Choline oxidation by gut bacteria is a likely harbinger of heart disease. In 2015, Emily Balskus and her research team at Harvard discovered that?microorganisms use the enzyme choline TMA-ylase to break a C–N bond in cholineto form trimethylamine, which then oxidizes to trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO). The Cleveland Clinic’s Stanley Hazen previously linked TMAO to heart problems.
*Strecker is better known for his synthesis of amino acids from nonbiochemical starting materials.
Chemical properties
Viscous, alkaline liquid. Soluble in water and alcohol. Amounts are expressed in milligrams of choline.
The Uses of CHOLINE
Choline is a substance grouped as a member of the vitamin b complex, although not a vitamin by definition. it is water soluble and is important in nerve function and fat metabolism. it occurs in egg yolk, beef liver, and grains.
Indications
For nutritional supplementation, also for treating dietary shortage or imbalance
Background
A basic constituent of lecithin that is found in many plants and animal organs. It is important as a precursor of acetylcholine, as a methyl donor in various metabolic processes, and in lipid metabolism.
Definition
ChEBI: A choline that is the parent compound of the cholines class, consisting of ethanolamine having three methyl substituents attached to the amino function.
Pharmacokinetics
This compound is needed for good nerve conduction throughout the CNS (central nervous system) as it is a precursor to acetylcholine (ACh). Choline is also needed for gallbladder regulation, liver function and lecithin (a key lipid) formation. Choline also aids in fat and cholesterol metabolism and prevents excessive fat build up in the liver. Choline has been used to mitigate the effects of Parkinsonism and tardive dyskinesia. Choline deficiencies may result in excessive build-up of fat in the liver, high blood pressure, gastric ulcers, kidney and liver dysfunction and stunted growth.
Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of CHOLINE
| Melting point: | 232-233 °C (decomp) |
| Boiling point: | 195.35°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.09 g/mL at 20 °C |
| refractive index | n |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| pka | 13.9(at 25℃) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 62-49-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Choline (62-49-7) |
Safety information for CHOLINE
Computed Descriptors for CHOLINE
CHOLINE manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
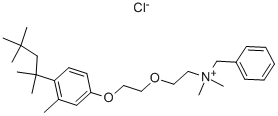
![benzyldimethyl[2-[2-[4-(1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl)tolyloxy]ethoxy]ethyl]ammonium hydroxide](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/26248-39-5.gif)
You may like
-
 62-49-7 Choline 98%View Details
62-49-7 Choline 98%View Details
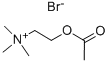
62-49-7 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
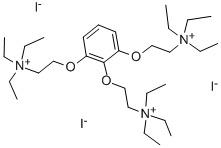
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1