Gallamine triethiodide
Synonym(s):;Gallamine Triethiodide - CAS 65-29-2 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:65-29-2
- Empirical Formula: C30H60I3N3O3
- Molecular Weight: 891.53
- MDL number: MFCD00011832
- EINECS: 200-605-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
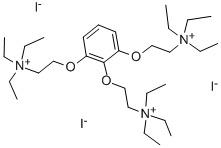
What is Gallamine triethiodide?
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Flaxedil,Davis and Geck,US,1951
The Uses of Gallamine triethiodide
Gallamine Triethiodide is used as a neuromuscular blocking agent, paralyzing locally during anesthetization.
The Uses of Gallamine triethiodide
Muscle relaxant;M2 antagonist allosteric
The Uses of Gallamine triethiodide
Gallamine triethiodide has been used:
- as a relaxant for measuring spinal trigeminal nucleus recordings from single neurons.
- as an antagonist in neuroblastoma cells as M2 receptor
- to reduce eye movement during retinal surgery in rat
Indications
For use as adjuncts to anesthesia to induce skeletal muscle relaxation and to facilitate the management of patients undergoing mechanical ventilation
What are the applications of Application
Gallamine Triethiodide is a cardioselective mAChR M2 antagonist, regarded as a neuromuscular blocking agent.
Background
A synthetic nondepolarizing blocking drug. The actions of gallamine triethiodide are similar to those of tubocurarine, but this agent blocks the cardiac vagus and may cause sinus tachycardia and, occasionally, hypertension and increased cardiac output. It should be used cautiously in patients at risk from increased heart rate but may be preferred for patients with bradycardia. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1992, p198)
Manufacturing Process
12.6 grams of pyrogallol are dissolved in 100 cc of hot toluene. 14 grams of
sodamide (85%)are added to the solution at about 100°C in 5 portions over a
period of 15 minutes, with agitation. There are then added with agitation,
over a period of 30 minutes, 100 cc of a toluene solution containing 474
grams of diethylaminochlorethane per liter of toluene.
The mixture is then heated for 1 hour, the toluene being refluxed, whereafter
it is left to cool, 50 cc of water are added and, after decanting, the solution is again washed with two quantities of 50 cc of water. The toluene solution is
dried over potassium carbonate and distilled in vacuo. There is thus obtained
28 grams of 1.2.3-tri-(β-diethylaminoethoxy)benzene, boiling at 206°C under
1 mm pressure.
20 grams of 1.2.3-tri-(β-diethylaminoethoxy)-benzene is heated for 5 hours
under reflux on the water bath with 30 grams of ethyl iodide. The hot mixture
is dissolved in 50 cc of water, filtered after addition of 2 grams of decolorizing
black, evaporated to dryness on the water bath and recrystallized from 120 cc
of alcohol. The product can be further recrystallized in mixtures of acetone
and water.
The triethiodide of 1.2.3-tri-(β-diethylaminoethoxy)-benzene is thus obtained
as white crystals which, after drying, have a rather indefinite melting point at
about 152° to 153°C, (Maquenne block).
Therapeutic Function
Muscle relaxant
General Description
Gallamine triethiodide,[v-phenenyl-tris(oxyethylene)]tris[triethylammonium] triiodide(Flaxedil), is a skeletal muscle relaxant that works byblocking neuromuscular transmission in a manner similar tothat of d-tubocurarine (i.e., a nondepolarizing blockingagent). It does have some differences, however. It has astrong vagolytic effect and a persistent decrease in neuromuscularfunction after successive doses that cannot be overcome by cholinesterase inhibitors. Gallamine triethiodidealso has muscarinic antagonistic properties and bindswith greater affinity to the M2 receptors than to the M1 receptor.This latter characteristic may cause its strongvagolytic action.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Gallamine triethiodide has anti-muscarinic effect. It is a competitive antagonist for the muscarinic receptor. Gallamine is regarded as neuromuscular blocking agent.
Pharmacokinetics
Gallamine Triethiodide is a nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking drug (NDMRD) used as an adjunct to anesthesia to induce skeletal muscle relaxation. The actions of gallamine triethiodide are similar to those of tubocurarine, but this agent blocks the cardiac vagus and may cause sinus tachycardia and, occasionally, hypertension and increased cardiac output. Muscle groups differ in their sensitivity to these types of relaxants with ocular muscles (controlling eyelids) being most sensitive, followed by the muscles of the neck, jaw, limbs and then abdomen. The diaphragm is the least sensitive muscle to NDMRDs. Although the nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking drugs do not have the same adverse effects as succinylcholine, their onset of action is slower. They also have a longer duration of action, making them more suitable for maintaining neuromuscular relaxation during major surgical procedures.
Clinical Use
Gallamine Triethiodide is contraindicated in patients with myastheniagravis, and one should remember that its action is cumulative,as with curare. The antidote for gallamine triethiodideis neostigmine.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, intravenous, parenteral, intraduodenal, intraperitoneal, and intramuscular routes. Whenheated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NH3, NOx, and Ií.
Synthesis
Gallamine, 1,2,3-tris-(2-triethylaminoethoxy)benzene triiodide, is synthesized from pyrogallol, the hydroxyl groups of which are esterified by 2-diethylaminoethylchloride in the presence of sodium amide. The resulting 1,2,3-tris-(2-triethylaminoethoxy) benzene is further alkylated at all three nitrogen atoms by ethyliodide, giving gallamine.

Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of Gallamine triethiodide
| Melting point: | 235 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Density | 1.4288 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 100 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| color | Crystals from Me2CO (aq) |
| Merck | 13,4364 |
Safety information for Gallamine triethiodide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Gallamine triethiodide
| InChIKey | REEUVFCVXKWOFE-UHFFFAOYSA-K |
| SMILES | C1(OCC[N+](CC)(CC)CC)=C(C=CC=C1OCC[N+](CC)(CC)CC)OCC[N+](CC)(CC)CC.[I-].[I-].[I-] |
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Gallamine triethiodide CAS 65-29-2View Details
Gallamine triethiodide CAS 65-29-2View Details
65-29-2 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1